What's new in Compose Multiplatform 1.7.3
Edit pageLast modified: 13 November 2024Here are the highlights for this feature release:
See the full list of changes for this release on GitHub.
Dependencies
Gradle plugin
org.jetbrains.compose, version 1.7.3. Based on Jetpack Compose libraries:Lifecycle libraries
org.jetbrains.androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-*:2.8.3. Based on Jetpack Lifecycle 2.8.5.Navigation libraries
org.jetbrains.androidx.navigation:navigation-*:2.8.0-alpha10. Based on Jetpack Navigation 2.8.0.Material3 Adaptive libraries
org.jetbrains.compose.material3.adaptive:adaptive-*:1.0.0. Based on Jetpack Material3 Adaptive 1.0.0
Breaking changes
Minimum AGP version raised to 8.1.0
Neither Jetpack Compose 1.7.0 nor Lifecycle 2.8.0, which are both used by Compose Multiplatform 1.7.0, supports AGP 7. So, when you update to Compose Multiplatform 1.7.3, you may have to upgrade your AGP dependency, as well.
note
Newly implemented previews for Android composables in Android Studio require one of the latest AGP versions.
Java resources API is deprecated in favor of the multiplatform resource library
In this release, we explicitly deprecate the Java resources APIs available in the compose.ui package: the painterResource(), loadImageBitmap(), loadSvgPainter(), and loadXmlImageVector() functions, as well as the ClassLoaderResourceLoader class and functions relying on it.
Consider transitioning to the multiplatform resource library. While you can use Java resources with Compose Multiplatform, they don't benefit from extended features provided by the framework: generated accessors, multimodule support, localization and so on.
If you still have to access Java resources, you can copy the implementation suggested in the pull request to make sure your code works even after you upgrade to Compose Multiplatform 1.7.3 and switch to multiplatform resources where possible.
New default behavior for processing touch in iOS native elements
Before 1.7.3, Compose Multiplatform could not respond to touch events that landed in interop UI views, so interop views handled these touch sequences entirely.
Compose Multiplatform 1.7.3 implements more sophisticated logic for handling interop touch sequences. By default, there is now a delay after the initial touch, which helps the parent composable understand whether the touch sequence was meant to interact with the native view and react accordingly.
For more information, see the explanation in the iOS section of this page or read the documentation for this feature.
Disabling minimum frame duration on iOS is mandatory
Developers often failed to notice the printed warning about the high refresh rate displays, and users were deprived of smooth animations on their 120-Hz-enabled devices. We are now strictly enforcing this check. Apps built with Compose Multiplatform will now crash if the CADisableMinimumFrameDurationOnPhone property in the Info.plist file is absent or set to false.
You can disable this behavior by setting the ComposeUIViewControllerConfiguration.enforceStrictPlistSanityCheck property to false.
Deprecated Modifier.onExternalDrag on desktop
The experimental Modifier.onExternalDrag and related APIs have been deprecated in favor of the new Modifier.dragAndDropTarget. The DragData interface was moved into the compose.ui.draganddrop package.
If you are using the deprecated APIs with Compose Multiplatform 1.7.0, you are going to encounter a deprecation error. With 1.8.0 the onExternalDrag modifier is going to be removed altogether.
Across platforms
Shared element transitions
Compose Multiplatform now offers an API for seamless transitions between composables that share consistent elements. These transitions are often useful in navigation, helping users follow the trajectory of changes in the UI.
For a deep dive into the API, see the Jetpack Compose documentation.
Type-safe Navigation
Compose Multiplatform has adopted Jetpack Compose’s type-safe approach to passing objects along a navigation route. New APIs in Navigation 2.8.0 allow Compose to provide compile-time safety for your navigation graph. These APIs achieve the same result as the Safe Args plugin for XML-based navigation.
For details, see Google’s docs about type safety in Navigation Compose.
Multiplatform resources
Resources packed into Android assets
All multiplatform resources are now packed into Android assets. This allows Android Studio to generate previews for Compose Multiplatform composables in Android source sets.
note
Android Studio previews are available only for composables in Android source sets. They also require one of the latest versions of AGP: 8.5.2, 8.6.0-rc01, or 8.7.0-alpha04.
This also offers direct access to multiplatform resources from WebViews and media player components on Android, since resources can be reached by a simple path, for example, Res.getUri(“files/index.html”).
Here's an example of an Android composable that displays a resource HTML page with a link to a resource image:
AndroidView(factory = { WebView(it).apply{...}
The example works with this simple HTML file:
<title>Cat Resource</title>{...}
Both resource files in this example are located in the commonMain source set:
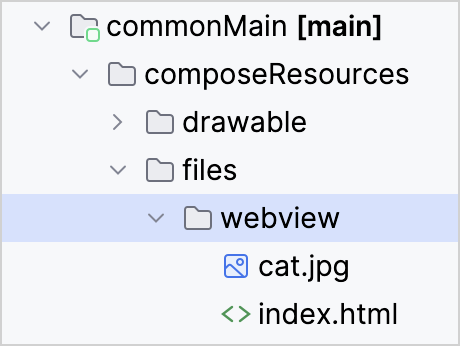
Custom resource directories
With the new customDirectory setting in the configuration DSL, you can associate a custom directory with a specific source set. This makes it possible, for example, to use downloaded files as resources.
Multiplatform font cache
Compose Multiplatform brings Android's font cache functionality to other platforms, eliminating excessive byte reading of Font resources.
Support for multiplatform test resources
The resource library now supports using test resources in your projects, meaning you can:
Add resources to test source sets.
Use generated accessors that are available only in the corresponding source sets.
Pack test resources into the app only for test runs.
Resources mapped to string IDs for easy access
Resources of each type are mapped with their file names. For example, you can use the Res.allDrawableResources property to get the map of all drawable resources and access a necessary resource by passing its string ID:
Image(painterResource(Res.allDrawableResources["compose_multiplatform"]!!), null)Functions for converting byte arrays into ImageBitmap or ImageVector
There are new functions for converting a ByteArray into an image resource:
decodeToImageBitmap()turns a JPEG, PNG, BMP, or WEBP file into anImageBitmapobject.decodeToImageVector()turns an XML vector file into anImageVectorobject.decodeToSvgPainter()turns an SVG file into aPainterobject. This function is not available on Android.
See the documentation for details.
New common modules
material3.adaptive:adaptive*
Material3 adaptive modules are now available in common code with Compose Multiplatform. To use them, explicitly add the corresponding dependencies to the common source set in the module's build.gradle.kts file:
commonMain.dependencies {
implementation("org.jetbrains.compose.material3.adaptive:adaptive:1.0.0-alpha03")
implementation("org.jetbrains.compose.material3.adaptive:adaptive-layout:1.0.0-alpha03")
implementation("org.jetbrains.compose.material3.adaptive:adaptive-navigation:1.0.0-alpha03")
}material3.material3-adaptive-navigation-suite
Material3 adaptive navigation suite, necessary for building adaptive navigation with Compose, is available in common code with Compose Multiplatform. To use it, explicitly add the dependency to the common source set in the module's build.gradle.kts file:
commonMain.dependencies {
implementation(compose.material3AdaptiveNavigationSuite)
}material3:material3-window-size-class
To use WindowSizeClass classes, explicitly add the material3-window-size-class dependency to the common source set in the module's build.gradle.kts file:
commonMain.dependencies {
implementation("org.jetbrains.compose.material3:material3-window-size-class:1.7.3")
}The calculateWindowSizeClass() function is not available in common code yet. However, you can import and call it in platform-specific code, for example:
// desktopMain/kotlin/main.kt
import androidx.compose.material3.windowsizeclass.calculateWindowSizeClass
// ...
val size = calculateWindowSizeClass()material-navigation
The material-navigation library is available in common code in addition to Compose Multiplatform Navigation. To use it, add the following explicit dependencies to the common source set in the module's build.gradle.kts file:
commonMain.dependencies {
implementation("org.jetbrains.androidx.navigation:navigation-compose:2.8.0-alpha10")
implementation("org.jetbrains.compose.material:material-navigation:1.7.0-beta02")
}Skia updated to Milestone 126
The version of Skia used by Compose Multiplatform, via Skiko, has been updated to Milestone 126.
The previous version of Skia used was Milestone 116. You can see the changes made between these versions in the release notes.
GraphicsLayer – a new drawing API
The new drawing layer added in Jetpack Compose 1.7.0 is now available in Compose Multiplatform.
Unlike Modifier.graphicsLayer, the new GraphicsLayer class allows you to render Composable content anywhere. It is useful in cases where animated content is expected to be rendered in different scenes.
See the reference documentation for a more detailed description and examples.
LocalLifecycleOwner moved out of Compose UI
The LocalLifecycleOwner class has been moved from the Compose UI package to the Lifecycle package.
This change allows you to access the class and call its Compose-based helper APIs independently of a Compose UI. Keep in mind, however, that without the Compose UI bindings, a LocalLifecycleOwner instance will have no platform integration and thus no platform-specific events to listen to.
iOS
Improved touch interop between Compose Multiplatform and native iOS
This release improves touch handling for iOS interop views. Compose Multiplatform now tries to detect whether a touch is meant for an interop view or should be processed by Compose. This makes it possible to process touch events that happen in a UIKit or a SwiftUI area inside your Compose Multiplatform app.
By default, Compose Multiplatform will delay transmitting touch events to interop views by 150 ms:
If within this time frame there is movement over a distance threshold, the parent composable will intercept the touch sequence, and it will not be forwarded to the interop view.
If there is no noticeable movement, Compose will not process the rest of the touch sequence, which will instead be processed solely by the interop view.
This behavior aligns with how the native UIScrollView works. It helps prevent situations where a touch sequence that starts in the interop view is intercepted without a chance for Compose Multiplatform to process it. This could lead to a frustrating user experience. For example, imagine a large interop video player used in a scrollable context such as a lazy list. It is tricky to scroll the list when most of the screen is taken up by a video that intercepts all touches without Compose Multiplatform being aware of them.
Native performance improvements
With Kotlin 2.0.20, the Kotlin/Native team made a lot of progress in making Compose apps on iOS perform faster and smoother. Compose Multiplatform 1.7.3 release makes use of these optimizations, as well as brings performance improvements from Jetpack Compose 1.7.0.
When comparing Compose Multiplatform 1.6.11 paired with Kotlin 2.0.0 and Compose Multiplatform 1.7.3 paired with Kotlin 2.0.20, we see better results across the board:
The LazyGrid benchmark simulates
LazyVerticalGridscrolling, which is closest to real-life use cases, and performs ~9% faster on average. It also shows significantly reduced number of missed frames, which usually make the users perceive the UI as less responsive. Try it out for yourself: apps made with Compose Multiplatform for iOS should feel much smoother.The VisualEffects benchmark renders a lot of randomly placed components and works 3.6 times faster: average CPU time per 1000 frames was reduced from 8.8 seconds to 2.4.
The AnimatedVisibility composable animates showing and hiding an image and demonstrates ~6% faster rendering.
On top of that, Kotlin 2.0.20 introduces experimental support for concurrent marking in the garbage collector. Enabling concurrent marking shortens garbage collector pauses and leads to even bigger improvements for all benchmarks.
You can check out the code for these Compose-specific benchmarks in the Compose Multiplatform repository:
Desktop
Drag and drop
The drag-and-drop mechanism, which enables users to drag content into or out of your Compose application, has been implemented in Compose Multiplatform for desktop. To specify potential sources and destinations for dragging and dropping, use the dragAndDropSource and dragAndDropTarget modifiers.
note
While these modifiers are available in common code, they currently only work in desktop and Android source sets. Stay tuned for future releases.
For common use cases, see the dedicated article in the Jetpack Compose documentation.
BasicTextField, renamed from BasicTextField2, adopted on desktop
Jetpack Compose has made the BasicTextField2 component stable and renamed it BasicTextField. In this release, Compose Multiplatform has adopted the change for desktop targets, and there are plans to cover iOS as well in the stable 1.7.0 version.
The new BasicTextField:
Allows you to manage state more reliably.
Offers the new
TextFieldBufferAPI for programmatic changes to text field content.Includes several new APIs for visual transformations and styling.
Provides access to
UndoStatewith the ability to return to previous states of the field.
Render settings for ComposePanel
By specifying the new RenderSettings.isVsyncEnabled parameter in the ComposePanel constructor, you can hint to the backend rendering implementation to disable vertical synchronization. This can reduce visual latency between inputs and changes in the UI but can also lead to screen tearing.
The default behavior stays the same: The ComposePanel attempts to synchronize drawable presentations with VSync.
Web
skiko.js is redundant for Kotlin/Wasm applications
The skiko.js file is now redundant for Kotlin/Wasm applications built with Compose Multiplatform. You can remove it from the index.html file and improve the load times of your app. skiko.js will be removed from the Kotlin/Wasm distribution completely in future releases.
note
The
skiko.jsfile is still necessary for Kotlin/JS applications.
Thanks for your feedback!
