Quick start guide
New to RustRover? This guide will help you explore the IDE's workspace and features and try out all the main aspects of the Rust development process.
note
For instructions on how to install RustRover, refer to the installation guide.
You have three options to start working on a Rust project.
Launch RustRover.
Do one of the following:
Click New Project on the Welcome screen.
Select File | New | Project from the main menu.
Click the Project widget in the main window header and selectProject widget in the main window header and select New Project.

In the left-hand pane, make sure Rust is selected.
Specify the project location and name.
Specify the location of the Rust toolchain and standard library.
If the toolchain and standard library are installed, RustRover will detect them automatically. Otherwise, you will be suggested to download Rustup.

Select the desired project template and click Create.
In the main menu, go to File | Open. In the file chooser, select the directory containing the root Cargo.toml file (or Cargo.toml itself) and click Open:

In the dialog that opens, select Open as project.

When opening the project for the first time, RustRover will prompt you to confirm that you consider it safe.

Click Trust Project if you are certain the project poses no threats and you would like to enable all IDE features. If you have any doubts, select Preview in Safe Mode. For more information, refer to Project security.
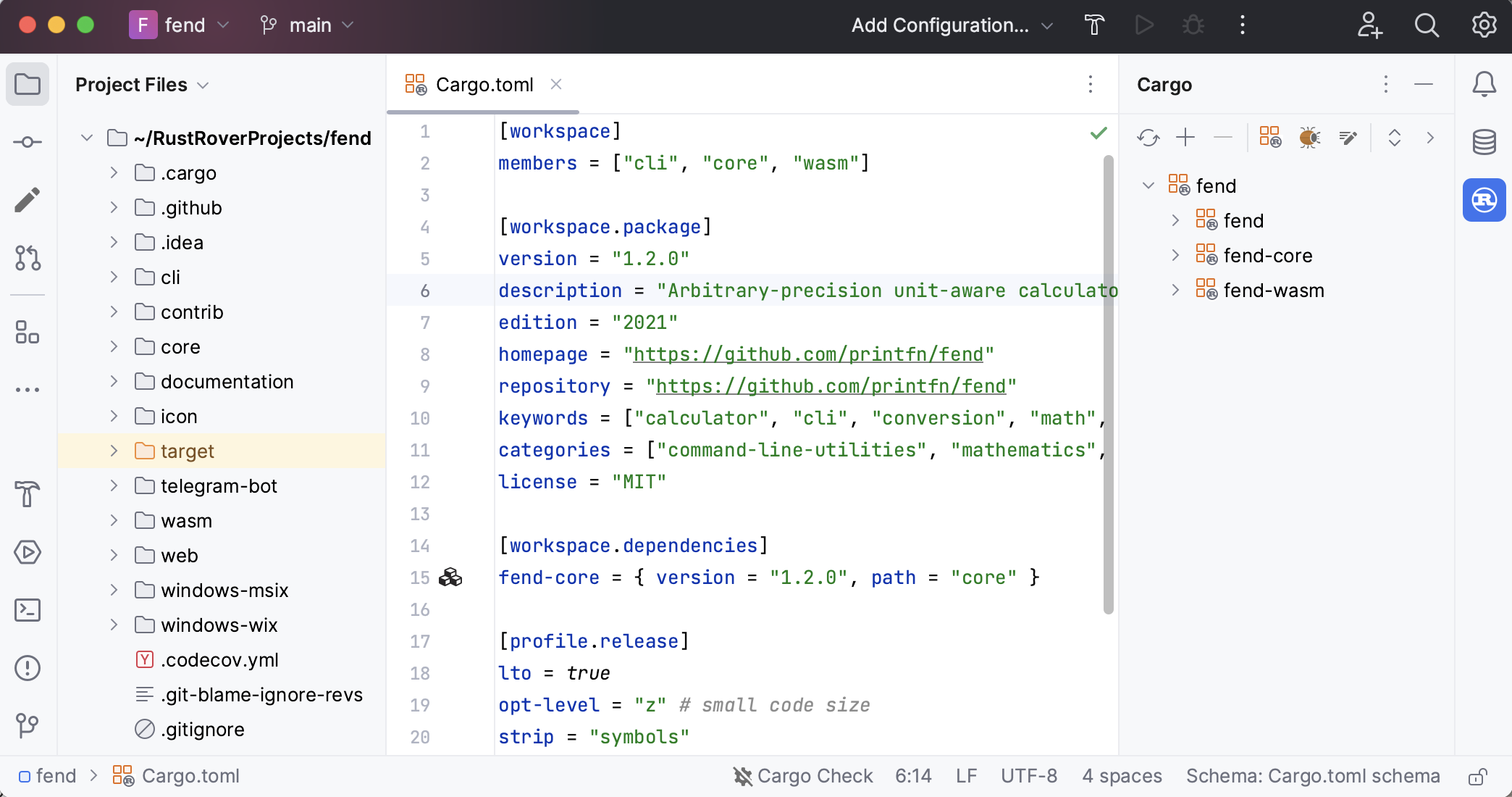
RustRover's feature set is designed to simplify the Rust development process. Let's take a closer look at what it has to offer.
To help you quickly read and understand Rust code, RustRover provides highlighting, inlined hints, macro expansion, quick access to documentation, and more.
Here are some shortcuts you may find useful:
Action | Shortcut |
|---|---|
AltEnter | |
Go to declaration | CtrlClick |
Get type info | CtrlShift0P |
Ctrl0Q | |
CtrlShift0I |
For more information, refer to Code reference information.
To help you fight errors and inconsistencies in code, RustRover offers built-in inspections and integrates with external linters.
For a summary of all detected problems, use the Inspections widget in the upper-right corner of the editor. To see the details, click the widget and refer to the Problems tool window (or select View | Tool Windows | Problems):
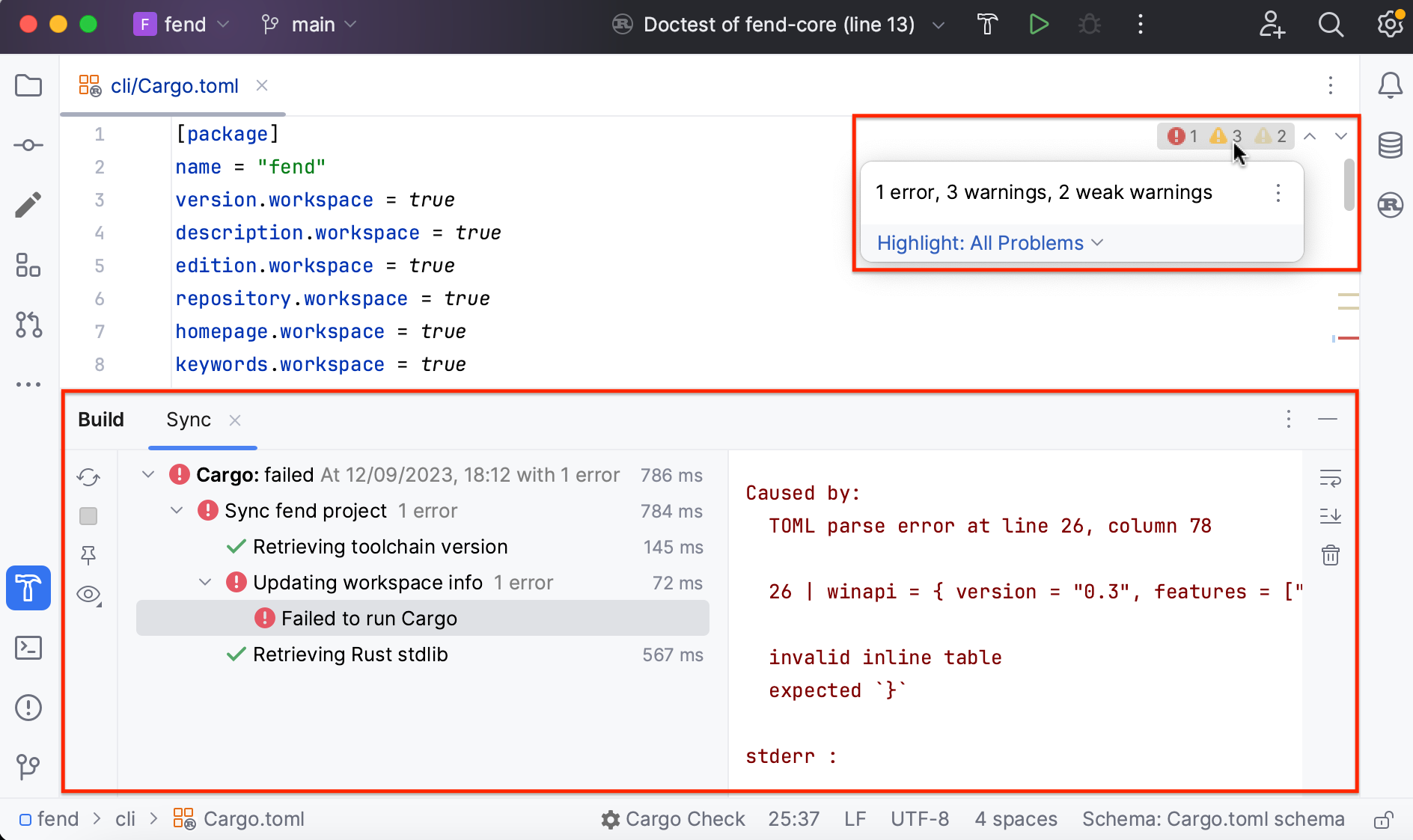
Inspections run on the fly for all files currently open in the editor. You can also run them manually for a larger scope. To view inspection results, use the Problems tool window (View | Tool Windows | Problems).
RustRover will suggest quick-fixes and intentions where possible. Quick fixes are marked with a red bulb (![]() ) and address errors. Intentions are marked with a yellow bulb (
) and address errors. Intentions are marked with a yellow bulb (![]() ) and suggest possible enhancements and optimizations.
) and suggest possible enhancements and optimizations.
If an inspection has detected a problem in your code, you can quickly apply a fix in the editor. Place the caret at the highlighted piece of code and press AltEnter.
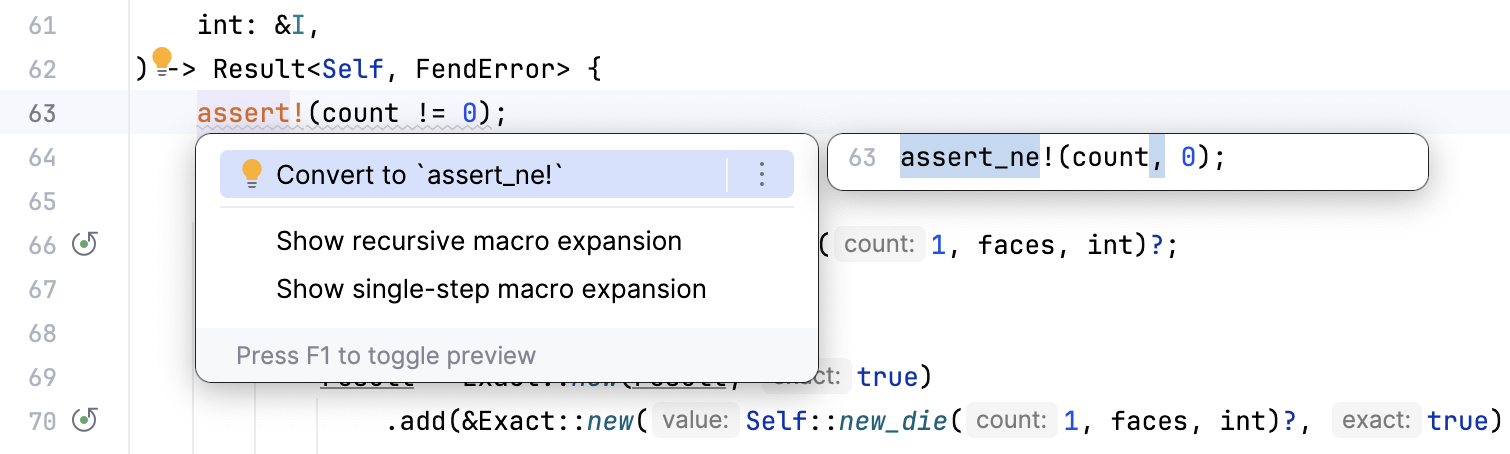
For more information, refer to Code inspections.
In addition to the built-in set of inspections, RustRover uses external linters to verify your code. You can choose between Cargo Check and Clippy and preset the calls the way you like.
note
By default, RustRover runs Cargo Check on the fly.
With an external linter running on the fly, you can enjoy the variable lifetime visualization feature: whenever the linter reports a borrow checker error, simply click the variable and you will see a visualization of its lifetime.

For more information, refer to External linters.
You can easily format your code using either the IDE's built-in formatter or Rustfmt (enabled by default).
Open settings by pressing CtrlAlt0S and navigate to Rust | Rustfmt.
To enable Rustfmt, set the Use Rustfmt instead of built-in formatter checkbox. To disable Rustfmt, clear the checkbox.
note
Note that, when Rustfmt is enabled, RustRover will only use it for formatting whole files and Cargo projects. For code fragments, groups of files, and directories, RustRover will automatically switch to the built-in formatter.

Click OK to apply the changes.
Open the file you want to reformat in the editor.
Press CtrlAltShift0L or select Code | Reformat File.
In the Reformat File dialog, select additional options if necessary and click Run.

For more information, refer to Built-in formatter and Rustfmt.
The Cargo tool windowCargo tool window is designed to help you with Cargo tasks. By default, it is pinned to the tool windows bar. You can show or hide it by clicking the window indicator on the sidebar (alternatively, select View | Tool Windows | Cargo from the main menu).
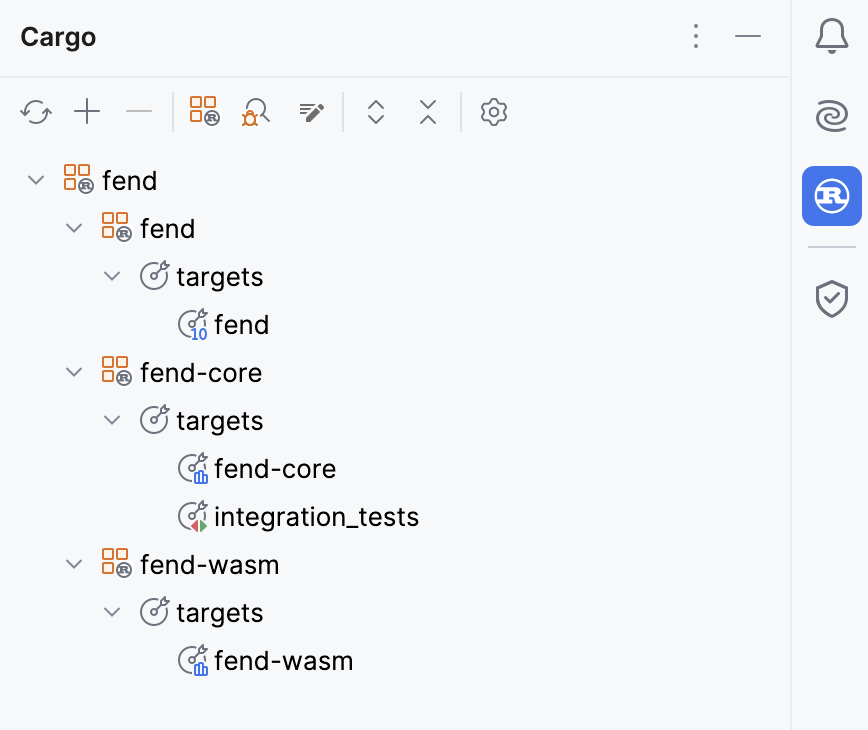
Use the top panel to:
For more information, refer to Cargo tool window.
You can share your code in Rust Playground without leaving the editor.
Select the code fragment you'd like to share (otherwise, the IDE will copy the whole file).
Right-click and choose Rust | Share in Playground.
RustRover will create a GitHub Gist and display a notification popup with a link to the playground.
Use the Build action to compile your code and Run to execute it. There are several ways to perform these actions:
To build or run a particular target, open the Cargo tool window (View | Tool Windows | Cargo) and double-click the target.

To run from a particular entry point, locate it in the editor, click
in the gutter, and select Run:

To run a particular file or module, open the Project view, right-click the necessary file or module, and select Run:

If you want to build or run code using a predefined configuration (with custom parameters and settings), select it in the switcher on the main toolbar and:
click
to build (CtrlF9)
click
to run (ShiftF10)

You can always build/run using a Cargo command.
For more information, refer to Building and running.
RustRover provides a full-fledged debugger – with breakpoints, variable monitoring, stepping, memory and disassembly views, and other handy features.
To start debugging from a particular entry point, locate it in the editor, click
in the gutter, and select Debug:

To debug code using a predefined configuration (with custom parameters and settings), select it in the configuration switcher on the main toolbar and click
:

You can always start a debug session by running a Cargo command.
For more information, refer to Start the debugger session.
Learn how to perform basic debugging actions from these guides:
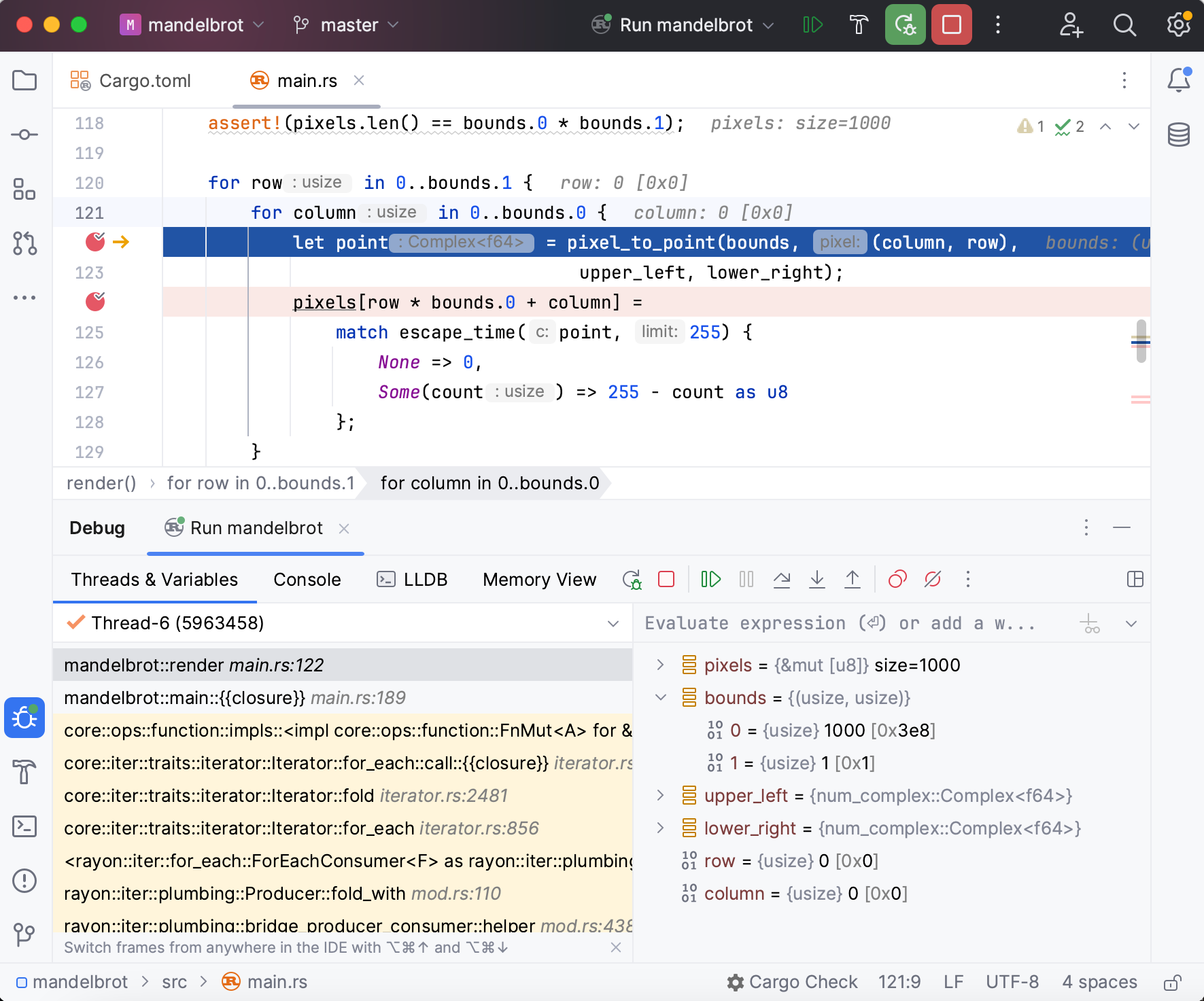
For more information, refer to the Debug section.
You will likely support your code with tests, doctests, and/or benchmarks. Here are a few quick ways to run them:
To run a single test or doctest, open it in the editor, click
in the gutter, and select Run:

To run a test/benchmark target, open the Cargo tool window (View | Tool Windows | Cargo) and double-click the target:
 Gif
GifYou can always run tests using a Cargo command.
The Run tool window will open, automatically displaying the results:
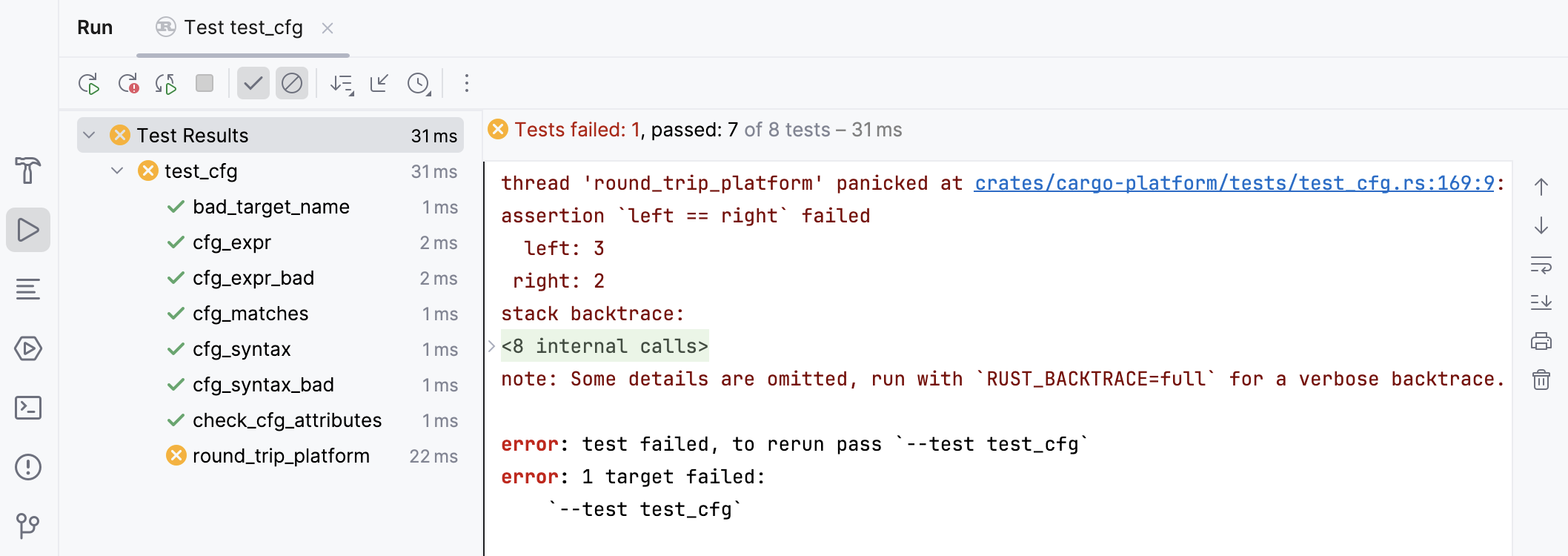
For more information, refer to the Test section.
RustRover allows you to explore code coverage statistics.
To get code coverage statistics, do one of the following:
Locate the desired entry point, click
in the gutter, and select Run with Coverage:

Locate the necessary file in Project view, right-click, and select Run with Coverage:

If you want to run a predefined configuration (with custom parameters and settings), select it in the switcher on the main toolbar, then press
 and select Run with Coverage:
and select Run with Coverage: 
The Coverage tool window (View | Tool Windows | Coverage) will open, automatically displaying the results:
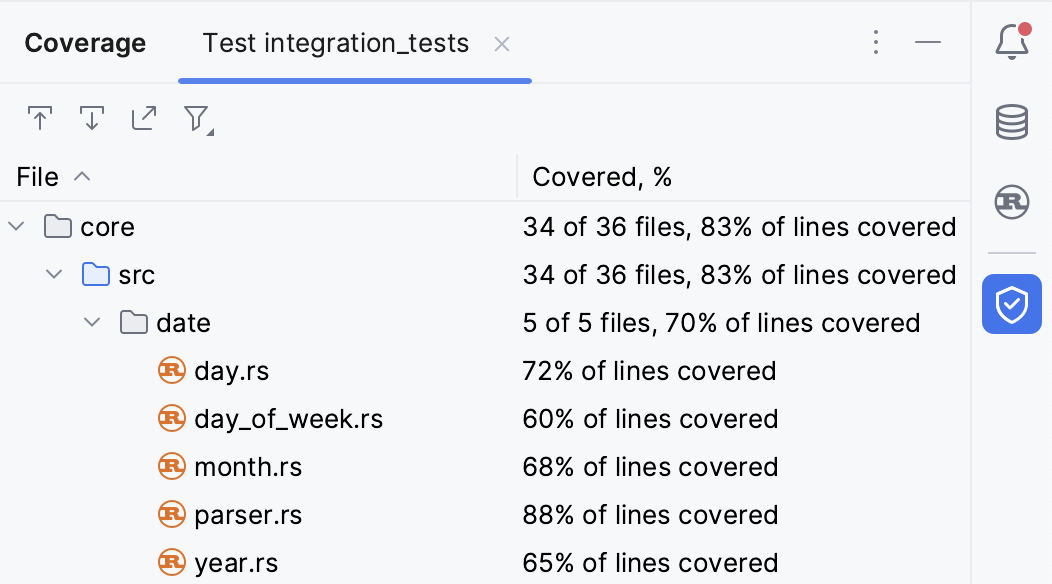
For more information, refer to Code coverage.
You can customize RustRover functionality to match your own needs. Here are some of the available customizations:
Thanks for your feedback!
