Integrating TeamCity with Docker
TeamCity comes with Docker Support, implemented as a bundled plugin.
Requirements
The integration requires Docker installed on the build agents. To use the Docker Compose build runner, install Docker Compose as well.
Since version 2019.2.1, TeamCity periodically checks if Docker is available on active build agents. Based on the docker.server.version and docker.version variables received from the agents, TeamCity distributes builds that use Docker only between agents with the installed Docker engine.
If a build configuration uses the Docker runner or the Docker Wrapper extension, TeamCity automatically adds the docker.server.version agent compatibility requirement for this configuration.
Supported Environments
TeamCity Docker Support can run on Windows, Linux, and macOS build agents. It uses the docker executable on the build agent machine, so it should be runnable by the build agent user.
note
On Linux, the integration will run if the installed Docker is detected.
On Windows, the integration works for Linux and Windows container modes.
On macOS, the official Docker support for Mac should be installed for the user running the build agent.
Parameters Reported by Agent
During the build, the build agent reports the following parameters:
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Docker CLI version |
| The Docker Compose file version, if the Docker Compose build step is used. |
| Docker Engine version |
| The Docker Engine OS platform, can have the |
If you are using the Command Line build step (and not the TeamCity-provided Docker steps), these parameters can be used as agent requirements to ensure your build is run only on the agents with Docker installed.
Features
The TeamСity-Docker integration provides the following features which facilitate working with Docker under TeamCity:
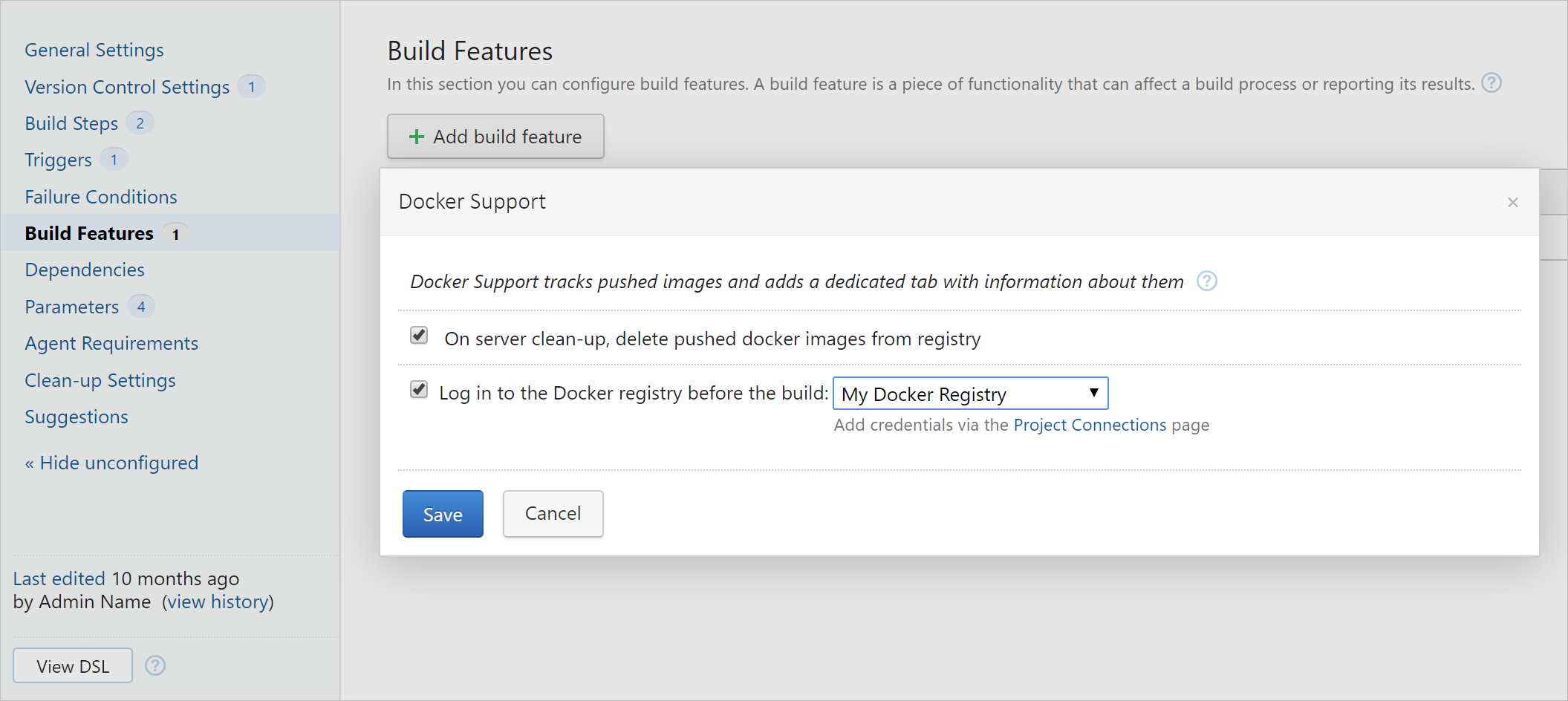
Docker Support Build Feature
Adding this build feature will enable Docker events monitoring: such operations as docker pull and docker run will be detected.
The build feature adds the Docker Info tab to the build results page providing information on Docker-related operations. It also provides the following options:
ability to clean up the images
automatic login to an authenticated registry before the build and logout of it after the build
These options require a configured connection to a Docker registry:
Clean-up of images
If you have a build configuration which publishes images, you need to remove them at some point. You can select the corresponding option and instruct TeamCity to remove the images published by a certain build when the build itself is cleaned up. It works as follows: when an image is published, TeamCity stores the information about the registry of the images published by the build. When the server clean-up is run and it deletes the build, all the configured connections are searched for the address of this registry, and the images published by the build are cleaned up using the credentials specified in the connection found.
Automatic Login to/Logout of Docker Registry
If you need to log in to a registry requiring authentication before a build, select the corresponding option and a connection to Docker configured in the Project Settings.
Automatic logout will be performed after the build finishes.
Docker Connection for Project
The Project Settings | Connections page allows you to configure a connection to docker.io (default) or a private Docker registry. More than one connection can be added to the project. The connection will be available in all the subprojects and build configurations of the current project.
tip
After configuring the Docker Registry connection for a TeamCity project, you need to select it when creating the Docker Support feature in the respective build configuration.
Registry Address Format
By default, https://docker.io is used.
To connect to a registry, use the following format: [http(s)://]hostname:port.
If the protocol is not specified, the connection over https is used by default.
Connecting to Private Cloud Registry
TeamCity supports the Azure container registry storing Docker images; you can authenticate using Service principal (the principal ID and password are used as connection credentials) or Admin account.
Amazon Elastic Container Registry (AWS ECR) is supported: specify the AWS region and your AWS Security Credentials when configuring the connection.
Connecting to Insecure Registry
To connect to an insecure registry:
Configure all TeamCity agents where Docker is installed to work with insecure repositories as stated in the Docker documentation. This is sufficient to allow the connection to the private registry over HTTP.
To connect to an insecure registry over HTTPS with a self-signed certificate, in addition to the step above, import the self-signed certificate to the JVM of the TeamCity server as described here. You can consult the Docker documentation on using self-signed certificates.
Docker Runner
The Docker runner supports the build, push, and tag Docker commands.
When creating TeamCity projects / build configurations from a repository URL, the runner is offered as a build step during auto-detection, provided a Dockerfile is present in the VCS repository.
Docker Command
The runner provides the following settings, depending on the selected command:
Command | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
build | Dockerfile source | Depending on the selected source, the settings below will vary. The available options include File, a URL or File content. |
Path to file | Available if File is selected as the source. Specify the path to the Docker file. The path should be relative to the checkout directory. | |
Context folder | Available if File is selected as the source. Specify the context for the Docker build. If blank, the enclosing folder for Dockerfile will be used. | |
URL to file | Available if URL is selected as the source. The URL can refer to three kinds of resources: Git repositories, pre-packaged tarball contexts, and plain text files. See the Docker documentation for details. | |
File Content | Available if the file cis selected as the source. You can enter the content of the Dockerfile into the field. | |
Image platform | Select <Any> (default), Linux or Windows. | |
Image name:tag | Provide a newline-separated list of image name: tag(s) | |
Additional arguments for the | Supply additional arguments to the docker build command. See Docker documentation for details. | |
push | Remove image from agent after push | If selected, TeamCity will remove the image with |
Image name:tag | Provide a newline-separated list of image name:tag(s) | |
other | Command name | Docker sub-command, like |
Working directory | ||
Additional arguments for the command | Additional arguments that will be passed to the Docker command. |
You can enforce starting Docker commands on a TeamCity agent via sudo. Add the teamcity.docker.use.sudo=true setting in the build agent configuration file or as an agent's system property. On the agent start, the TeamCity agent log will inform that the sudo prefix is used to run Docker commands.
To configure the sudoers file for the sudo command, use visudo as follows:
buildagentuser ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:SETENV:<full_path_to_docker>We recommend removing (or commenting out) the Defaults requiretty line from the sudoers file to prevent the problem with docker login.
Docker Compose Runner
The runner allows starting Docker Compose build services and shutting down those services at the end of the build.
The Docker Compose runner supports one or several Docker Compose YAML file(s) with a description of the services to be used during the build. The path to the docker-compose.yml file(s) should be relative to the checkout directory. When specifying several files, separate them with a space.
The executed commands are:
# The commands are executed with the current working directory, where the docker-compose file resides.
docker-compose -f <docker-compose.yml> [-f <docker-compose2.yml>] up -d
# At the end of the build, for each docker compose build step the build agent will run:
docker-compose -f <docker-compose.yml> [-f <docker-compose2.yml>] down -vIf the checkbox pull image explicitly is enabled, docker-compose pull will be run before the docker-compose up command.
When using Docker Compose with images which support HEALTHCHECK, TeamCity will wait for the healthy status of all containers that support this parameter.
If the start of Docker Compose was successful, the TeamCity agent will register the TEAMCITY_DOCKER_NETWORK environment variable containing the name of the Docker Compose default network. This network will be passed transparently to the Docker Wrapper when used in some build runners.
Docker Wrapper
TeamCity provides the Docker Wrapper extension for Command Line, Maven, Ant, and Gradle runners. Each of the supported runners has the dedicated Docker Settings section.
Docker Settings
In the Docker Settings section of the build step settings, you can specify a Docker image which will be used to run the build step. Once an image is specified, all the following options become available.
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Run step within Docker container | Specify a Docker image name as stated in the Docker Hub. TeamCity will start a container from the specified image and will try to run this build step within this container. For example, |
Docker image platform | Select <Any> (default), Linux, or Windows. |
Pull image explicitly | If enabled, the image will be pulled from the Hub repository via |
Additional docker run arguments | Allows specifying additional options for
|
How It Works
Technically, the command of the build runner is wrapped in a shell script, and this script is executed inside a Docker container with the docker run command. All the details about the started process, text of the script, and so on, are written into the build log (the Verbose mode enables viewing them).
The checkout directory and most build agent directories are mapped inside the Docker process.
At the end of the build step with the Docker wrapper, a build agent runs the chown command to restore access of the buildAgent user to the checkout directory. This mitigates a possible problem when the files from a Docker container are created with the root ownership and cannot be removed by the build agent later.
If the process environment contains the TEAMCITY_DOCKER_NETWORK environment variable set by the previous Docker Compose build step, this network is passed to the started docker run command with the --network switch.
Environment Variables Handling
TeamCity passes environment variables from the build configuration into the Docker process, but it does not pass environment variables from the build agent, as they may not be relevant to the Docker container environment. The list of the passed environment variables can be seen in Verbose mode in the build log.
Docker Disk Space Cleaner
Docker Disk Space Cleaner is an extension to the Free Disk Space build feature ensuring a certain amount of disk space for a build.
TeamCity regularly cleans up its related Docker images which were tagged/pulled:
in a build with the Docker Support build feature, or
in a Docker or Docker Compose build step, or
in a build step with the enabled Docker Wrapper extension
For such builds,
The TeamCity agent tracks Docker images tagged or pulled during builds (the list of images is stored in the
buildAgent/system/docker-used-images.datfile).During clean-up / freeing disk space, TeamCity agent tries to remove these images if they were not used within 3 days, 1 day, 0 on subsequent attempts to free disk space.
Besides that, TeamCity cleans local Docker Caches using the command:
Since 2018.1.2:
docker system prune --volumes. Works for Docker v.17.06.1 or later.Before 2018.1.2:
docker system prune -a
Service Message to Report Pushed Image
If TeamCity (for some reason) cannot determine that an image has been pushed, a user can send a special service message to report this information to the TeamCity server:
##teamcity[dockerMessage type='dockerImage.push' value='<full_image_tag>,size:<size in bytes>,digest:<hash>']For example:
##teamcity[dockerMessage type='dockerImage.push' value='myRegistry/repo-test:17,size:2632,digest:sha256:8dc5a195c3dcdc7c288d16288ff3f9ab1d8a5a230e09afb9c8dc9215e861aa55']Conforming with Docker download rate limits
Since November 1st 2020, Docker Hub introduces download rate limits for public image pulls.
If your TeamCity builds use Docker Wrapper or Docker Compose to pull images from Docker Hub, make sure these pulls do not exceed the following limits:
Anonymous Docker users: 100 pulls per 6 hours
Docker users with the Free plan: 200 pulls per 6 hours
If you have a Team or Pro Docker account, the number of pulls stays unlimited.
A regular TeamCity agent stores a once pulled image in its cache. This allows running an indefinite number of builds using the same pulled image on a regular basis.
However, there are few cases to consider:
If you are using cloud agents, all required images will be downloaded every time a new cloud agent is launched.
If the Pull image explicitly option is enabled in the build step settings, the image will be downloaded in every new build run, even on a local agent. We recommend that you disable this option to prevent reaching the rate limit.
During the Free Disk Space stage of the build, TeamCity may clean up old unused Docker images from the local cache.
If previously your builds were accessing Docker Hub anonymously, you can double the number of allowed pulls by creating a Free Docker user profile and configuring a Docker connection in your TeamCity project. TeamCity agents will be able to use this connection to authenticate in Docker Hub before each build.