Spring Boot
Last modified: 01 August 2022Required plugins: Spring and Spring Boot (bundled)
Spring Boot is an extension of the Spring framework that simplifies the initial configuration of Spring applications. It enables you to quickly create a working standalone Spring application with minimum default configuration.
Spring Initializr is a web application that can generate a Spring Boot project. You can select the necessary configuration, including the build tool, language, version of the Spring Boot framework, and any dependencies for your project. IntelliJ IDEA provides the Spring Initializr project wizard that integrates with the Spring Initializr API to generate and import your project directly from the IDE.
Create a Spring Boot project
From the main menu, select File | New | Project….
In the left pane of the New Project wizard, select Spring Initializr.
Go through the steps of the Spring Initializr wizard.
For an example, see Tutorial: Create your first Spring application.
Spring Initializr generates a valid project structure with the following files:
A build configuration file, for example, build.gradle for Gradle or pom.xml for Maven.
A class with the
main()method to bootstrap the application.An empty JUnit test class.
An empty Spring application configuration file: application.properties
By default, IntelliJ IDEA applies code formatting to the generated files. If you want the files to remain formatted as they are generated by Spring Initializr, open the IDE settings with Ctrl+Alt+S, select Languages & Frameworks | Spring | Spring Boot and disable the Reformat code option in the New Initializr Projects group.
Custom configuration files
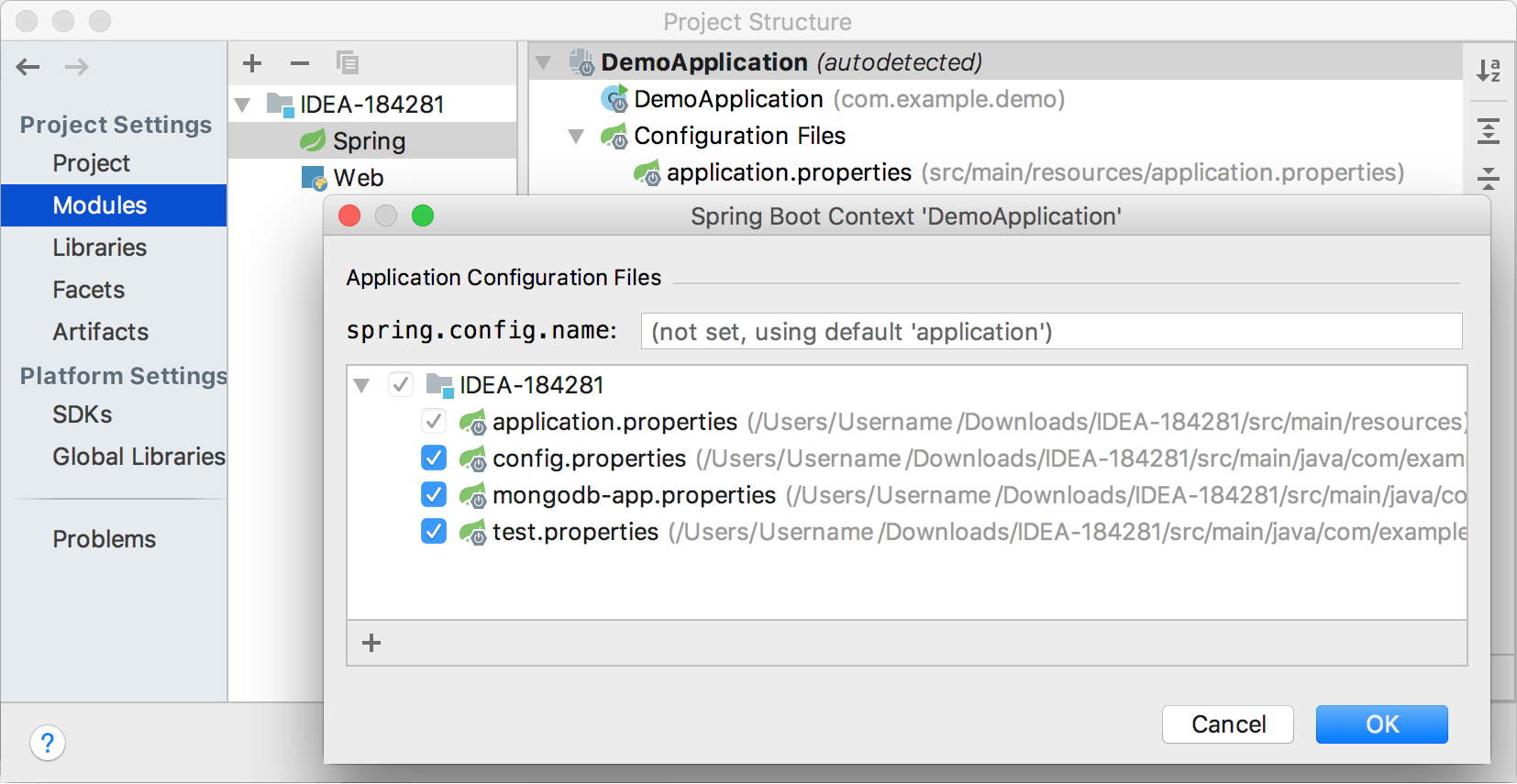
Spring Initializr creates one default configuration file that may not always be sufficient for development. If you do not want to use the default configuration file, or if you want to run your code in different environments, you can use custom configuration files defined in your project.
Let IntelliJ IDEA know which files are configuration files in your project to enable relevant highlighting and coding assistance:
From the main menu, select File | Project Structure or press Ctrl+Alt+Shift+S to open the Project Structure dialog.
From the left-hand list, select Facets.
Select the Spring facet from the list in the middle and click
in the right-hand section.
If you want to use a custom configuration file instead of the default one, type its name in the
spring.config.namefield.If you want to use multiple configuration files, click
and select files from the project tree.
Valid configuration files are marked with
.
Click OK and apply the changes.
note
Some custom configuration files are detected automatically. For example, profile-specific configuration files with names that match the current naming pattern will be added to the context.
Runtime endpoints
Spring Boot includes additional features for monitoring and managing the state of your application in the production environment through HTTP endpoints or with Java Management Extensions (JMX). For more information, see Spring Boot Actuator: Production-ready Features.
Enable the Spring Boot endpoints
Add the Spring Boot Actuator dependency for your project.
MavenGradleOpen the pom.xml file and add the following dependency under
dependencies:<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency>Open the build.gradle file and add the following dependency under
dependencies:implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-actuator'
When you run your application with this dependency, you will be able to access the exposed actuator endpoints via HTTP. For example, if the application is running on localhost port number 8080, the default URL for the health endpoint will be http://localhost:8080/actuator/health.
Expose the Spring Boot endpoints through JMX
By default, IntelliJ IDEA enables the JMX agent for the Spring Boot run configuration, so when you run your application, the IDE can access the actuator endpoints.
From the main menu, select Run | Edit Configurations.
In the Run/Debug Configurations dialog, select your Spring Boot run configuration, and then select the Enable JMX agent option.
View the Spring Boot endpoints
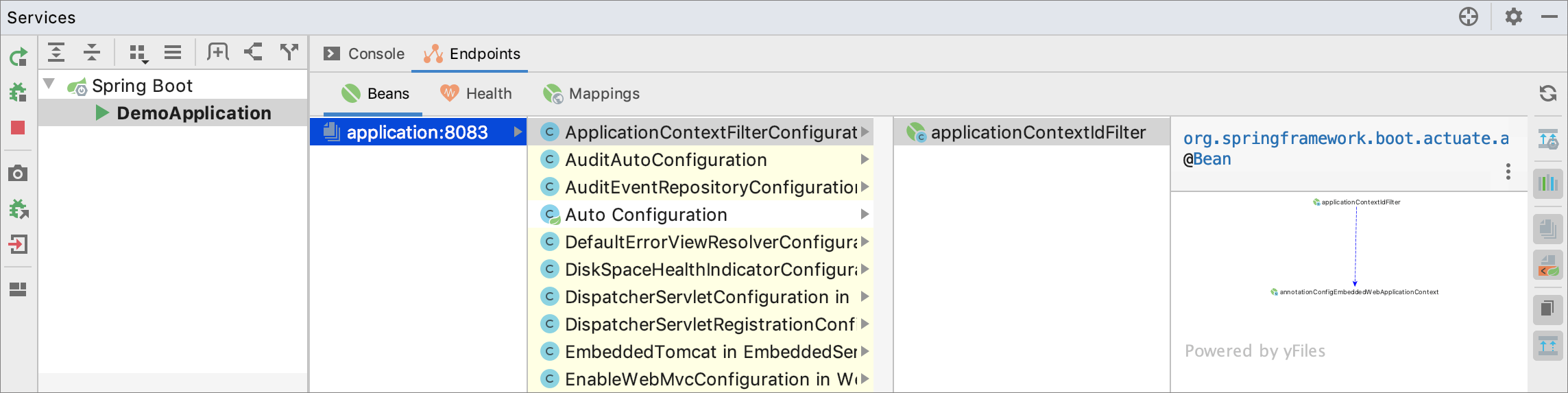
Run your Spring Boot application and open the Services tool window: select View | Tool Windows | Services or press Alt+8.
Select your running Spring Boot application and open the Endpoints tab.
note
If the Spring Boot run configurations are not available in the Services tool window, either add them or use the Run or Debug tool window.
You can use tabs to view endpoints of the following types: runtime beans, health information, and request mappings.
Beans
The Beans tab under Endpoints shows the runtime beans of your Spring Boot application. Double-click any bean to open its declaration in the editor. These beans are indicated using the ![]() icon in the gutter. Click this icon to view dependent and injected beans.
icon in the gutter. Click this icon to view dependent and injected beans.
The Beans tab includes the following toolbar actions:
Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Refresh the runtime beans information collected by the JMX agent. |
| Show the complete graph for all your runtime beans instead of a list. Required plugin: Diagrams (bundled). |
| Show beans from libraries. |
| Show available Spring application contexts. |
| Show available configuration files. |
| Show the documentation for the selected bean. |
| Show the direct dependencies for the selected bean. Required plugin: Diagrams (bundled). |
Health
The Health tab under Endpoints shows the status of your application. There are some auto-configured health indicators and you can also write custom health indicators.
For more information, see Health.
Mappings
The Mappings tab under Endpoints shows the request mappings of your application. It lists all methods with the @RequestMapping annotation or its shortcuts, such as @GetMapping.
If you click the path mapping URI, you can select to run the corresponding HTTP request, open an HTTP requests file with the request, or open the request URL in the web browser (if it's a GET request). For more information, see HTTP Client.
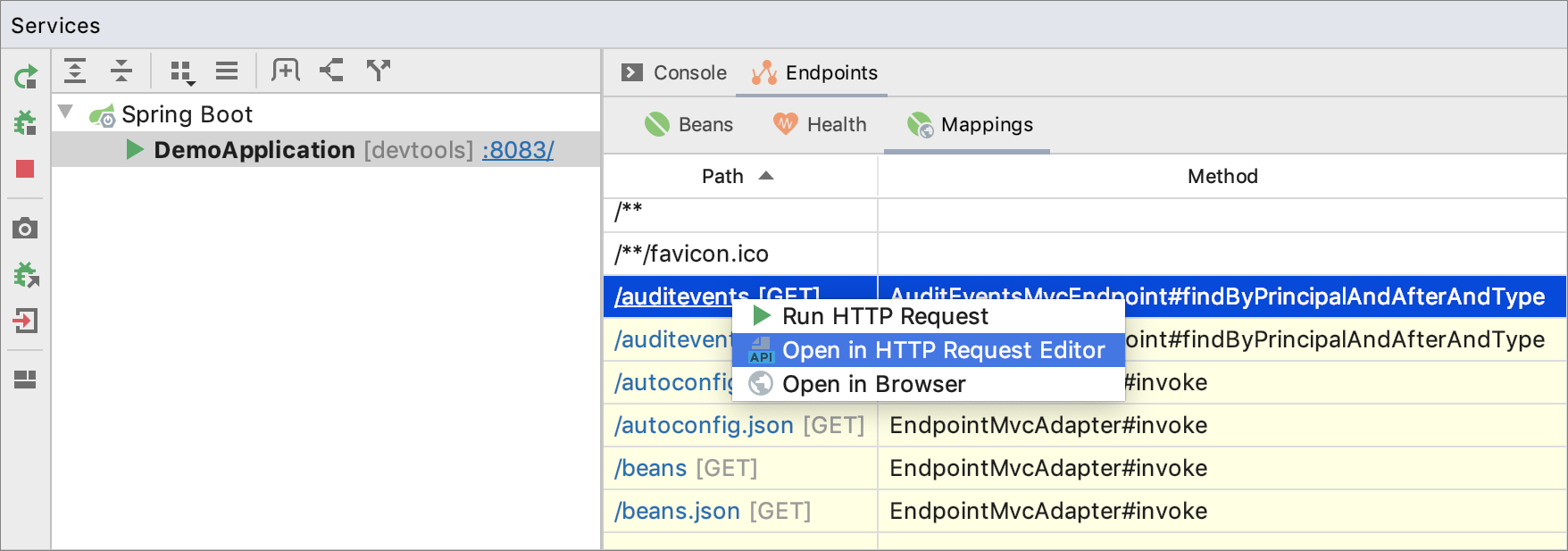
Double-click a method to open its declaration in the editor. Spring registers such methods as handlers and IntelliJ IDEA indicates them with the icon in the gutter. Click this icon to run the corresponding HTTP request, open it in a requests files, or in the web browser (if it's a
GET request).
The Mappings tab includes the following toolbar actions:
Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Refresh the request mappings collected by the JMX agent. |
| Open the root application URL in a web browser. |
| Select which request methods to show. |
| Show request mappings from libraries. |
Application update policies
With the spring-boot-devtools module, your application will restart every time files on the classpath change. If IntelliJ IDEA is configured to continuously compile changed files, you can set a trigger file. In this case your application will restart only after you modify the trigger file. For more information, see Automatic Restart.
Enable automatic restart
Add the
spring-boot-devtoolsmodule dependency for your project.MavenGradleOpen the pom.xml file and add the following dependency under
dependencies:<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency>Setting the
spring-boot-devtoolsdependency asoptionalprevents it from being used in other modules that use your project.Open the build.gradle file and add the following dependency under
dependencies:developmentOnly("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-devtools")Setting the
spring-boot-devtoolsdependency asdevelopmentOnlyprevents it from being used in other modules that use your project.
To update a running application, select Run | Debugging Actions | Update Application Ctrl+F10 from the main menu, or select your application in the Services tool window and click . Depending on your needs, you can configure what the IDE will do when you execute this action.
note
If the Spring Boot run configurations are not available in the Services tool window, either add them or use the Run or Debug tool window.
Configure the application update policy
From the main menu, select Run | Edit Configurations.
Select the necessary Spring Boot run configuration to open its settings. Click Modify options.

In the list that opens, point to On 'Update' action. You can choose to update only the resources, update both the classes and the resources (build your application), update the trigger file (which will trigger a restart), or try to perform a class hot swap, and if it fails, update the trigger file.
note
For the Update trigger file and the Hot swap classes and update trigger file if failed policies, the IDE sets a trigger file when you start the application.
In the Modify options list, point to On frame deactivation and select an action that the IDE will do after you switch to another application: update the resources, or build your application.
tip
You can create several Spring Boot run/debug configurations with different update policies and switch between them.