GitLab Integration
Follow the instructions on this page to integrate with VCS repositories that are hosted on gitlab.com, self-hosted GitLab Community Edition (CE), or self-hosted GitLab Enterprise Edition (EE) server.
A GitLab integration enables the following features in YouTrack:
Apply commands to YouTrack issues in commit messages. For more information, see Apply Commands in VCS Commits.
Track commits that are related to specific issues in the activity stream for each issue. For more information, see Commits.
Display the status of pull (merge) requests directly in the activity stream of any issue that is referenced in the title or description of the pull request. For details, see Pull Requests.
Add links to YouTrack issues in commit messages or branch names. For more information, see Link Issues in VCS Commits.
Prerequisites
To set up an integration with GitLab, your YouTrack installation must be accessible to inbound connections over the internet. Specifically, you need to make sure that your network doesn't block connections between your VCS server and YouTrack.
If you're integrating with a GitLab CE or GitLab EE installation and want to establish a secure (HTTPS) connection with the server, you may need to import the SSL certificate for your GitLab server into YouTrack.
If your GitLab server has a valid certificate signed by a well-known certificate authority (CA), the JVM vendor may have already added the root (CA) certificate to the certificate store. You should be able to connect to the server without importing its SSL certificate.
If the certificate for your server is self-signed, you need to import the certificate and public key to establish a secure connection. For security, use this option only when both YouTrack and your GitLab server run on a private computer network. This operation is only available to users with Low-level Admin Read and Low-level Admin Write permissions. For instructions, see SSL Certificates.
Enable the YouTrack Integration in GitLab
The first thing you should do is enable the YouTrack integration in GitLab. This formats references to YouTrack issues in commit messages as links to the target issues in YouTrack. The following limitations apply:
This functionality is supported in GitLab versions 11.9.0 and later.
The integration only recognizes issue prefixes that begin with an uppercase letter. Issue prefixes that begin with lowercase letters or numeric values are not recognized.
To learn more about this integration, refer to the GitLab Docs.
To enable the YouTrack Integration:
Access the project that you want to integrate with in GitLab.
From the Settings menu, select Integrations.
From the list of available integrations, select YouTrack.
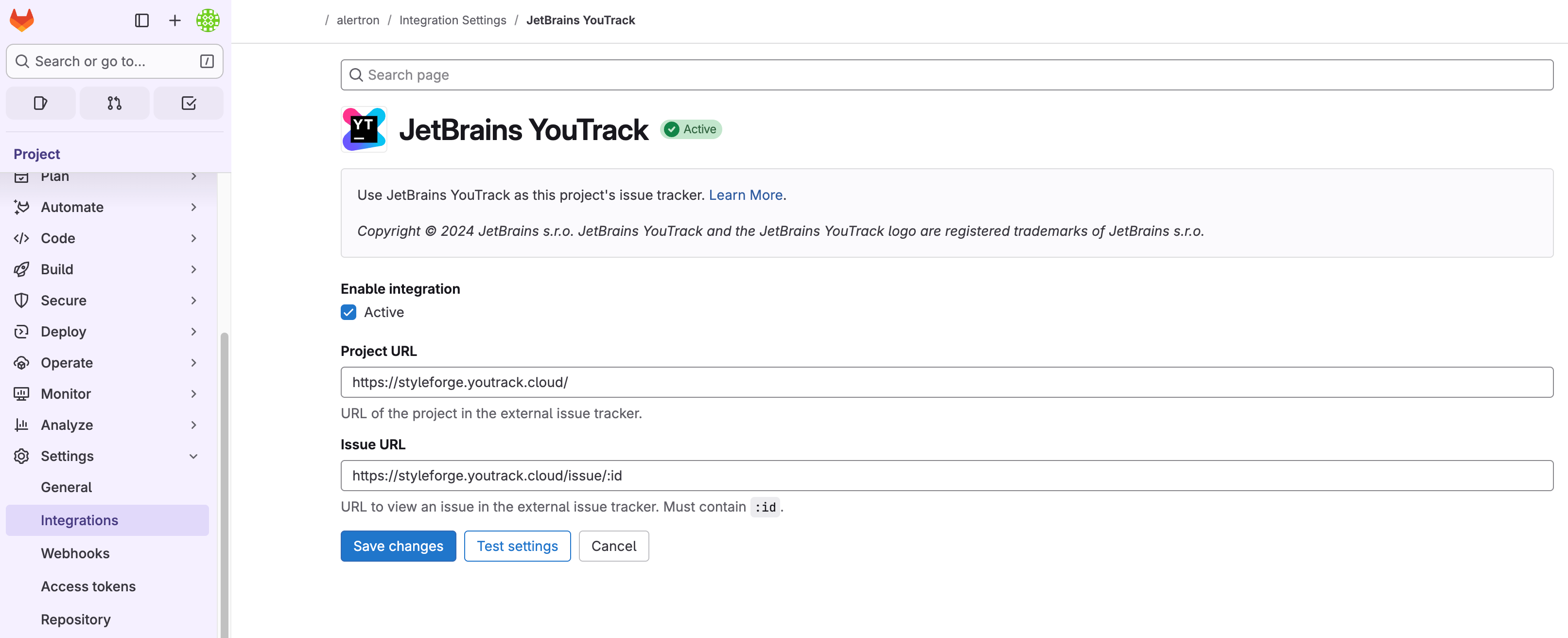
Enable the Active option for the Enable integration setting.
Specify values for the following settings:
Setting
Description
Project URL
Enter the base URL for your YouTrack service.
Example:
https://<your YouTrack name>.youtrack.cloudFor YouTrack Cloud instances hosted on
myjetbrains.com, your base URL includes the trailing/youtrack.You don't need to add the project name or ID to the URL.
Issue URL
Enter your base URL followed by
issue/:id.Click the Save changes button.
With this configuration, any reference recognized as an issue in YouTrack is set as a link.
The link is formed according to the pattern that is set for the Issue URL.
The
:idplaceholder is replaced with the issue ID, which includes the project prefix.
This means that you can add links in GitLab to any issue in any project from your YouTrack installation, even when you haven't configured an integration for the project in YouTrack. However, related VCS changes are only shown in issues where the GitLab integration has been set up for the project in YouTrack. To enable this integration feature, continue with the setup as described in the following section.
Configure the GitLab Integration
Next, you need to establish a connection between a project in YouTrack and a repository in GitLab. To connect with GitLab, you need to generate and store an access token. The YouTrack integration is configured to work with any of the following token types:
Token | Description |
|---|---|
Personal access token | These tokens grant YouTrack access to the repository based on the access that is granted to your GitLab account. We generally discourage using personal tokens for integrations, as it ties the integration to an account that belongs to a single person whose involvement in a project may change over time. |
Project access token | These tokens grant YouTrack access to the repository where the scope is restricted to the project itself. This is generally considered to be better than a personal token, because it isn't associated with a specific user account. |
Group access token | These tokens provide access to resources within a specific group or organization in GitLab and can be useful for teams that work on multiple projects. |
Follow these guidelines when creating an access token in GitLab:
Project and group access tokens require the
apiandread_repositoryscopes. Personal access tokens requireapi,read_user, andread_repository.Project or group access tokens require the Owner or Maintainer role.
To learn more about access tokens in GitLab, please refer to the GitLab documentation.
You can use a single access token to set up multiple integrations. If you don't already have an access token, use the direct link from YouTrack to generate it during this setup procedure.
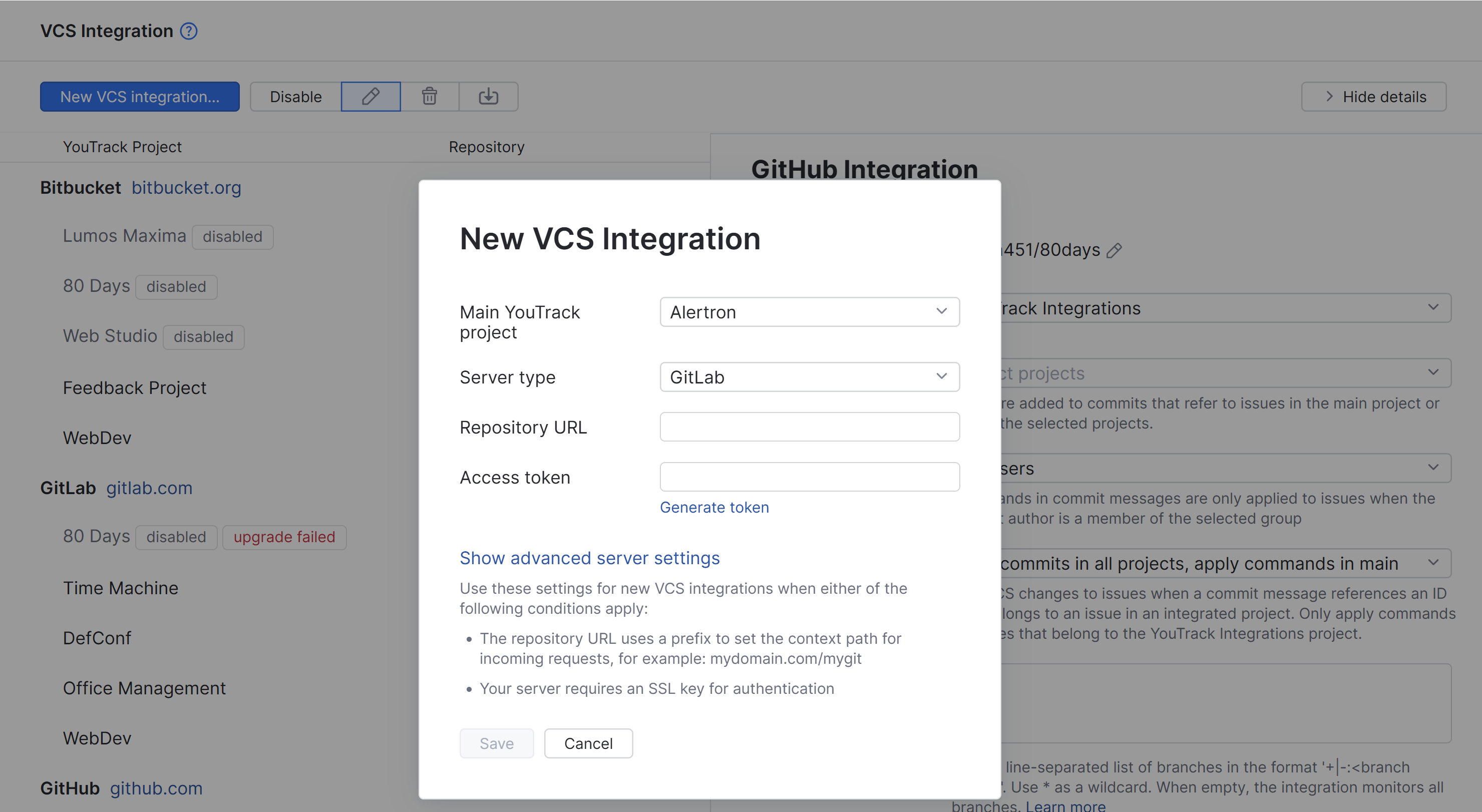
To connect to a GitLab repository:
From the main navigation menu in YouTrack, select
.
Click the New VCS Integration button.
From the Main YouTrack project list, select the name of the primary project that you want to integrate with the VCS repository. You can add integrations with additional YouTrack projects after you have set up the connection to the repository.
For the Server type, select GitLab.
Paste the URL that points to your GitLab repository into the Repository URL input field.
Paste your access token into the Access token input field. If you don't already have an access token, follow these steps:
Click the Generate token link to open the Project Access Tokens page in GitLab.
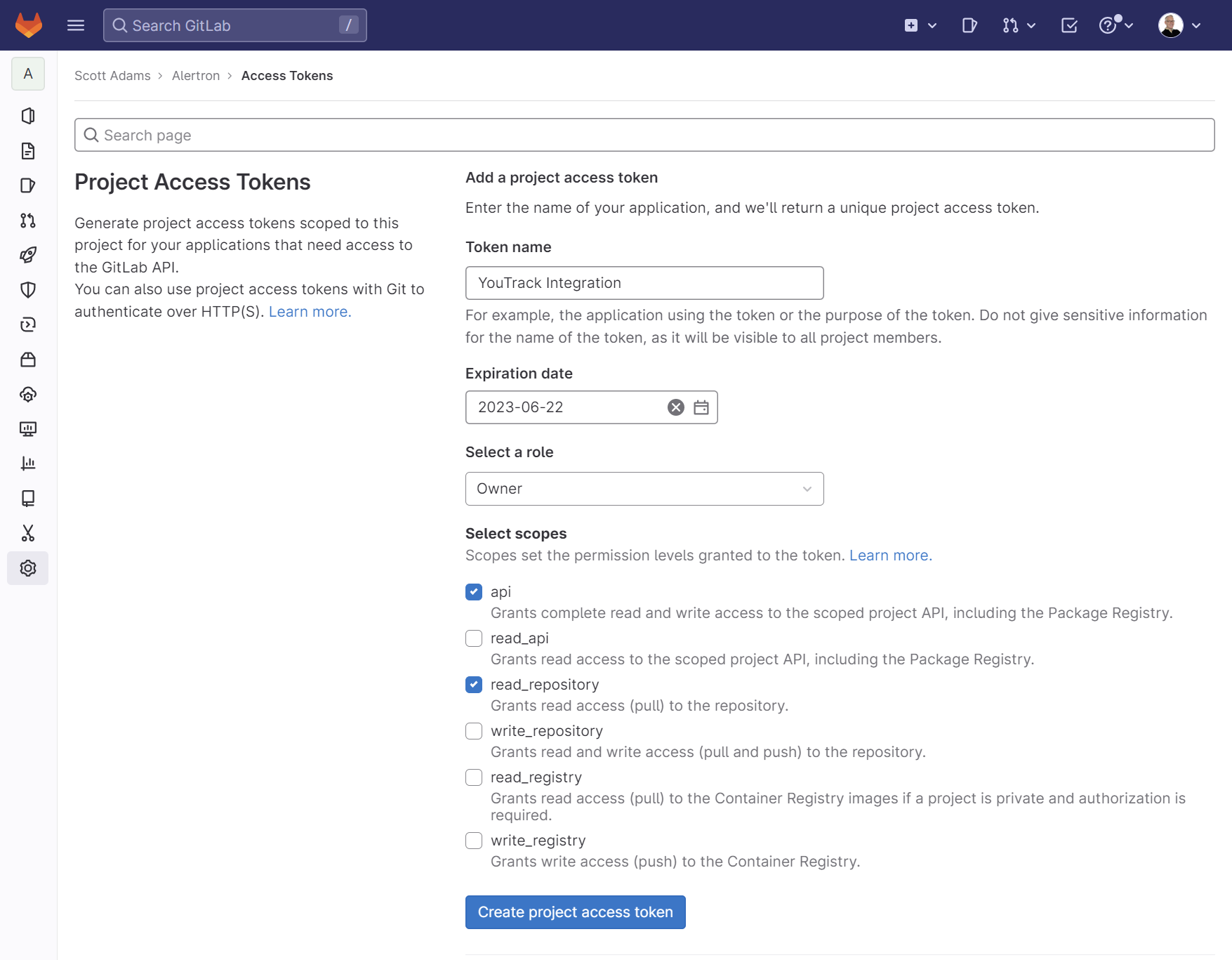
Enter a name for the token.
Set the Scopes for the token. Project access tokens require
apiandread_repositoryscopes.Grant the access token a role. Project access tokens require the Owner or Maintainer role.
Click the Create project access token button.
Copy the token to the clipboard.
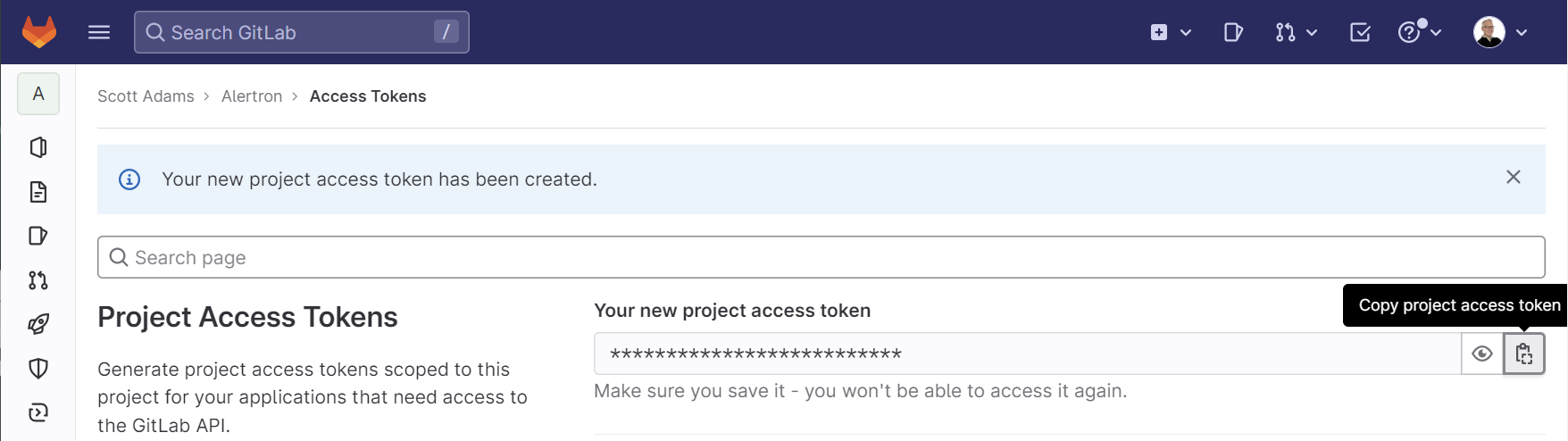
Note that you can also use personal and group access tokens to set up this integration, but the procedure for generating these tokens will vary. To learn more about access tokens in GitLab, please refer to the GitLab documentation.
Switch back to the New VCS Integration dialog in YouTrack and paste the token into the Access token field.
Click the Save button.
Your YouTrack project is integrated with the selected repository in GitLab.
Commits from the GitLab repository that reference an issue in the project are displayed in the activity stream of the referenced issue.
The sidebar displays additional settings for configuring the VCS integration.
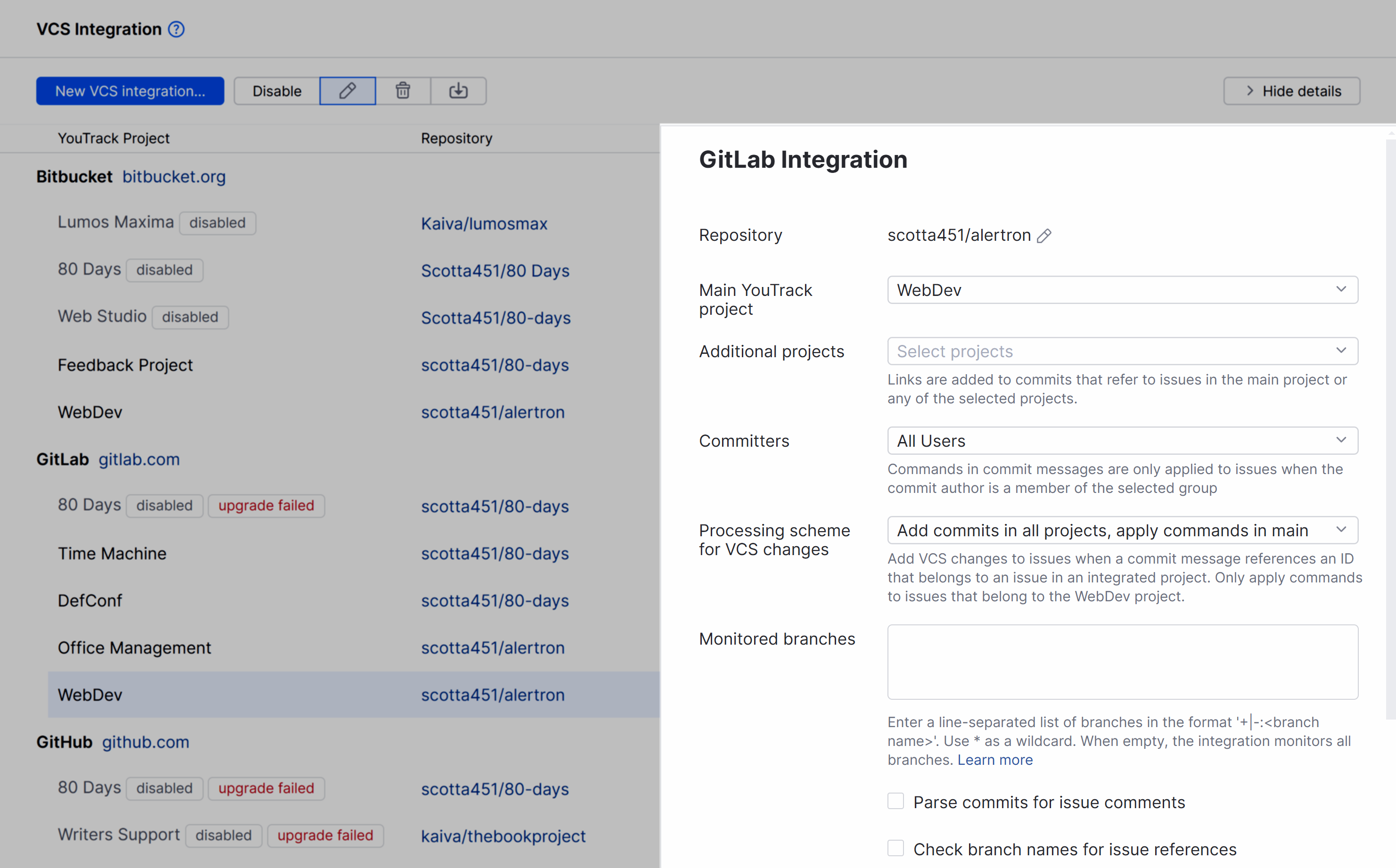
To learn more about these settings, see Integration Settings.
Advanced Server Settings
If you are unable to establish a connection to your repository using the basic settings on the New VCS Integration dialog, click the Show advanced server settings link.
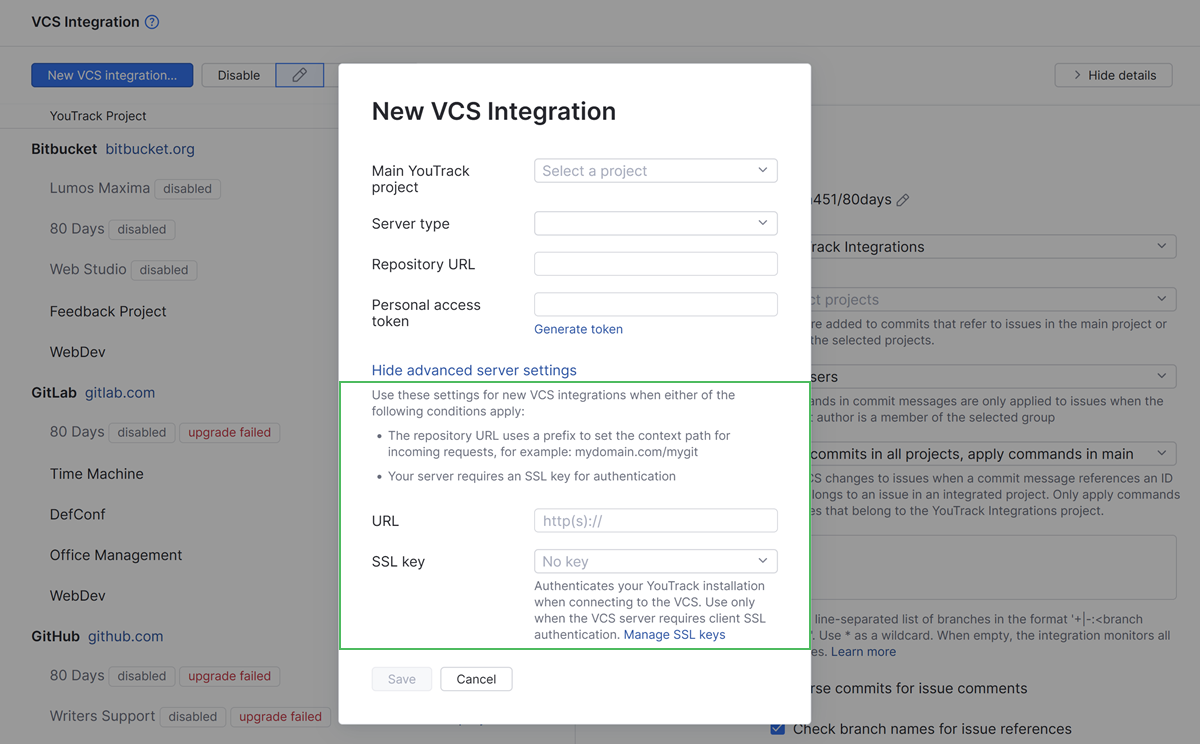
You only need to enter values for these settings for new VCS integrations with the target server. If you already have a working integration with a single repository on the server, you can add integrations with other repositories without setting these parameters again.
Use the following guidelines to set the values for these settings:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
URL | This setting helps to identify the path to the GitLab repository. If the repositories for your GitLab CE or EE server are available under To resolve this problem, enter the base URL for your GitLab server plus the context path that points to your repository. For example: |
SSL key | If your server environment is set up to require client SSL authentication, select the keystore that contains the private key for your YouTrack server. This key identifies your YouTrack server when it tries to establish a connection with GitLab. This setting is only used to support HTTPS authentication as required by connections to your internal network. The list only displays SSL keys that are already imported into YouTrack. To learn how to generate keystore files and upload them to YouTrack, see SSL Keys. |
Integration Settings
By default, the VCS integration processes changes that are committed to the repository by any user in any branch. Any user who has access to the issue in YouTrack can view these changes in the issue activity stream.
If you only want to process changes by specific users in designated branches or restrict the visibility of VCS changes in YouTrack, you can customize the integration settings. Use the following settings to customize the integration:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Repository | Displays the path to the repository in the integrated version control system. If needed, you can edit the location of the repository after you have set up the integration. For instructions, see Edit Repository Settings. |
Main YouTrack project | Sets the primary project in which the VCS integration is active. |
Additional projects | Integrates the linked repository with one or more additional projects. |
Committers | Restricts the ability to update issues with commands in commit messages to members of the specified group. VCS changes from users who are not members of the selected group are still attached to related issues, but any commands that are specified in their commits are ignored. |
Processing scheme for VCS changes | Choose how to process VCS changes when the commit message references an issue ID. The following options are supported:
|
Monitored branches | Stores the names of the branches that you want to monitor for changes.
If the address that you entered as the Repository URL when you connected to the repository points to a specific branch, this branch is automatically added to the list of monitored branches when you set up the connection. |
Parse commits for issue comments | When enabled, specific lines of text in commit messages are copied to issues as comments. When you copy parts of the commit message to the issue as comments, you can trigger @mention notifications and expose information to users who don't have access to VCS changes. This setting does not affect how commit messages are shown in VCS changes. The entire commit message, including commands and issue comments, is always shown as part of the VCS change record in the activity stream. You should only enable this option when:
To learn more about how YouTrack processes commit messages, see Apply Commands in VCS Commits. |
Check branch names for issue references | When enabled, the integration checks for references to issues in branch names for commits and pull requests. This option was added for teams that use a branch-per-ticket process, so their developers don't have to mention issue IDs in their commit messages explicitly. |
VCS changes visibility | Restricts the visibility of VCS changes to one or more groups of users in YouTrack. When unrestricted, the list of VCS changes is visible to any user who has permission to read the issue. |
Available Actions
When you select an integrated version control system in the list, the following actions are available in the toolbar:
Action | Description |
|---|---|
Disable | Shuts off the connection between the integrated project and the VCS repository. The configuration is not changed and can be enabled at any time. |
Edit | Opens the integration settings dialog in the sidebar for the selected project and repository. |
Delete | Removes the settings for the integrated project from YouTrack. This action also removes all VCS changes that were added to issues for commits in the linked repository. While the action itself cannot be undone, you can use the Import action to restore VCS changes that were removed accidentally. |
Import commits and open pull requests | Checks the commit history in the linked repository and adds VCS changes to issues that are referenced in commit messages. This option is only available for integrations that are currently enabled. You can use this action to restore VCS changes that were removed when an integration was accidentally deleted or to migrate links to issues in a new project. |
Troubleshooting
Condition — References to issues in VCS commits are not shown as VCS changes in YouTrack.
Cause | Solution |
|---|---|
The webhooks in the integrated VCS don't exist, are disabled, or are otherwise malformed. | Check the webhooks in the settings for your VCS repository. Make sure that the webhooks exist and that they are enabled. If you suspect that there is a problem with a webhook, delete or disable it in the settings for your VCS and set up a new VCS integration in YouTrack. |
Condition — Commands that are specified in VCS commits are not applied to issues in YouTrack.
Cause | Solution |
|---|---|
The users who commit changes to the repository are not members of the Committers group in the integration settings. | Either add the committers to the specified group in YouTrack or modify the selection in the integration settings. |
The users who commit changes to the repository do not have permission to update issues in the connected project. | Either add these users to the project team or grant them a role in the project that includes the Read Issue and Update Issue permissions. |
YouTrack can't find a user account that matches the author of the commit message. | The user must either use the same email address for their accounts in both YouTrack and GitLab or add the value stored as the Name in their GitLab profile to the list of VCS usernames in their Hub accounts. For more information, see Match Change Authors and YouTrack Users. |
Condition — You are unable to connect to your GitLab repository. Follow the instructions below to resolve the problem.
Cause | Solution |
|---|---|
The user whose personal access token is used for authentication with GitLab does not have access to any projects in GitLab. | Access the Members settings for your GitLab project and add this user to the project. You can also share the project with a group where this user is a member. This user does not require a specific access level — Guest access is sufficient. |
Condition — You are unable to establish a connection between YouTrack and your GitLab CE/EE server. See if any of the following causes are present.
Cause | Solution |
|---|---|
The external service is unavailable. | Verify that your GitLab server is running. |
The connection is blocked by a firewall. | Open the ports in the firewall that are used by YouTrack and the GitLab server. |
The connection to the external service is blocked by the proxy server. You are trying to connect over the wrong port. | Set the system properties for your server that let YouTrack connect to other services through the proxy server. For instructions, see Proxy Configuration. |
The GitLab server requires a secure connection. | Import the certificate for your GitLab server into YouTrack. For instructions, see SSL Certificates. |
Your SSL certificate for the GitLab server has expired. | Renew and import the updated certificate into YouTrack. For instructions, see SSL Certificates. |
Condition — You are unable to set up a connection to a repository on your GitLab CE/EE server and see an HTTP 422 Unprocessable Entity error in the logs. Follow the instructions below to diagnose and resolve the problem.
Cause | Solution |
|---|---|
The base URL for your YouTrack server uses a non-default port. For example: | Open the menu for your GitLab server and enable the Allow requests to the local network from webhooks and integrations in the Outbound requests section of the page. |
The base URL for your YouTrack server is either set to use | The best solution in this case is to update the base URL for your YouTrack installation to use a proper web address. Alternatively, you can use the Java start parameter |