Create and use custom template tags
Available only in PyCharm Professional: download to try or compare editions
This functionality relies on the Django plugin, which is bundled and enabled in PyCharm by default. If the relevant features are not available, make sure that you did not disable the plugin.
Press to open settings and then select Plugins.
Open the Installed tab, find the Django plugin, and select the checkbox next to the plugin name.
With Django you can set up a new tag to introduce a functionality that is not covered by the built-in template tags. PyCharm provides you with corresponding code and navigation assistance.
Under the application directory, create the templatetags package (it should contain the __init__.py file). For example, Django
/DjangoApp ./templatetags In the templatetags package, create a .py file, for example my_custom_tags, and add some code to it to declare a custom tag.
For more information about custom template tags coding practices, refer to Django documentation.

Open you template file in the editor and add the corresponding template tag to it.
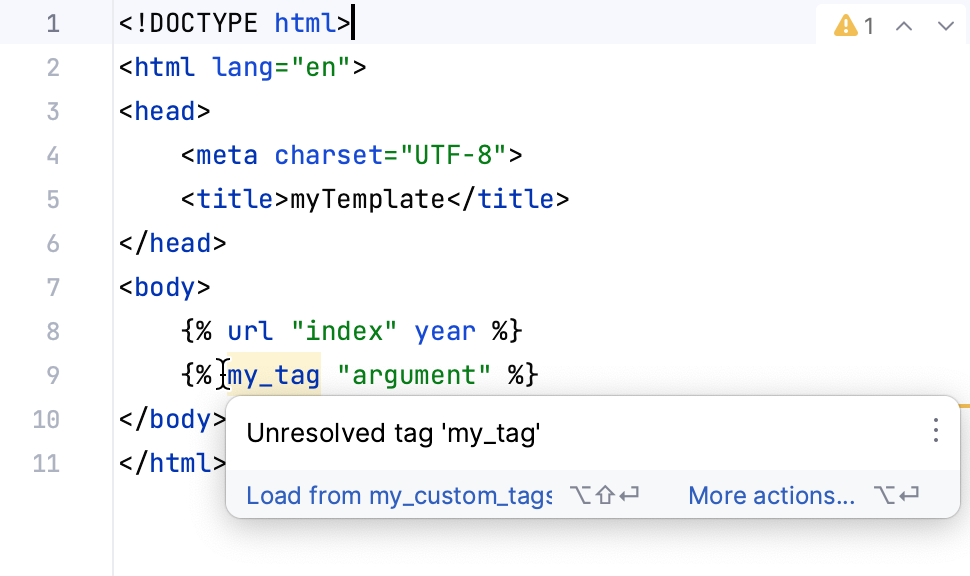
PyCharm displays the
Unresolved taginspection error because you have not loaded the custom tag into the template file.Use a quick-fix to resolve the missing reference. Place the caret at the custom tag name, press , and select the file to load.

PyCharm adds the
{% load %}tag to the template file to fix the reference.
PyCharm also recognizes custom template tags that are recorded as builtins tags in the TEMPLATES section of the settings.py file.
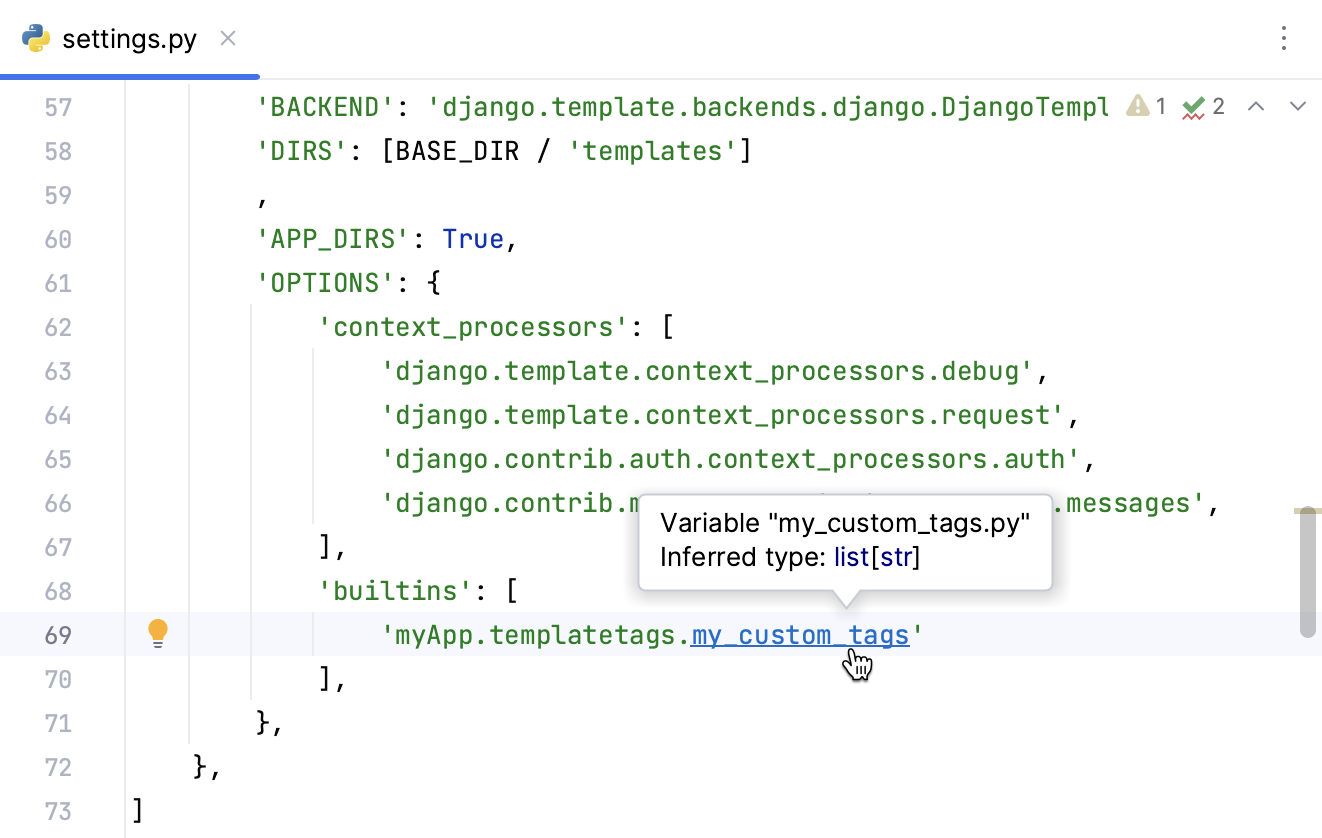
Once you record a custom tag in the settings file, you can navigate to the file with its declaration. Place the caret at the template tag filename and press .