Types
The Types view shows a list of objects in the selected object set. For convenience, all objects are grouped by their type: each row in the list represents a specific type. All objects of that type existing in the set are counted under this row. You can use the Types view to identify objects that consume too much memory or shouldn't be in memory.
The list consists of the following columns:
Name | Description |
|---|---|
Type | Type name. |
Objects count | The number of objects of the same type. |
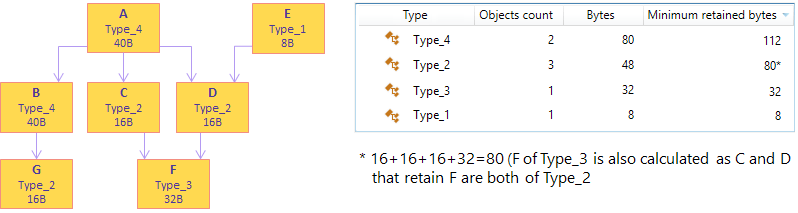
Bytes | The overall shallow size of objects in bytes. |
Minimum retained bytes | The overall size of all exclusively retained objects in bytes. This is a lower estimate of how many bytes will be freed if you remove all objects of a certain type. |
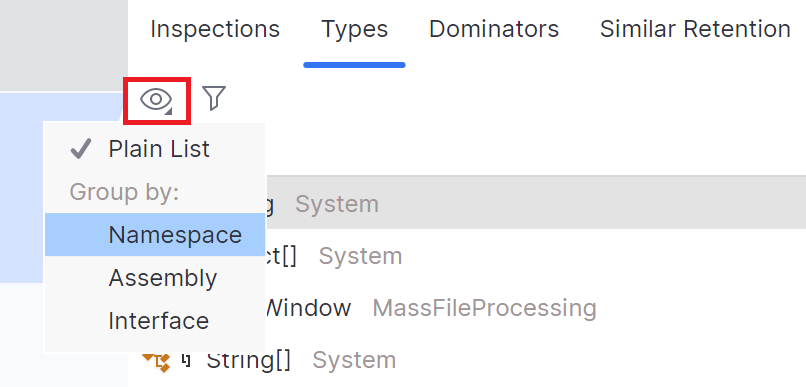
For convenience, you can group the list in four different ways:
Plain List
Objects are displayed in a plain list. This is the easiest way to identify objects with the highest memory usage.
Group by Namespace
Objects are grouped by their namespace. This type of grouping is very convenient when you want to focus on determining issues in your own classes.
Group by Assembly
Objects are grouped by the assembly they come from. This type of grouping can also be used to separate your own classes from the system ones.
Group by Interface
Objects are grouped by interfaces they implement. If an object implements more than one interface, it will be displayed under each implemented interface.
You can filter out objects that are of no interest to your analysis by type .
Start typing the desired string pattern. dotMemory will highlight matching strings.
You can make your search more efficient by using the following tips:
Use CamelHumps. E.g.
fowill return objects of bothSystem.Drawing.FontandMS.Utility.FrugalObjectListtypes.Use special symbols, like wildcards and others. The full list is shown in the table below.
- Special symbols and filter examples
Symbol
Description
Example
*Wildcard
*All objects in the set
sys.*.dataAll types and namespaces that match the pattern. E.g.
System.Data,System.Windows.Controls.Datagrid, andSystem.Windows.Data.Binding.sys.*.data.Only namespaces that match the pattern. E.g.
System.Windows.Data.Bindingbut notSystem.Windows.Controls.Datagrid.Arrays
[]Leave only arrays
str[]Arrays, containing
strin their type or namespace. E.g.String[].[,[,,...or
[,][,,]...Leave only arrays of the specified or higher (if brackets are not closed) dimension
str[,,Arrays with the dimension 3 and higher containing
strin their type or namespace. E.g.String[,,]andString[,,,].str[,,]Three-dimensional arrays containing
strin their type or namespace. E.g.String[,,].!aExclude arrays from the result
!a strObjects (excluding arrays) containing
strin their type or namespace. E.g.Stringbut notString[].Generic type arguments
<Leave only types with generic type arguments
str<Only objects containing
strin their type or namespace and having generic type arguments. E.g.FileStreamStorage<Char>but notList<String>.<strOnly objects containing
strin their generic type arguments. E.g.List<String>but notFileStreamStorage<Char>.<,<,,...or
<,><,,>...Leave only objects with the specified number of generic type arguments
fun<,,>Objects containing
funin their type or namespace and having three generic type arguments. E.g.Func<String, Object, Object>.fun<str,,taskObjects containing
funin their type or namespace and having three or generic type arguments that match the pattern. E.g.Func<Stream, IAsyncResult, TaskResult, EventArgs>.!gExclude generic type arguments from the search scope
!g strObjects (that do not have generic type arguments) containing
strin their type or namespace. E.g.Stringbut notList<String>.#c#struct#m#nsSearch by type, value type, method, or namespace.
#ns FeatureObjects containing
Featurein their namespace.
In the Types view, you can select the following subjects for further analysis:
note
The list supports multi-selection. To select more than one item, click desired items while holding the
Ctrlkey. To select a number of adjacent items, click the first one and then the last one while holding theShiftkey. This will allow analyzing a set of Selected objects.
Do one of the following:
Double-click the type in the list.
Right-click the type and choose Open this object set.
After this, the selected object set is added to the Analysis Path and you can use other object set views to analyze the objects in more detail.
Click the
 Open objects retained by this set button.
Open objects retained by this set button.After this, the Exclusively retained objects subject will be added to the Analysis Path and the list of desired objects will be displayed in the Group by Types view.