Forward reports
This section explains how you can forward Qodana reports to Qodana Cloud using this software:
Before you start
All configuration examples in this section use a project token generated by Qodana Cloud. This token is required for the paid Qodana linters and optional for use with the Community linters. You can see these sections to learn how to generate the project token in the Qodana Cloud UI:
The project setup section explains how to generate a project token when first working with Qodana Cloud.
The Manage a project section explains how to create a project token within an existing Qodana Cloud organization.
Once you obtain the project token, you can use the QODANA_TOKEN variable for identifying in a pipeline or workflow.
If you are using a Qodana Cloud instance other than https://qodana.cloud/, override it by setting the QODANA_ENDPOINT environment variable.
Docker and Qodana CLI
You can forward Qodana reports to Qodana Cloud using either Docker or Qodana CLI:
Besides QODANA_TOKEN, you need to provide several additional variables:
Variable name | Description |
|---|---|
| Project URL |
| Name of the branch analyzed |
| Commit hash |
| Job URL |
This is the command that uses all these variables:
Application of these tools implies that the values for all required variables should be provided manually, which is not convenient. Fortunately, you can overcome it using various CI/CD solutions that provide all data required by Qodana Cloud or contain predefined environment variables that refer to the data required by Qodana Cloud.
Azure Pipelines
In the Azure Pipelines UI, create the
QODANA_TOKENsecret variable and save the project token as its value.In the Azure pipeline file, add the
QODANA_TOKENvariable to theenvsection of theQodanaScantask:- task: QodanaScan@2024 env: QODANA_TOKEN: $(QODANA_TOKEN)
The rest variables and values required by Qodana Cloud are automatically generated by QodanaScan.
To learn more about Qodana integration with Azure Pipelines, see the Azure Pipelines section of this documentation.
Bitbucket Cloud
Here is the basic configuration snippet for the bitbucket-pipelines.yml file that lets you run Qodana in Bitbucket Cloud pipelines:
Here, the branches block specifies which branches to inspect.
The image block specifies the Qodana linter that will be invoked in the pipeline.
The script block contains the - export QODANA_TOKEN=$QODANA_TOKEN line that specifies the project token required by Qodana Cloud and saved as the $QODANA_TOKEN variable. The - qodana ... line in this block tells Bitbucket which directories to use while running the pipeline, and it can also contain Qodana options.
To learn more about Qodana integration with Bitbucket Cloud, see the Bitbucket Cloud section of this documentation.
CircleCI
To learn more about Qodana integration with CircleCI, see the CircleCI section of this documentation.
GitHub Actions
On the tab of the GitHub UI, create the
QODANA_TOKENencrypted secret and save the project token as its value. If you are using a Qodana Cloud instance other thanhttps://qodana.cloud/, override it by declaring theQODANA_ENDPOINTenvironment variable.On the tab of the GitHub UI, set up a new workflow and create the
.github/workflows/code_quality.ymlfile.To analyze the
mainandmasterbranches, as well as release branches and the pull requests coming to your repository, save this workflow configuration to the.github/workflows/code_quality.ymlfile:name: Qodana on: workflow_dispatch: pull_request: push: branches: # Specify your branches here - main # The 'main' branch - master # The 'master' branch - 'releases/*' # The release branches jobs: qodana: runs-on: ubuntu-latest permissions: contents: write pull-requests: write checks: write steps: - uses: actions/checkout@v3 with: ref: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }} # to check out the actual pull request commit, not the merge commit fetch-depth: 0 # a full history is required for pull request analysis - name: 'Qodana Scan' uses: JetBrains/qodana-action@v2025.2 env: QODANA_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.QODANA_TOKEN }}
To learn more about Qodana integration with GitHub, see the GitHub Actions section of this documentation.
GitLab CI/CD
Prepare your project as described in the Before you start section.
In the root folder of your GitLab-hosted project, create the
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile and save this configuration to that file:include: - component: $CI_SERVER_FQDN/qodana/qodana/qodana-gitlab-ci@v2025.2 inputs: args: --image,<image>
To learn more about Qodana integration with GitLab CI/CD, see the GitLab CI/CD section of this documentation.
Jenkins
In the Jenkins UI, create the credentials with the
qodana-tokenname as described in the Adding new global credentials section of the Jenkins documentation, and save the project token as the value for these credentials.In the root directory of your project, create the
Jenkinsfilefile and save this configuration to that file:pipeline { environment { QODANA_TOKEN=credentials('qodana-token') } agent { docker { args ''' -v "${WORKSPACE}":/data/project --entrypoint="" ''' image 'jetbrains/qodana-<image>' } } stages { stage('Qodana') { steps { sh '''qodana''' } } } }In the
imagesection of this script, specify the Qodana Docker image name.
To learn more about Qodana integration with Jenkins, see the Jenkins section of this documentation.
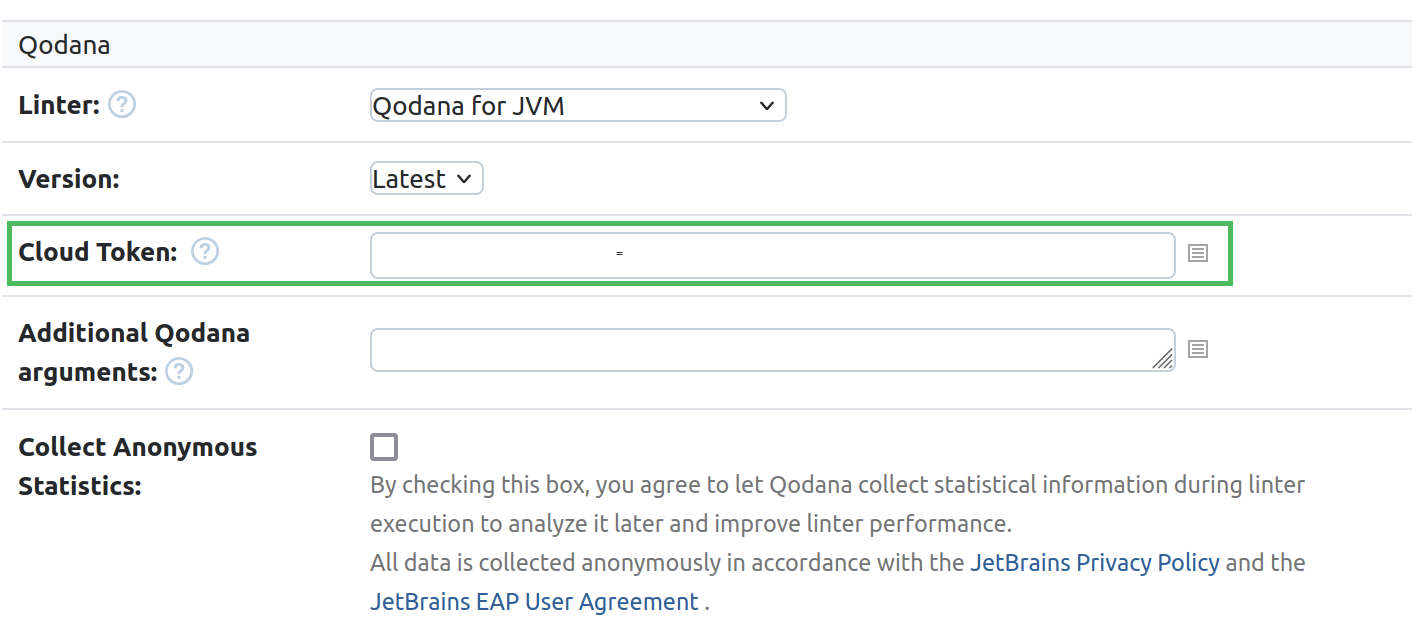
TeamCity
In the TeamCity UI, open the build step that will run Qodana.
In the field, insert the Qodana Cloud token value.
To learn more about Qodana integration with TeamCity, see the TeamCity section of this documentation.