Create and edit Jupyter notebooks
Create a Jupyter project
Go to .
Select a Jupyter project template.
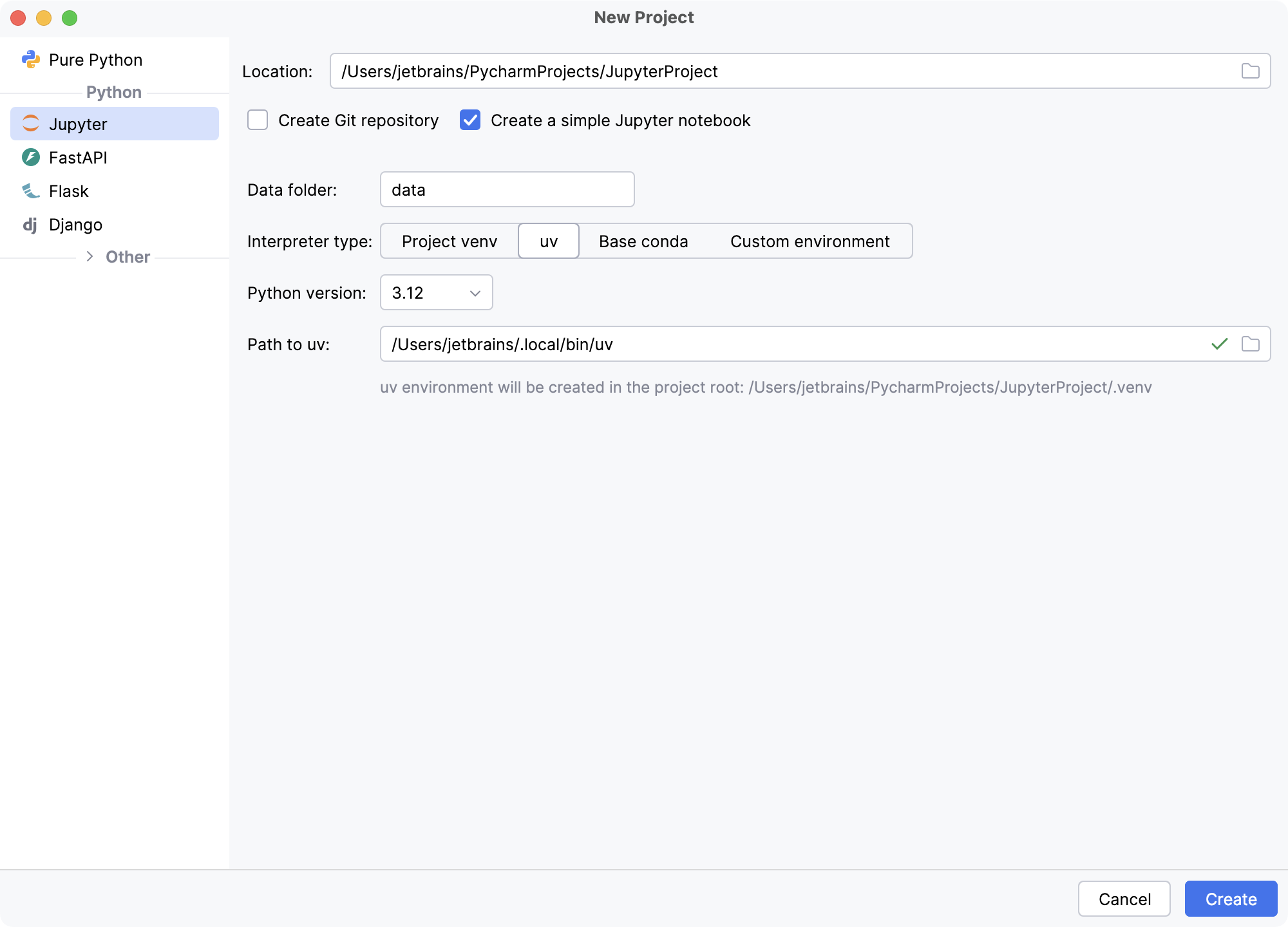
Select the project location. Click
in the Location field and specify the directory for your project. The project name will be automatically derived from the folder name in the specified path.
Select Create Git repository to put the project under Git version control.
Select Create a simple Jupyter notebook if you want PyCharm to add the
sample.ipynbfile to your project. This file contains a sample Jupyter Notebook and can help you get acquainted with the notebook editor UI and other features.If you want to proceed with the Project venv, uv or Base conda interpreter, select the corresponding option and click Create.
- Project venv
PyCharm creates a virtualenv environment based on the system Python in the project folder.
- uv
PyCharm configures a uv environment as the project interpreter.
- Base conda
PyCharm configures conda base environment as the project interpreter.
To configure an interpreter of another type or to use an existing environment, select Custom environment.
The following steps depend on your choice:
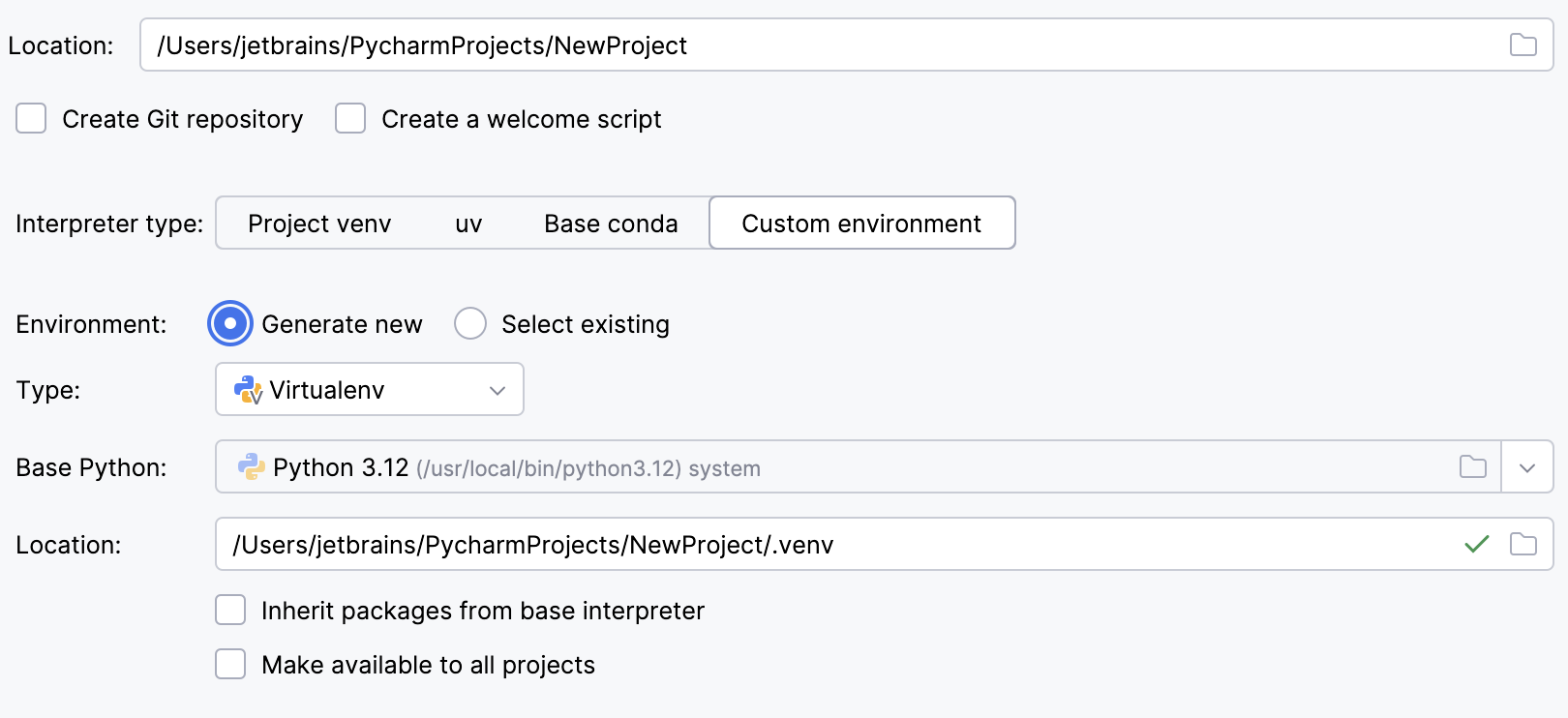
Select Virtualenv from the list of environment types.
Select the base interpreter from the list, or click
and find the Python executable in your file system.
Specify the location of the new virtual environment in the Location field, or click
and browse for the location in your file system. The directory for the new virtual environment should be empty.
Select the Inherit packages from base interpreter checkbox if you want all packages installed in the global Python on your machine to be added to the virtual environment you're going to create. This checkbox corresponds to the
--system-site-packagesoption of the virtualenv tool.Select the Make available to all projects checkbox if you want to reuse this environment when creating Python interpreters in PyCharm.
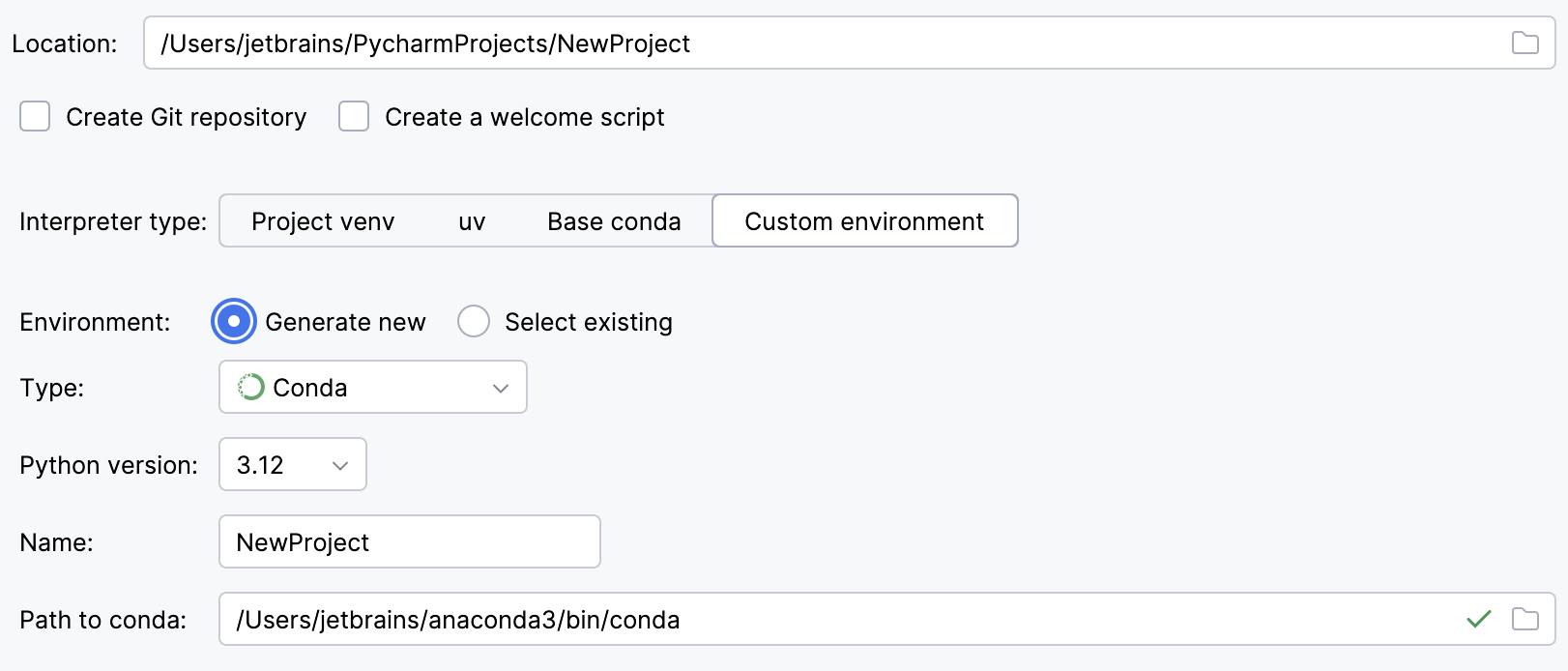
Select Conda from the list of environment types.
Select the Python version from the list.
Specify the environment name.
PyCharm will detect a conda installation.
If PyCharm did not detect the installation automatically, specify the location of the conda executable, or click
to browse for it.
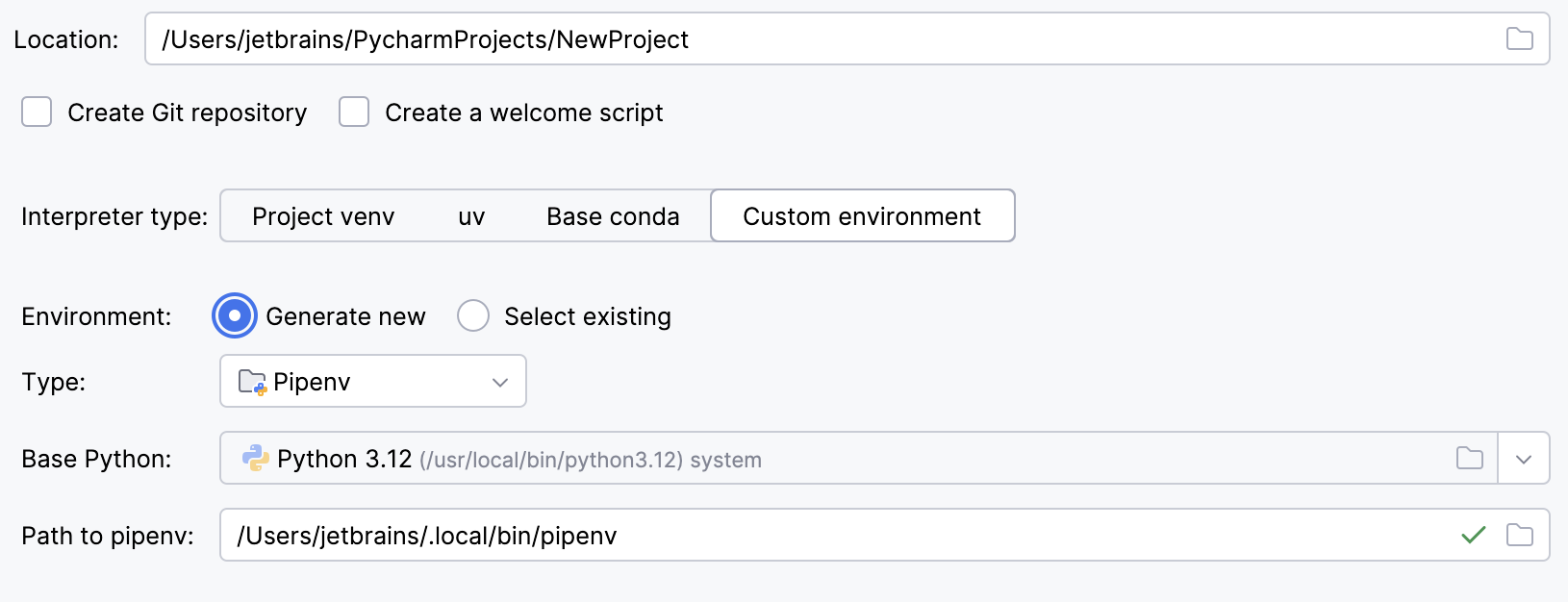
Select Pipenv from the list of environment types.
Select the base interpreter from the list, or click
and find the Python executable in your file system.
If you have added the base binary directory to your
PATHenvironmental variable, you do not need to set any additional options: the path to the pipenv executable will be autodetected.If PyCharm does not detect the pipenv executable, click Install pipenv via pip to allow PyCharm to install it for you automatically.
Alternatively, follow the pipenv installation procedure to discover the executable path and then specify it in the dialog.
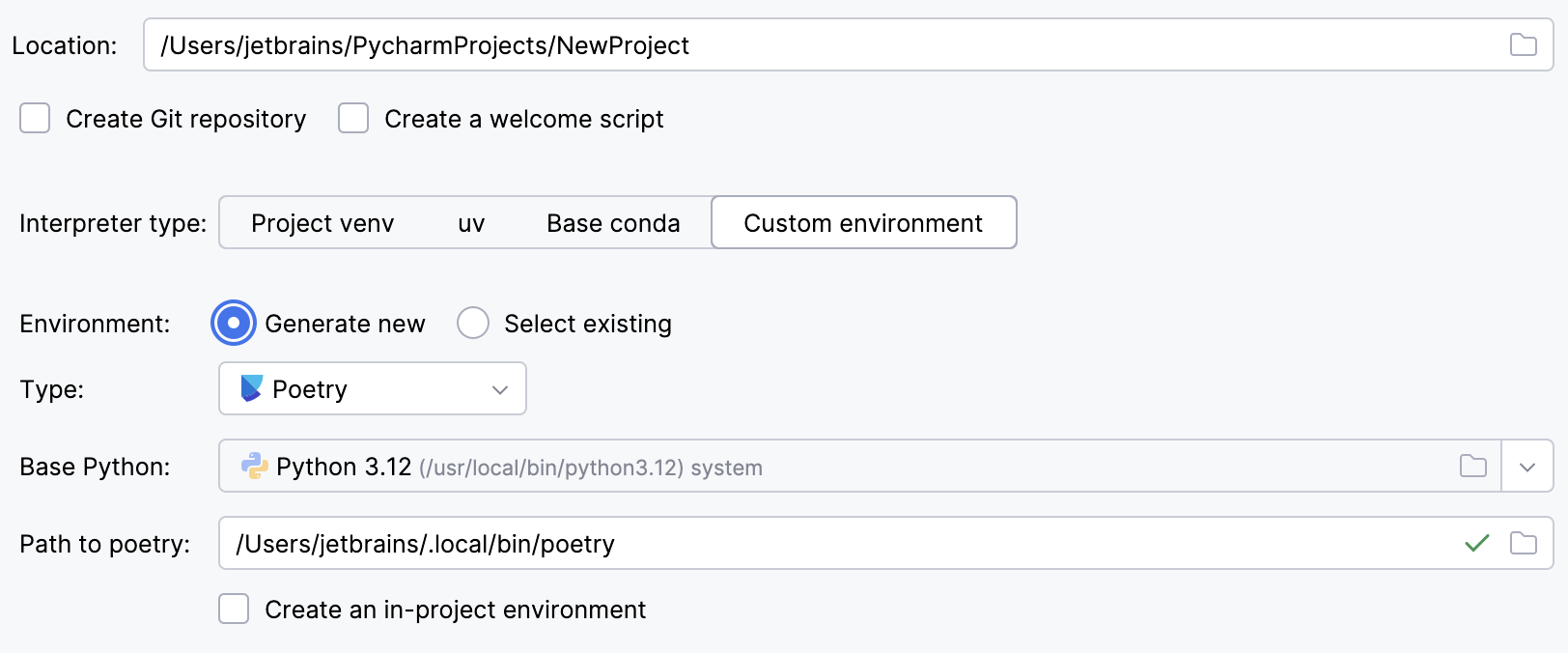
Select Poetry from the list of environment types.
Select the base interpreter from the list or click
and find the Python executable in your file system.
If PyCharm does not detect the Poetry installation, click Install poetry via pip to allow PyCharm to install Poetry for you automatically.
Alternatively, specify the location of the Poetry executable, or click
to browse for it.
To create a virtual environment within the project directory, select the Create an in-project environment checkbox.
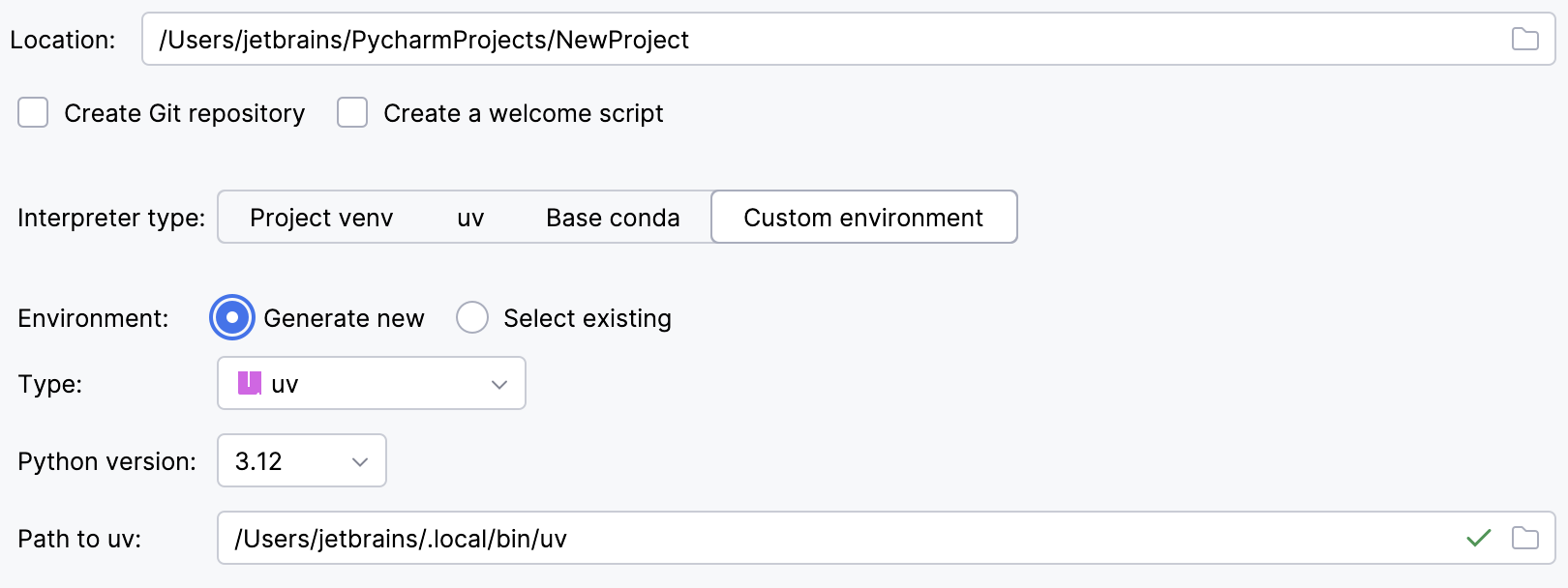
Select uv from the list of environment types.
Select the Python version from the list.
PyCharm will detect a uv installation.
Otherwise, specify the location of the uv executable, or click
to browse for it.
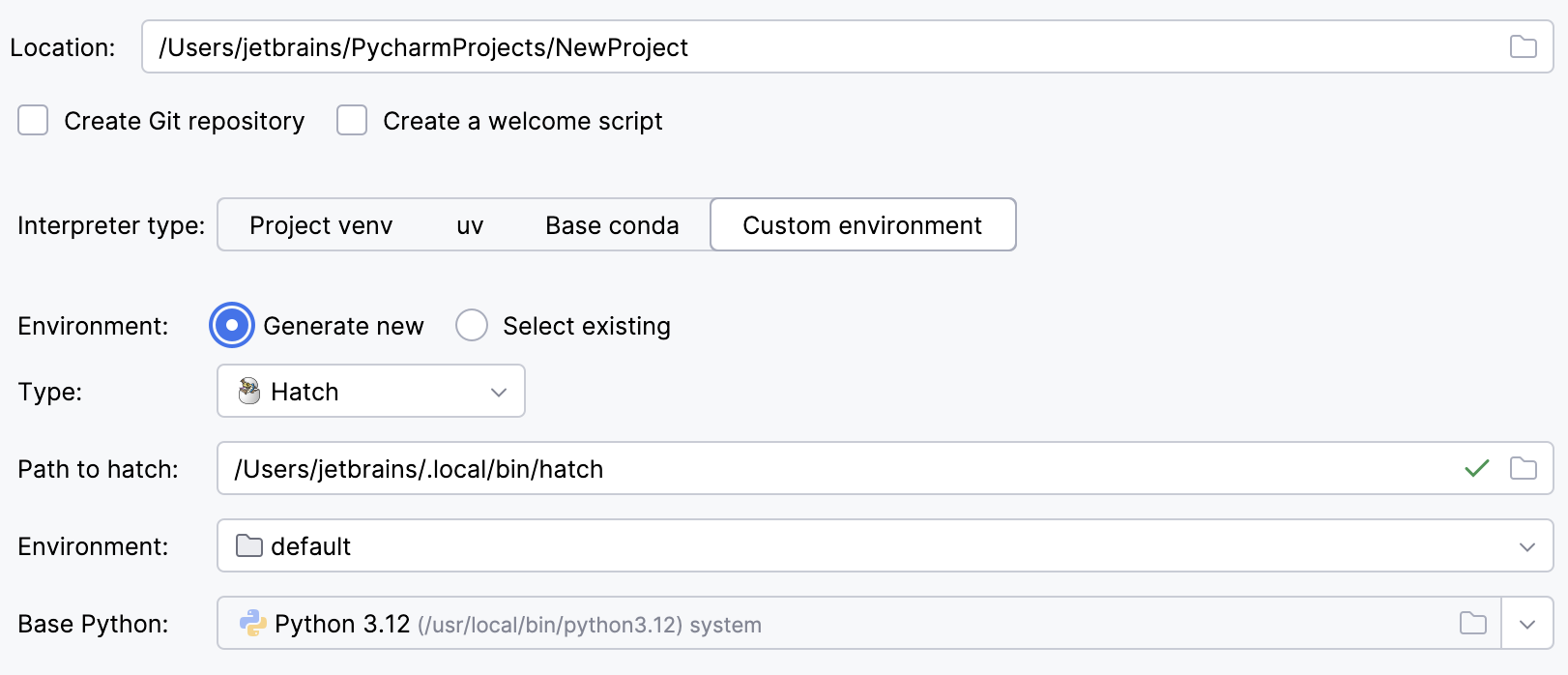
Select Hatch from the list of environment types.
PyCharm will detect a Hatch installation.
Otherwise, specify the location of the Hatch executable, or click
to browse for it.
Select an environment.
Hatch environments are workspaces designed for various project-specific tasks. If no environment is explicitly selected, Hatch will use the default environment.
Select the base interpreter from the list, or click
and find the Python executable in your file system.
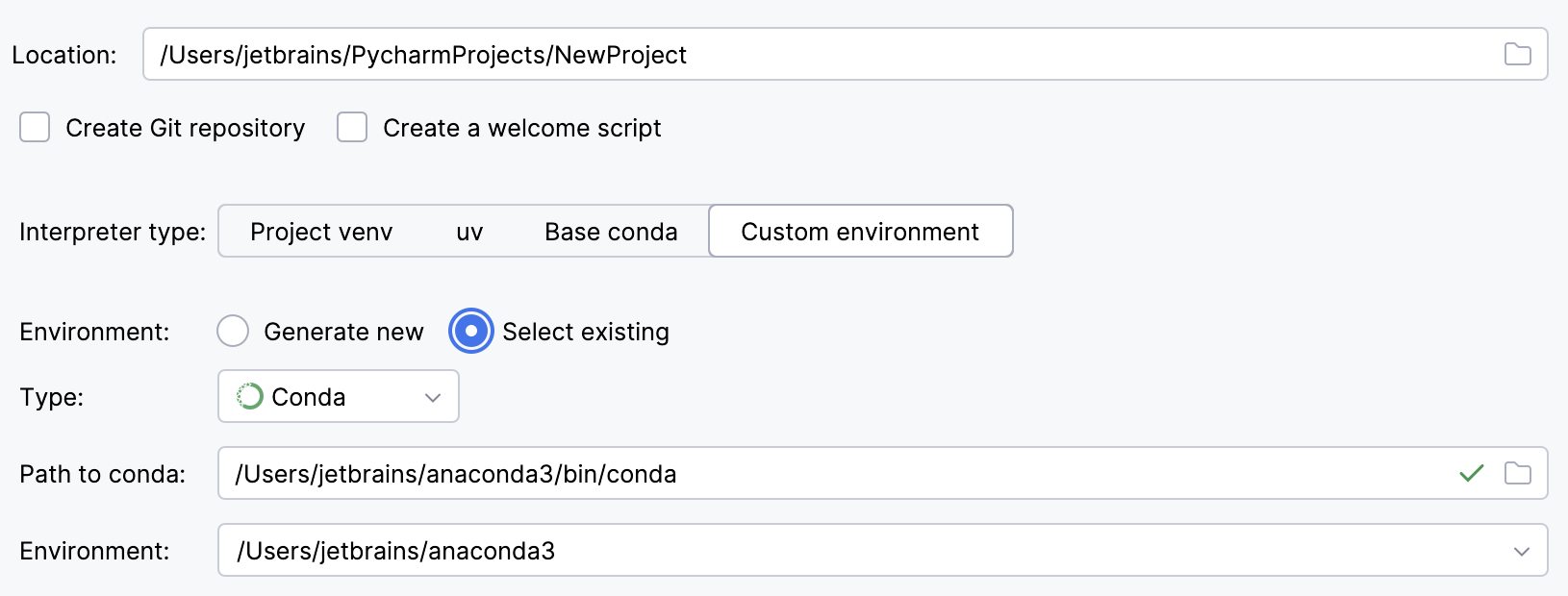
To reuse an existing conda environment:
Switch Type to Conda.
Specify the environment name.
PyCharm will detect a conda installation.
If PyCharm did not detect the installation automatically, specify the location of the conda executable, or click
to browse for it.
Select the environment from the list. If you specified the path to conda manually, you may need to reload environments.
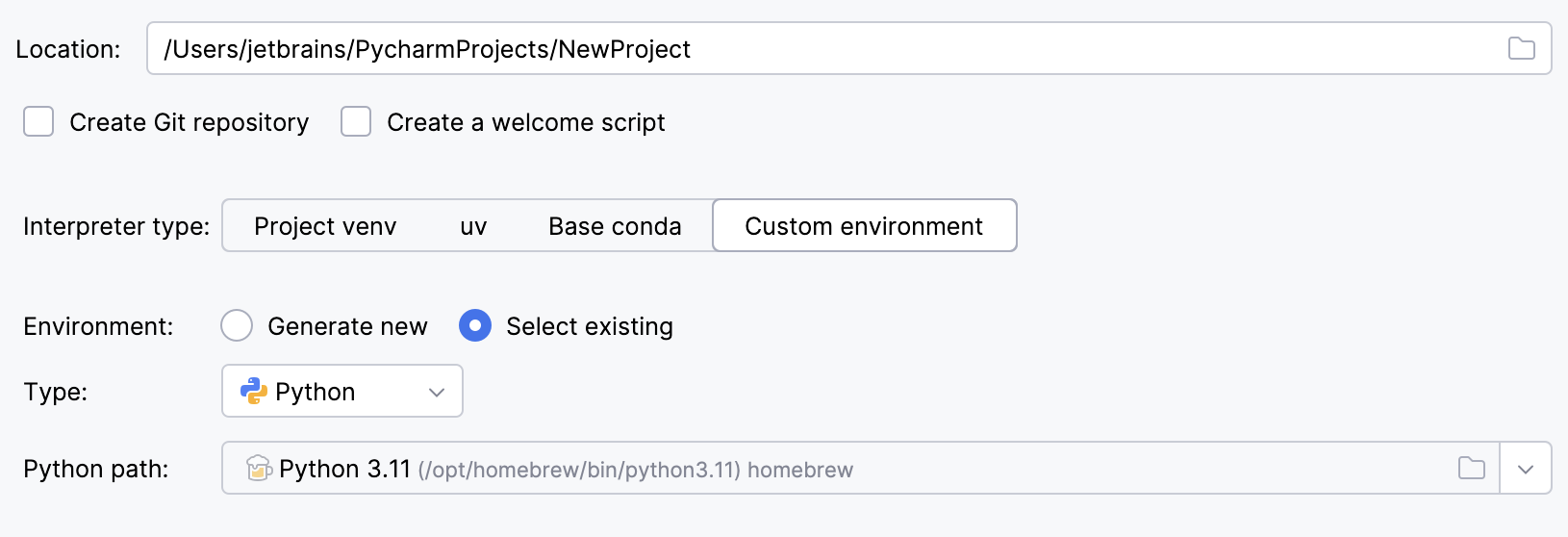
To reuse a different Python environment:
Switch Type to Python.
Select the Python executable from the list or click
to browse for it.
Click .
Create and open Jupyter notebooks
To open an existing .ipynb file, follow the same steps as for the files of the other types. If needed, you can create a notebook file.
Create a notebook file
Do one of the following:
Right-click the target directory in the Project tool window and select New from the context menu.
Press Alt+Insert
Select Jupyter Notebook.
In the dialog that opens, type a filename.
A notebook file has the *.ipynb extension and is marked with the corresponding icon .
Convert a Python file to a Jupyter notebook
Right-click the file in the tool window.
Select from the context menu.
Convert a Jupyter notebook to a Python file
Right-click the file in the tool window.
Select from the context menu.
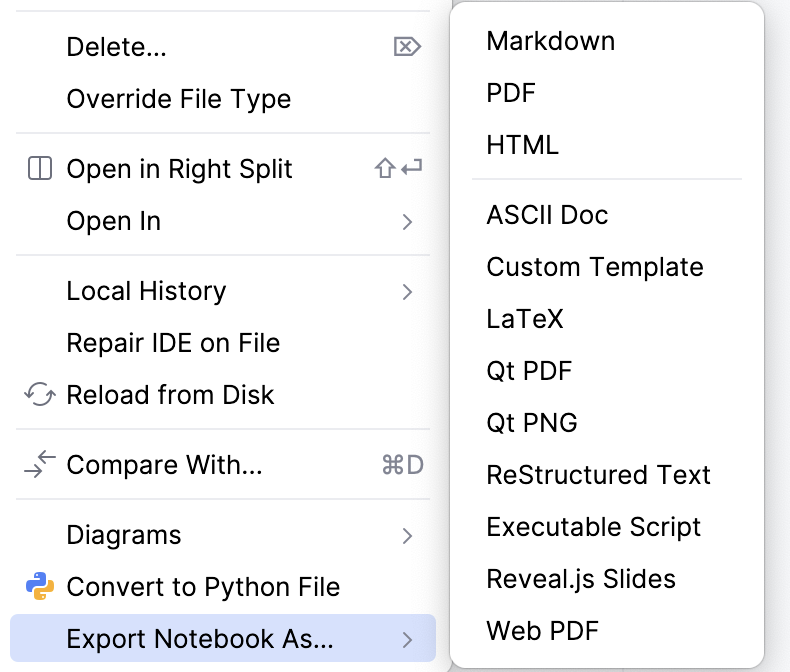
Export Jupyter notebooks
You can export Jupyter notebooks to various formats:
Right-click the Jupyter notebook file in the Project tool window.
Select and then select the format from the list.
Edit Jupyter notebooks
You can apply various editing actions to one cell or to the entire notebook. Press the Ctrl+A once to select a cell at the caret and press Ctrl+A twice to select all cells in the notebook.
The editor for Jupyter notebooks has two modes: the edit mode and the command mode. Depending on the mode, you can either edit code in notebook cells or use keyboard shortcuts to perform specific actions with cells.
Edit mode
To toggle the edit mode, press Enter or click any cell.
When a cell is in the edit mode, it has a highlighted line with a caret inside the cell.
When in the edit mode, you can navigate through all cells line-by-line using Up and Down keys.
Command mode
Edit cells
A newly created notebook contains one code cell. To change its type, right-click the cell and select Convert Cell to Markdown or Convert Cell to SQL from the context menu.
To edit a code cell, just click it.
To edit a Markdown cell, double-click it or press Enter and start typing. To preview the output, press Shift+Enter.
Markdown cell toolbar
After you select the part of the text in the Markdown cell, the toolbar appears.
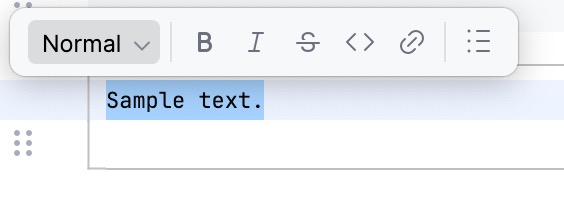
You can use it to apply the following formatting options:
Item
Icon
Shortcut
Description
Text style
Click the dropdown to change text formatting to various heading levels.
Bold text
Ctrl+B
Makes the selected text bold (
**text**).Italic text
Ctrl+I
Makes the selected text italic (
_text_).Strike through
Ctrl+I
Strikes through the selected text. (
~~text~~).Code
Ctrl+Shift+C
Formats text as inline code.
Create link
Ctrl+Shift+U
Adds a hyperlink.
Unordered list
Creates a list. You can choose one of the following types:
Unordered list
Ordered list
Checkmark list
Work with notebook cells
Add cells
To add a code cell above the selected cell, do one of the following:
In the edit mode, press Alt+Shift+A.
In the command mode, press A.
To add a code cell below the selected cell, do one of the following:
In the edit mode, press Alt+Shift+B.
In the command mode, press Ctrl+Enter.
Click
on the notebook toolbar.
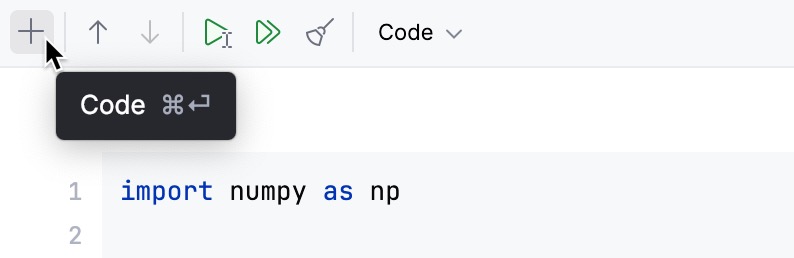
Use the popup between cells to add
code,Markdown,SQLorAIcells to your notebook: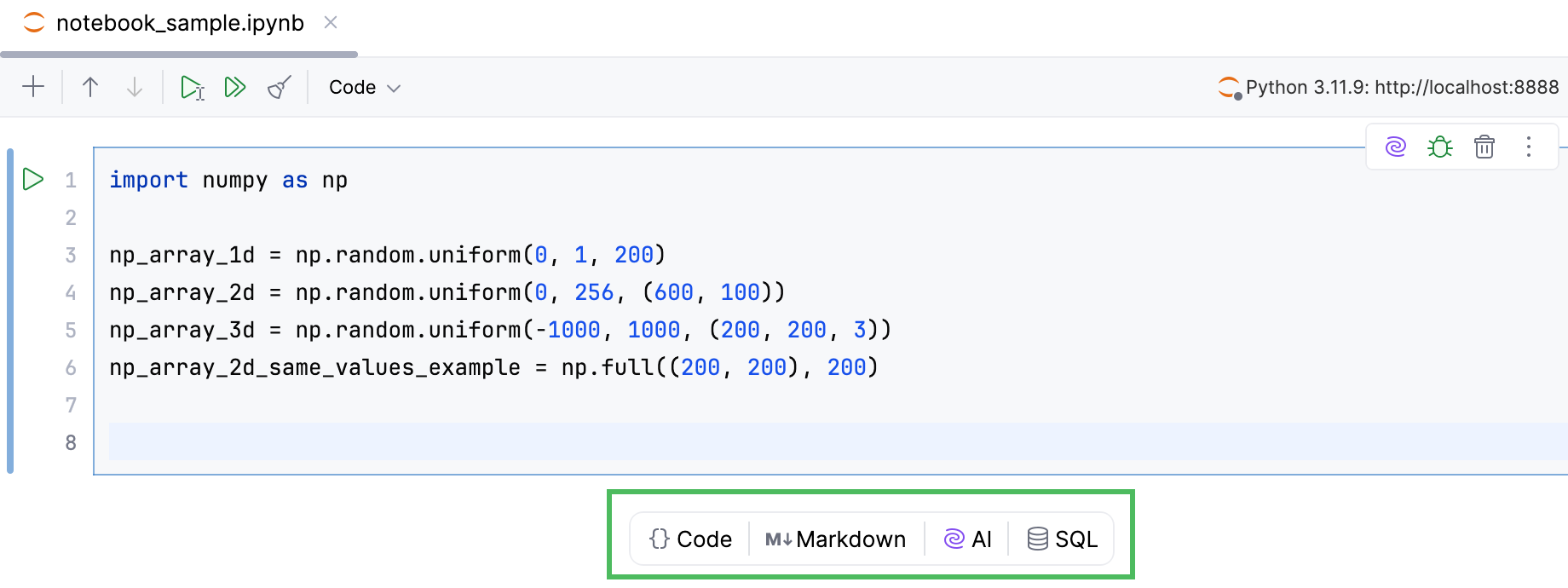
The popup will automatically appear if you hover between two cells in the notebook.
Select cells
To select a cell, click the gutter next to the cell.
To select several cells:
Click the gutter next to cells while holding Shift for a series of consecutive cells, or Ctrl for non-consecutive cells.
In the command mode, hold Shift and press the Up and Down keys.
You can execute, copy, merge, expand, comment and delete the selected cells.
Drag and drop cells
To rearrange your notebook cells:
Click and hold the cell handle in the gutter next to the cell.

Drag the cell to the required position and release the mouse button to drop it in the highlighted area.
Copy and paste cells
To copy a cell in the command mode, press Ctrl+C, C, or select
Copy Cell in the context menu of the cell toolbar.
To paste the copied cell below, press Ctrl+V or V.
To paste it above the current cell, press Shift with Ctrl+V/Shift+V.
You can also select the required action from the cell's context menu.
Split and merge cells
To merge a current cell with the cell below, right-click the cell and select the Merge Cell Below command from the context menu.
Similarly, you can merge a cell above the selected cell with the corresponding command.
To split a cell into two cells, place the caret in the line to break at, then right-click, and select the Split Cell from the context menu.
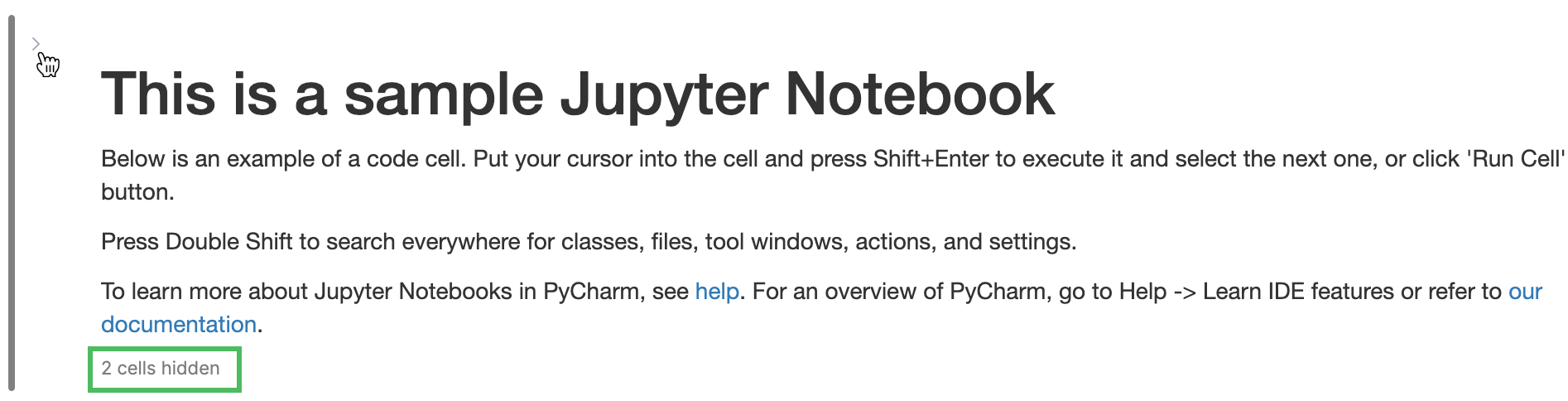
Expand and collapse cells
Click the cell handle in the gutter next to the cell to expand or collapse it.


Click the chevron next to the Markdown cell heading to collapse or expand code cells below. The number of collapsed cells will be shown under the heading.
Comment out cells
To comment out an active cell, switch to the command mode and press Ctrl+/.
To comment out multiple cells, select them in the command mode, then press Ctrl+/.
Delete cells
Click
Delete Cell on the cell toolbar.
Right-click the cell and select from the context menu.
Add cell tag
You can assign and view tags for each cell right in the notebook editor:
Click
on the cell toolbar.
Select Add Cell Tag from the context menu.
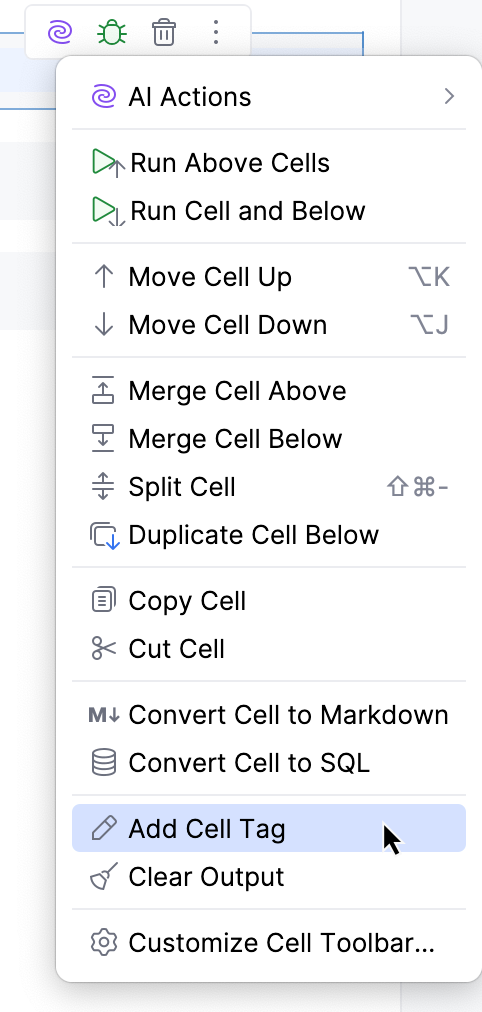
Enter the tag and click Confirm.
To remove the tag, right-click it and select Remove Tag.
Duplicate cells
To duplicate a cell, click
on the cell toolbar and select Duplicate Cell Below from the context menu. The new cell will appear directly below the original.
Right-click the cell and select from the context menu.
Use coding assistance
You can edit code cells with the help of Python code insights, such as syntax highlighting and code completion.
PyCharm enables code completion for the names of classes, functions, and variables. Start typing the name of the code construct, and the suggestion list appears.
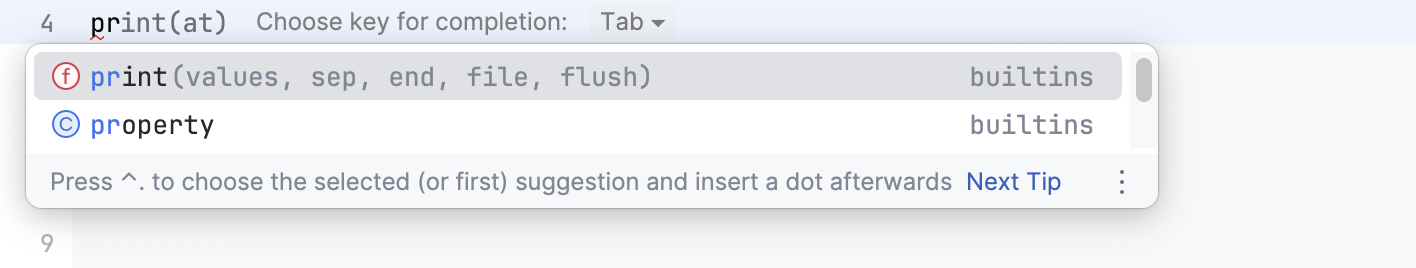
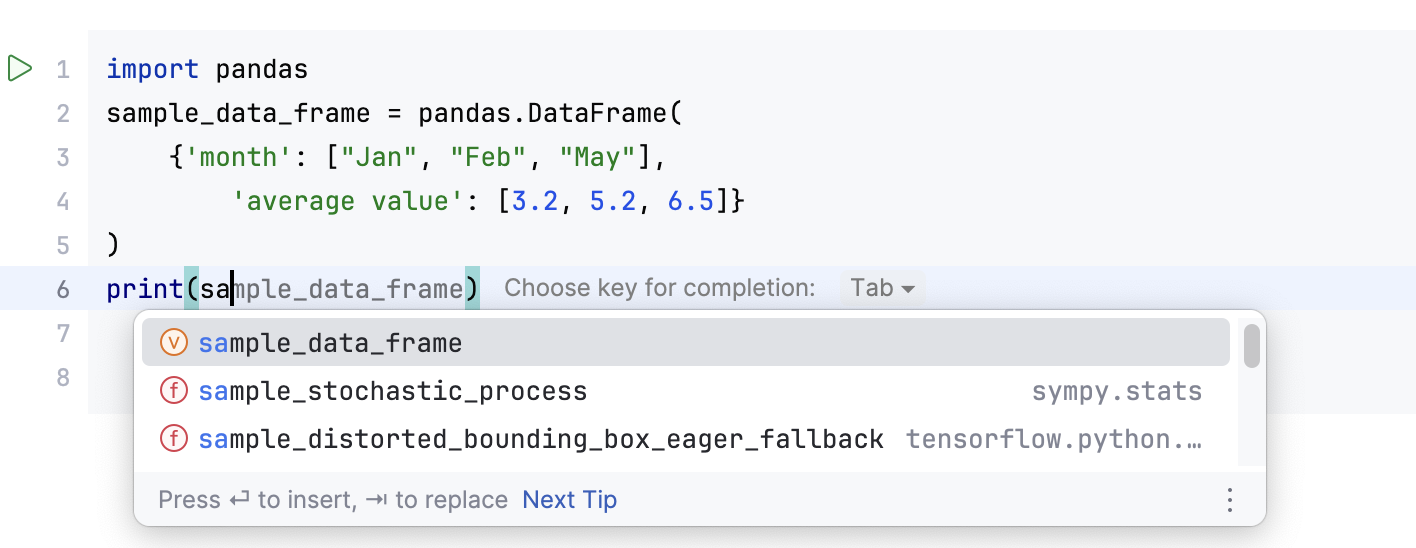
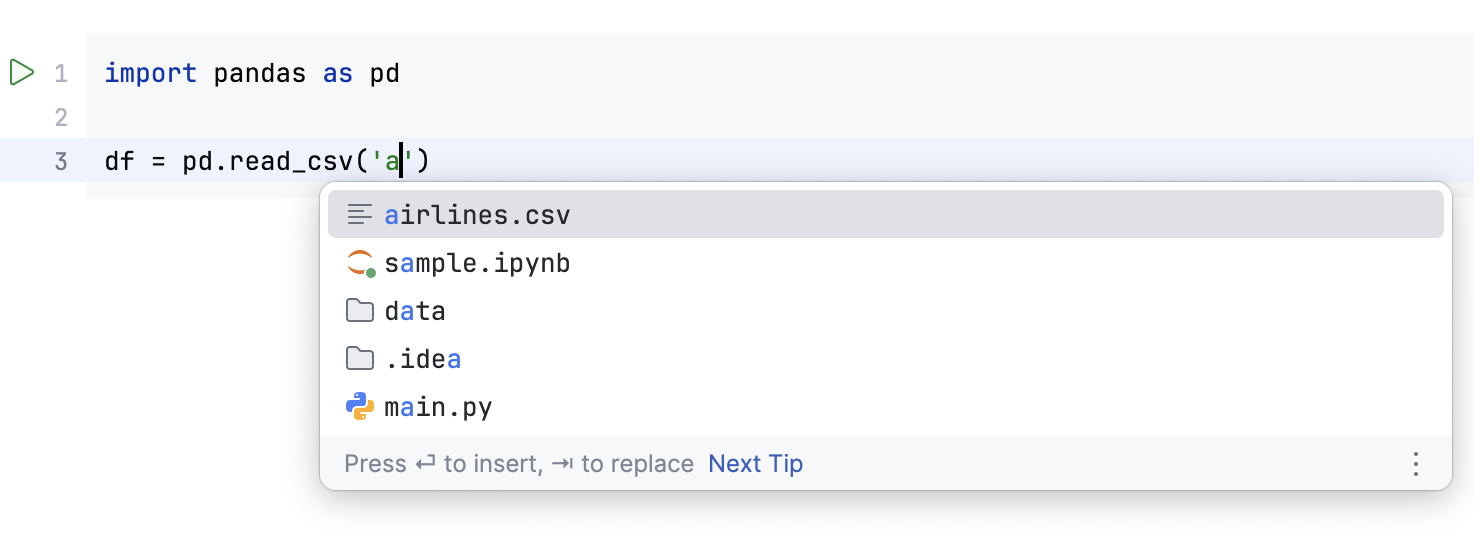
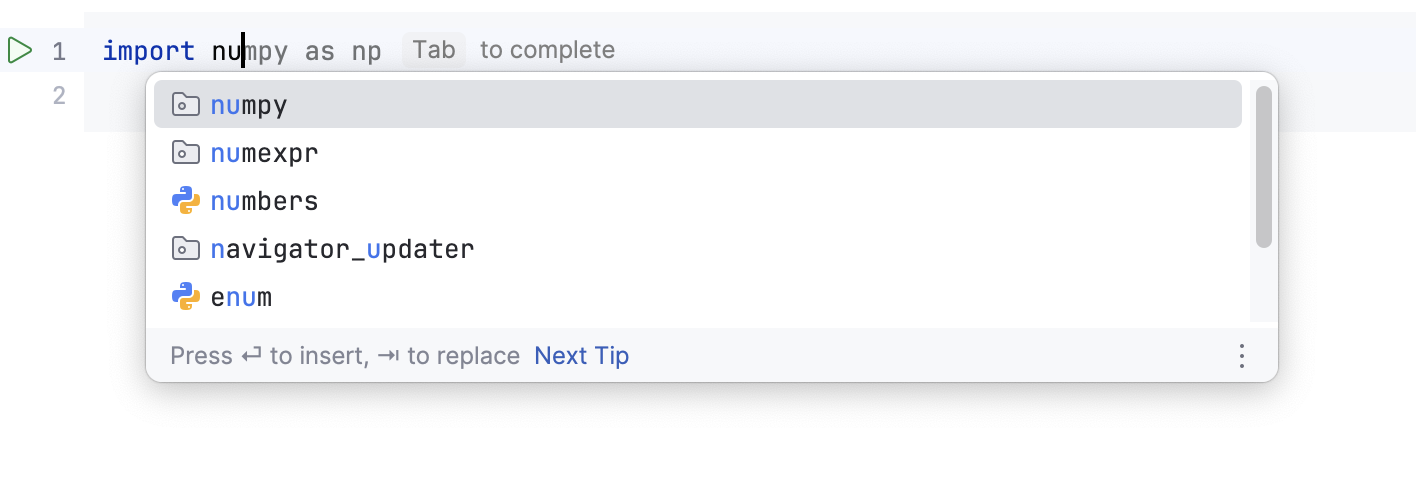
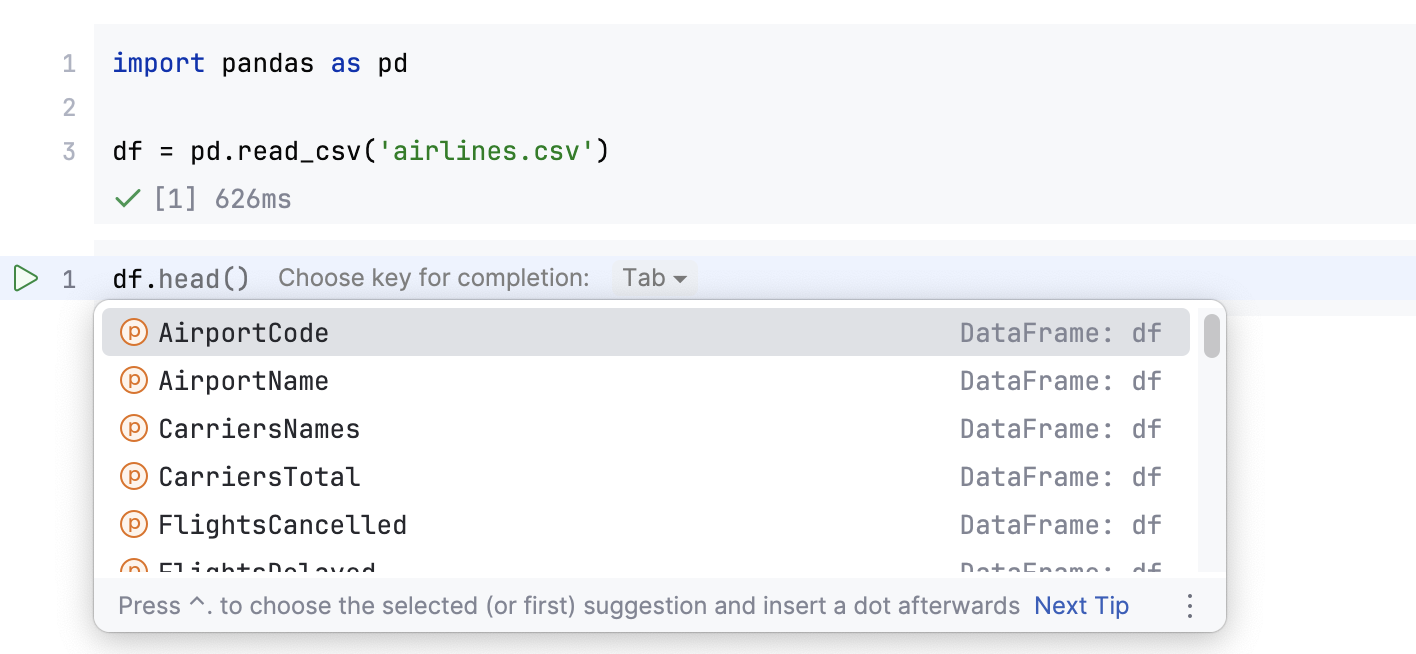
Intention actions and quick fixes. You can add the missing imports by using the intention actions.
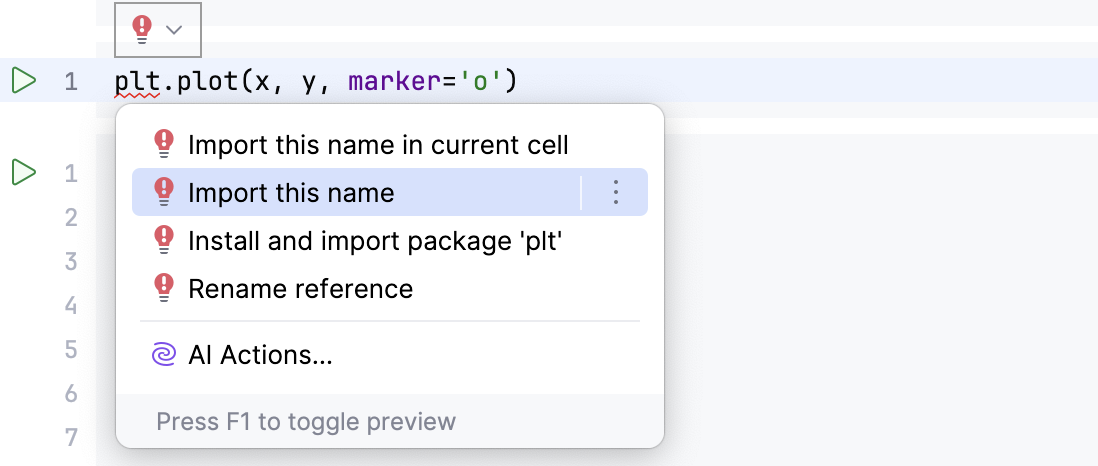
Note that you can add an import statement to the current cell or to the first cell of the notebook.
Customize a color scheme
You can configure Notebooks-aware syntax highlighting according to your preferences and habits.
In the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , go to .
Select the color scheme, accept the highlighting settings inherited from the defaults or customize them as described in Colors and fonts.
For more information on adjusting colors of specific Notebook elements, refer to Jupyter Notebooks Color Scheme.