Run inspections
Last modified: 21 July 2022PyCharm analyses code in the files that are opened in the editor and highlights problematic code as you type. Additionally, you can run the necessary inspection or a set of inspections on the selected scope of files manually. In this case, you will get a comprehensive report of all problems detected in the files.
Instant analysis of the current file
The IDE continuously checks your code and searches for problems. The widget in the top-right corner of the editor displays the number of problems of each severity detected in the current file:
![]()
tip
The widget has a simplified view. To enable it, hover the mouse over the widget, click
, and select Compact View.
Click the widget to open the list of problems on the Current File tab of the Problems tool window. You can also access the Problems tool window by selecting View | Tool Windows | Problems or by pressing Alt+6.
For each problem, you can see the suggested quick-fix by pressing Alt+Enter or by clicking . You can also jump to the corresponding line in the editor by pressing F4 or by double-clicking the problem in the tool window.
Alternatively, click to be able to view and fix problems in the tool window.
The color stripe in the scrollbar also marks the detected code problems and helps you quickly access the corresponding lines without scrolling the file. Hover over a mark on the stripe to see the detected problem in a tooltip. Click a mark to jump to the corresponding line.
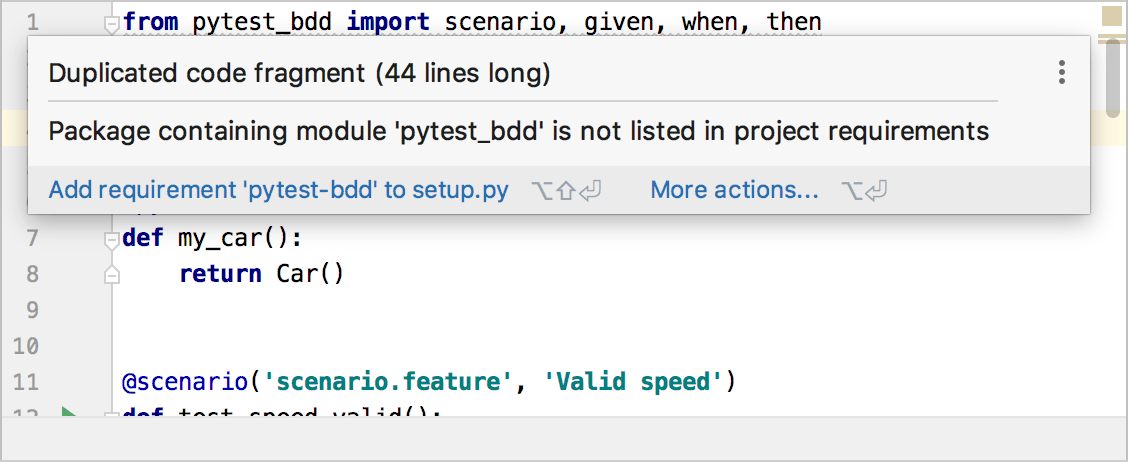
Navigate to detected problems
You can jump from one highlighted problem to another within a file by clicking
in the widget or by pressing F2 or Shift+F2 accordingly. By default, the IDE will navigate you to problems according to their severity: errors > warnings > weak warnings > server problems > typos.
You can configure PyCharm to take you through the problems one by one regardless of their severity. Hover the mouse over the widget in top-right corner of the editor, click , select 'Next Error' Action (F2) Goes Through, and enable All Problems.
Run inspections manually
Some inspections require global code analysis, and that is why they are disabled in the editor. These inspections are listed in Settings/Preferences | Editor | Inspections. Click and select Show only batch-mode inspections.
If you want to get a full report of all detected problems, run inspections manually.
Run all inspections
From the main menu, select Code | Running Code Cleanup with profile ''{0}''….
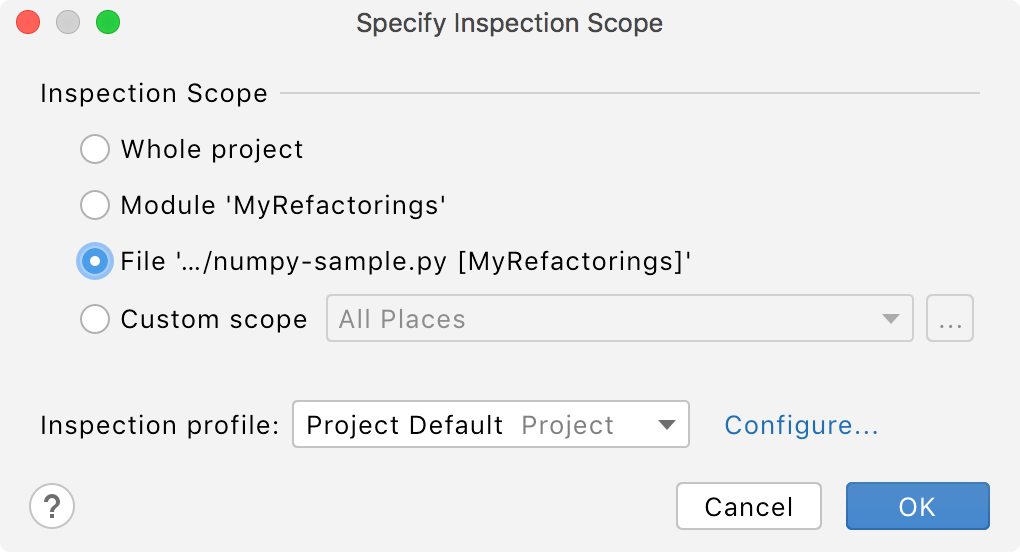
Select the scope of files that you want to analyze.
Click the
icon to configure a new scope.
Select the inspection profile that you want to apply.
To create a new profile or modify one of the existing profiles, click Configure.
Click OK to start the analysis.
Run a single inspection
Running a single inspection is useful in case you want to track a specific problem. If you find a warning in a file, you can inspect your entire project, or the necessary scope of files, to ensure that there are no more such warnings in your code base.
From the main menu, select Code | Analyze Code | Run Inspection by Name… or press Ctrl+Alt+Shift+I.
Type the inspection name in the popup. Use CamelHumps to match camel case words and white spaces with initial letters of the words. The suggestion list will show you inspections that match your search request.
If you are not sure that you are selecting the correct inspection, you can view its description. To do so, select an inspection in the popup and press Ctrl+Q.
Double-click the necessary inspection to open its settings.
In the dialog that opens, select the scope of files that you want to analyze.
The File mask(s) option helps you narrow down the number of files that will be inspected.
Select the checkbox and specify a pattern of characters and wildcards that matches the names of files you want to analyse. Use a comma to separate multiple file masks.
Some inspections might have additional options that you will be prompted to configure.
These settings will only be applied to this run, and will not affect this inspection's configuration in your current profile.
The IDE will show you the inspection results in the dedicated tool window tool window. There you can examine and fix detected problems.
Analyze code before committing it to Git
If your project is under Git version control, you can configure the IDE to analyze modified files before committing them.
Press Ctrl+K or select Git | Commit from the main menu.
In the Commit tool window, click
and in the Before commit area, select the Analyze code checkbox.
Alternatively, if you're using the Commit Changes dialog, in the Before Commit area, select the Analyze code checkbox.
Click Configure and select the required inspection profile from which the IDE will run inspections.
Commit tool windowCommit Changes dialog

Click Commit.
PyCharm analyzes the code from the modified files by running inspections from the selected profile.
If any errors or warnings are detected, you will see a notification.

In the notification, click Review to see the list of the detected problems in the Messages tool window. Click Commit to commit your changes without fixing the detected problems.
Run inspections offline
In addition to running code inspections from the IDE, you can launch inspections from the command line without actually running PyCharm. The inspection results will be stored in an XML file. For more information, refer to Run code inspections from the command line.
Change the order of scopes
By default, all enabled code inspections analyze all files in your project. Depending on your needs, you can run the same inspection in more than one scope of files with different settings.
If one file is included in two or more scopes, and you enable an inspection in these scopes, PyCharm will process them according to their order in the list of scopes — the uppermost scope will have the highest priority, and therefore, it will be analyzed first.
In the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S), select Editor | Inspections.
Select any inspection from the list.
From the In All Scopes list, select Edit Scopes Order.
Select the necessary scope, and use
and
to move it up and down the list.

If needed, create a new scope. To do so, click
(Edit Scopes), specify scope settings, and select the files and folders that you want to include in it.
