Azure Pipelines
Qodana Scan is an Azure Pipelines task packed inside the Qodana Azure Pipelines extension to analyze your code within existing pipelines using Qodana.
Before you start
All configuration examples in this section use a project token generated by Qodana Cloud. This token is required for the paid Qodana linters and optional for use with the Community linters. You can see these sections to learn how to generate the project token in the Qodana Cloud UI:
The project setup section explains how to generate a project token when first working with Qodana Cloud.
The Manage a project section explains how to create a project token within an existing Qodana Cloud Cloud organization.
Once you obtain the project token, go to your pipeline UI, create the
QODANA_TOKENsecret variable, and save the project token as its value.If you are using a Qodana Cloud instance other than
https://qodana.cloud/, override it by setting theQODANA_ENDPOINTenvironment variable.In your Azure DevOps organization, install the Qodana Azure Pipelines extension.
If you are using any VCS other than Azure Repos Git, you may need an additional step in your pipeline with Git credential configuration before the Qodana step. For example, if you are using GitHub, the following step can be used:
Basic configuration
You can run the Qodana Scan task on any OS and x86_64/arm64 CPUs, but it requires the agent to have Docker installed. Additionally, since most Qodana Docker images are Linux-based, the Docker daemon must support running Linux containers.
You can configure this task using either a YAML-formatted file or the Classic interface. The detailed description of all configuration options is available in the Configuration chapter.
Below are basic configuration examples that will be expanded in the subsequent chapters of this section.
Here, the persistCredentials: true line lets you reuse credentials for Git-related actions like pull request analyses or running Quick-Fixes.
The Cache task lets you open projects faster using cache.
The uploadResult: true line tells Qodana to produce a qodana-report artifact. After running Qodana, navigate to the log directory to see logs.
The QODANA_TOKEN variable refers to the project token generated by Qodana Cloud.
Add the Qodana Scan task to the pipeline configuration and then configure it as shown below.
To have access to the system token during pull request analyses, follow the instructions from the Microsoft website.
Using input arguments
Here, the -e option adds input arguments. If an argument has a value, you can use the notation like -i,frontend,-e,param=value.
Use the field to specify input arguments in the -i,frontend,-e,param=value notation.
Pull requests
This is how you can enable Qodana analysis for pull requests:
Here, QODANA_TOKEN refers to the project token generated by Qodana Cloud.
In the classic interface editor, check the option.
Quality gate and baseline
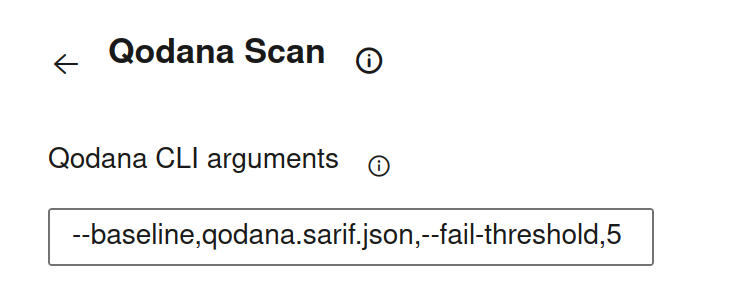
You can also configure the quality gate and baseline features as shown below.
In this configuration, the args: block configures the quality gate and baseline features using comma-separated options.
Use the field to configure the baseline and quality gate features using comma-separated options, for example:
Quick-Fixes
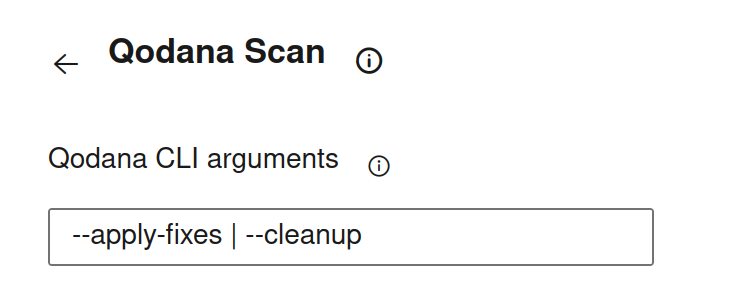
Configure a Quick-Fix strategy using either of the following configuration methods:
# Possible values: --apply-fixes | --cleanup args: --apply-fixesUse the field to configure the Quick-Fix feature, for example:
 # Possible values: apply | cleanup fixesStrategy: apply
# Possible values: apply | cleanup fixesStrategy: applyDepending on your needs, configure the
pushFixesproperty:Use this configuration to create a new branch with fixes and a pull request to the original branch:
pushFixes: pull-requestUse the field to configure the Quick-Fix feature.

Use this configuration to push fixes to the original branch:
pushFixes: branchUse the field to configure the Quick-Fix feature.

Set permissions to your job. In the Azure Pipelines UI, for the
Qodana for Azure Pipelines Build Serviceuser enable the following repository permissions:ContributeBypass policies when pushingif they may fail the push of Quick-FixesCreate branchif you use thepull-requestsetting
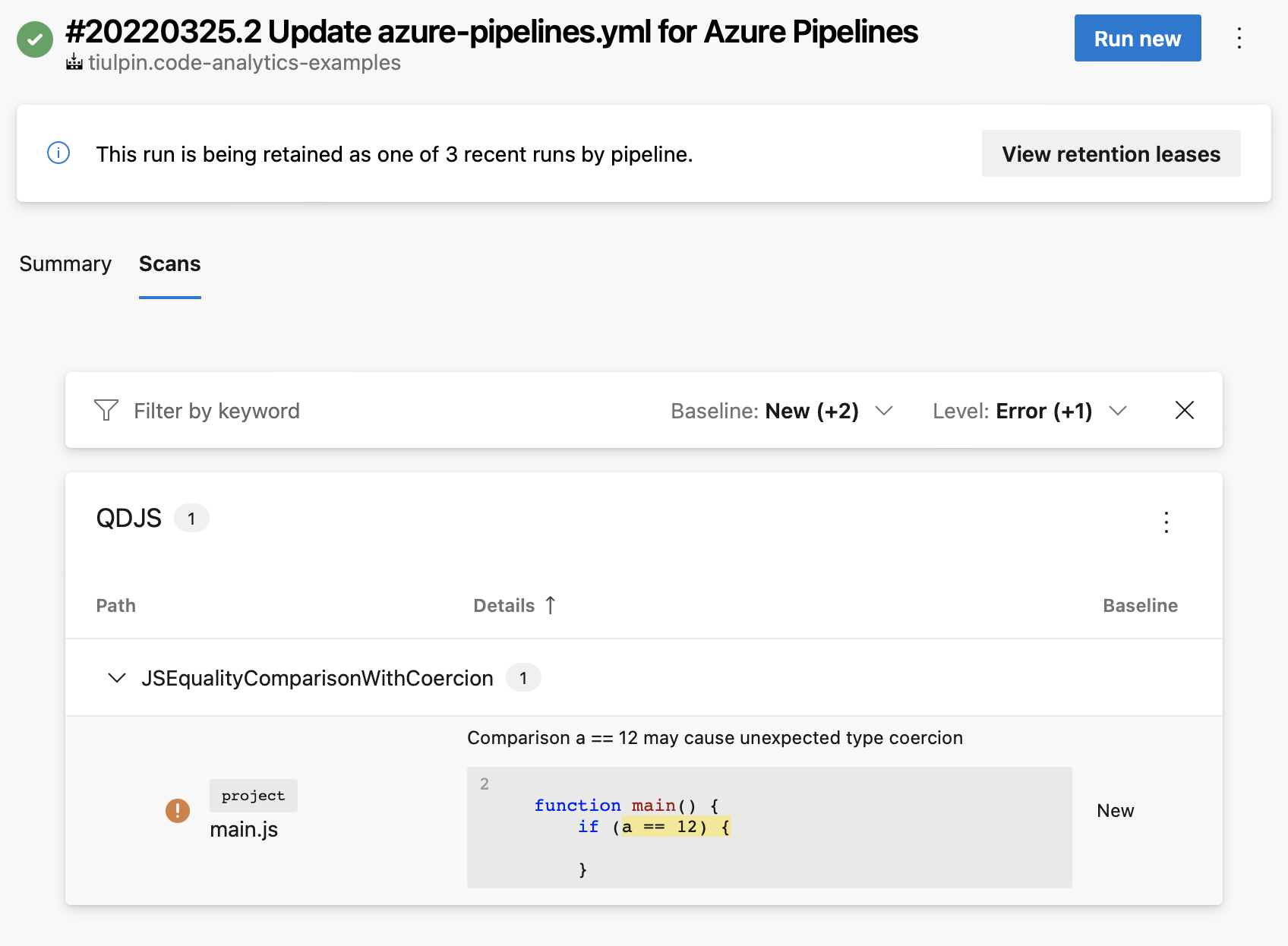
SARIF SAST Scans Tab
To display Qodana report summary in Azure DevOps UI on the Scans tab, install Microsoft DevLabs’ SARIF SAST Scans Tab extension and set the uploadSarif/Upload SARIF option in your pipeline configuration to true.
Configuration
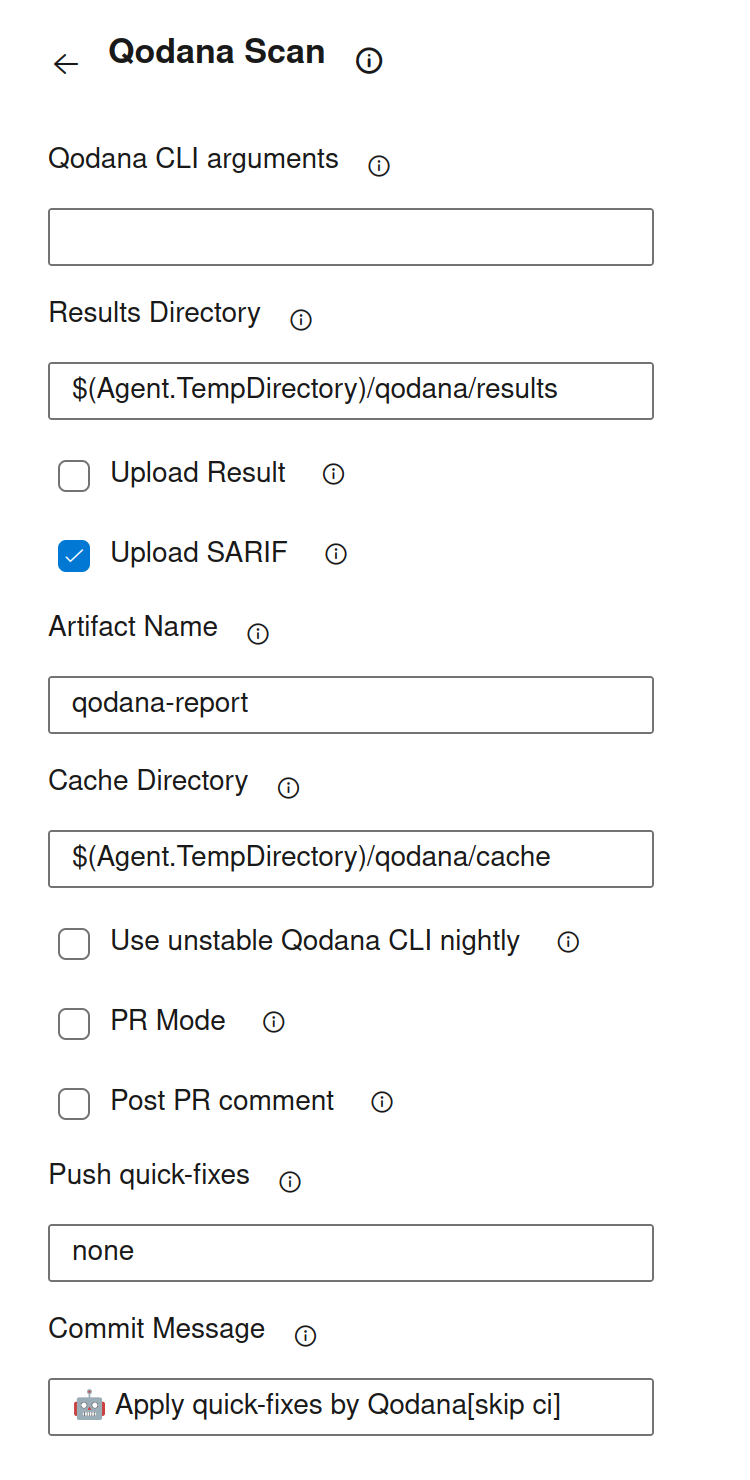
This table contains the list of configuration options corresponding to the inputs block of a pipeline configuration and their analogs in the classic interface.
YAML option | UI element of the classic interface | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qodana CLI arguments | Additional Qodana CLI If an argument has a value, you can pass it using Optional. | None |
| Results Directory | Directory to store the analysis results. Optional. |
|
| Upload Result | Upload Qodana results as an artifact to the job. Optional. |
|
| Upload SARIF | Upload qodana.sarif.json as an qodana.sarif artifact to the job. Optional. |
|
| Artifact Name | Specify Qodana results artifact name used for result uploading. Optional. |
|
| Cache Directory | Directory to store Qodana caches. Optional. |
|
| Use unstable Qodana CLI nightly | Enable using an unstable version of Qodana CLI. Optional. |
|
| PR Mode | Enable pull request analyses |
|
| Post PR comment | Post a comment with the Qodana results summary to the pull request. Optional. |
|
| Push Quick-Fixes | Push Qodana fixes to the repository, can be |
|
| Commit Message | Commit message used when Quick-Fixes are applied |
|