Database tool window
Overview
In the Database tool window (), you can work with databases and DDL data sources. You can view and modify data structures in your databases, and perform other associated tasks. To view a table, double-click the table. For more information about different viewing modes, see View data.
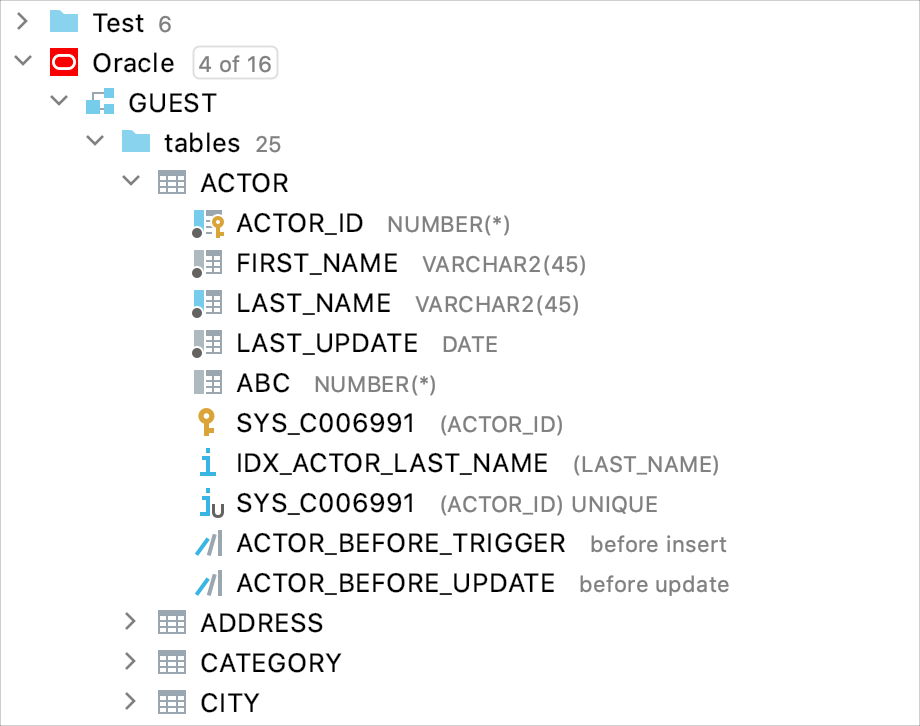
The available data sources are shown as a tree of data sources, schemas, tables and columns. If no data sources are currently defined, use the New command Alt+Insert to create a data source.
Most of the functions in this window are accessed by means of the toolbar icons or context menu commands. (If the toolbar is not currently shown, click on the title bar and select Show Toolbar.) Many of the commands have keyboard shortcuts. If the toolbar is hidden, the Refresh and Open Query Console commands can be access by means of the title bar icons (
and
respectively).
Controls on the toolbar
Icon | Command | Shortcut | Description | Available for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Collapse all the nodes. | All node types | |||
New | Alt+Insert | Create a new data source, role, database, schema, query console, table, column, index, or a primary or a foreign key. The list of options depends on which element is currently selected. | Data sources and their elements. If a DDL data source is selected, you can only choose to create another data source. | |
Duplicate | Ctrl+D | Create a copy of the selected data source. Specify the properties of the data source in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog that opens. | DB and DDL data source nodes | |
Refresh | Ctrl+F5 | Update the view of the selected element (that is to synchronize the view of the element with its actual state in the database). See also, Data sources and drivers dialog. | Data sources and their elements. | |
Data Source Properties | Open the Data Sources and Drivers dialog to manage your data sources and their settings. | All node types | ||
Deactivate | Ctrl+F2 | Close the database connection for the selected data source or data sources. (The names of the data sources with active database connections are shown in bold.) | Data sources with active connections and their elements | |
Edit Data | F4 | Open a table view of the object in the data editor. This option works for tables, views, and materialized views. | Corresponding elements in data sources. | |
Go to DDL | Ctrl+B | Update the source code of database objects by directly editing their DDL | Corresponding elements in data sources. | |
Jump to Query Console… | Ctrl+Shift+F10 | Open the list of query consoles for the selected data source. | Data sources and their elements (tables and table columns) | |
Filter | Open a list of database objects that you can filter for the selected database. The list of database objects depends on the selected database. To see a full list of available database objects and their icons, go to Icons for data sources and their elements. | Data sources and their elements |
Controls of the right-click menu
Context-menu actions appear when you right-click an object in the Database tool window.
Command | Shortcut | Description | Available for |
|---|---|---|---|
Properties | Open the Data Sources and Drivers dialog to manage your data sources and their settings. | Data source and DDL data source nodes. | |
New | Alt+Insert | Create a new data source, role, database, schema, query console, table, column, index, a primary or a foreign key. The list of options depends on which element is currently selected. | Data sources and their elements. If a DDL data source is selected, you can only choose to create another data source. |
Rename | Shift+F6 | Rename the selected data source, table or column. Specify the new name in the dialog that opens. | Data sources and their elements. |
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+C | Copy the fully qualified name of the selected data source, table or column to the clipboard. | Data sources and their elements. | |
Ctrl+D | Create a copy of the selected data source. Specify the properties of the data source in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog that opens. | Data source and DDL data source nodes. | |
Edit Data | F4 | Open a table view of the object in the data editor. This option works for tables, views, and materialized views. | Corresponding elements in data sources. |
Refresh | Ctrl+F5 | Update the view of the selected element (that is to synchronize the view of the element with its actual state in the database). See also, Data sources and drivers dialog. | Data sources and their elements. |
Deactivate | Ctrl+F2 | Close the database connection for the selected data source or data sources. (The names of the data sources with active database connections are shown in bold.) | Data sources with active connections and their elements |
Drop or Remove | Delete | Remove the selected item. | Data sources and their elements. |
Quick Documentation | Ctrl+Q | View basic information about the selected element.  To close the documentation popup, press Escape. | Data sources and their elements. |
Ctrl+B | Update the source code of database objects by directly editing their DDL | Corresponding elements in data sources. | |
Ctrl+Shift+F10 | Open the list of query consoles for the selected data source. | Data sources and their elements (tables and table columns) | |
Run Function or Run Procedure | Run the selected function or procedure. | Data source elements: functions, procedures. | |
(Oracle only) Introspection Level | Change the introspection level either for the whole database or for a particular schema. Children inherit a level that is set for a parent. | Oracle Data Source nodes. | |
Ctrl+Alt+G | Generate data definition structures for database objects. For example, you can generate DDL files for a single table or for all the tables in the schema. Also, you can customize generation settings. For example, you can set what syntax to use for table creation:  | Data source elements. | |
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+G | Generate DDL of the object and copy it to the clipboard. | Data sources and their elements. | |
Remove all the rows in the selected table. | Data source elements: tables. | ||
Open a popup with available schemas for the current data source.  | Data sources and their elements. | ||
Ctrl+D | Compare structures of two selected database objects (data sources, schemas, or tables). The comparison results are shown in the differences viewer. | Data sources and their elements. | |
Shift+Ctrl+Alt+F | Search for data in your databases or a group of databases without knowing data exact location. For more information about the full-text search, see Full-text search in databases. | Data sources and their elements. | |
Set or change the color for the selected element or elements. (The Database Color Settings dialog will open.) To set a color, right-click a data source and select Color Settings…. In the Database Color Settings dialog, select the dialog and coloring options. To have the data source color applied for query consoles and grids, select the In console editors and grids checkbox. 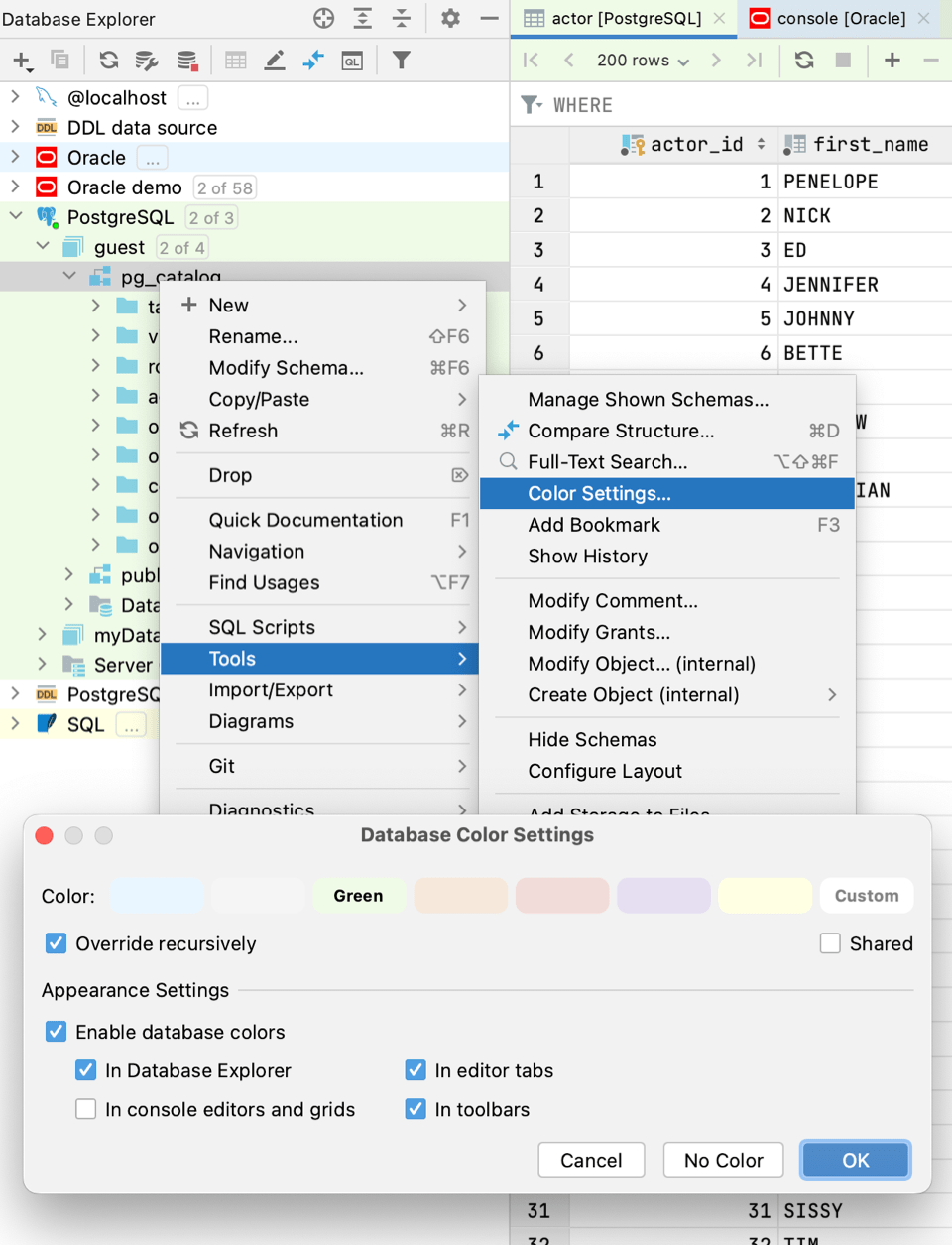 | Data sources and their elements. | ||
F11 | Add the selected item to bookmarks. | Data ources and their elements. | |
Generate a Java entity class for the selected table. In the dialog that opens, specify the directory in which the JAVA class file should be generated. | Data sources and their elements. | ||
Switch to the directory where the Generate POJOs.clj example script file is located. | Data sources and their elements. | ||
Save data for the selected tables and views in files. Select the output format (for example, SQL Inserts, Tab-separated (TSV), JSON-Clojure.json.clj). | Data source elements: tables and views. | ||
Import a text file containing delimiter-separated values (CSV, TSV, and so on) into your database. If a schema is currently selected, PyCharm will create a new table for the data that you are importing. If a table is selected, PyCharm will try to add the data to the selected table. | Data source elements: tables. | ||
F5 | Create a copy of the selected table. You can create a copy in a different scheme or data source. For example, you can copy the | Database objects: tables and views. | |
Create your DDL data source by dumping a regular data source to a root/repository folder. | Data sources and their elements. | ||
or Import/Export | Export with 'pg_dump' | Run mysqldump or pg_dump for the selected items. mysqldump and pg_dump are native MySQL and PostgreSQL tools. They are not integrated into PyCharm. You can read about them at dev.mysql.com and postgresql.org. | Data source nodes. | |
or Restore | Run | Data source nodes. | |
and | Ctrl+Alt+Shift+U and Ctrl+Alt+U | View a UML class diagram for the selected data source or table. You can select between the following options:
| Data sources and their elements. |
Generate a diagnostic representation of the database in a PyCharm internal format. This information might be helpful for the support team if some database objects exist in the database but do not show up in the Database tool window.  | Data sources and their elements. | ||
Reload the metadata from the database and generate a detailed log file of the process. This information might be helpful for the support team when your introspection takes too much time.  | Data sources and their elements. | ||
Generate three files that include information about the following:
This information might be helpful when introspection works incorrectly. For example, when you see something outdated or do not see new objects. 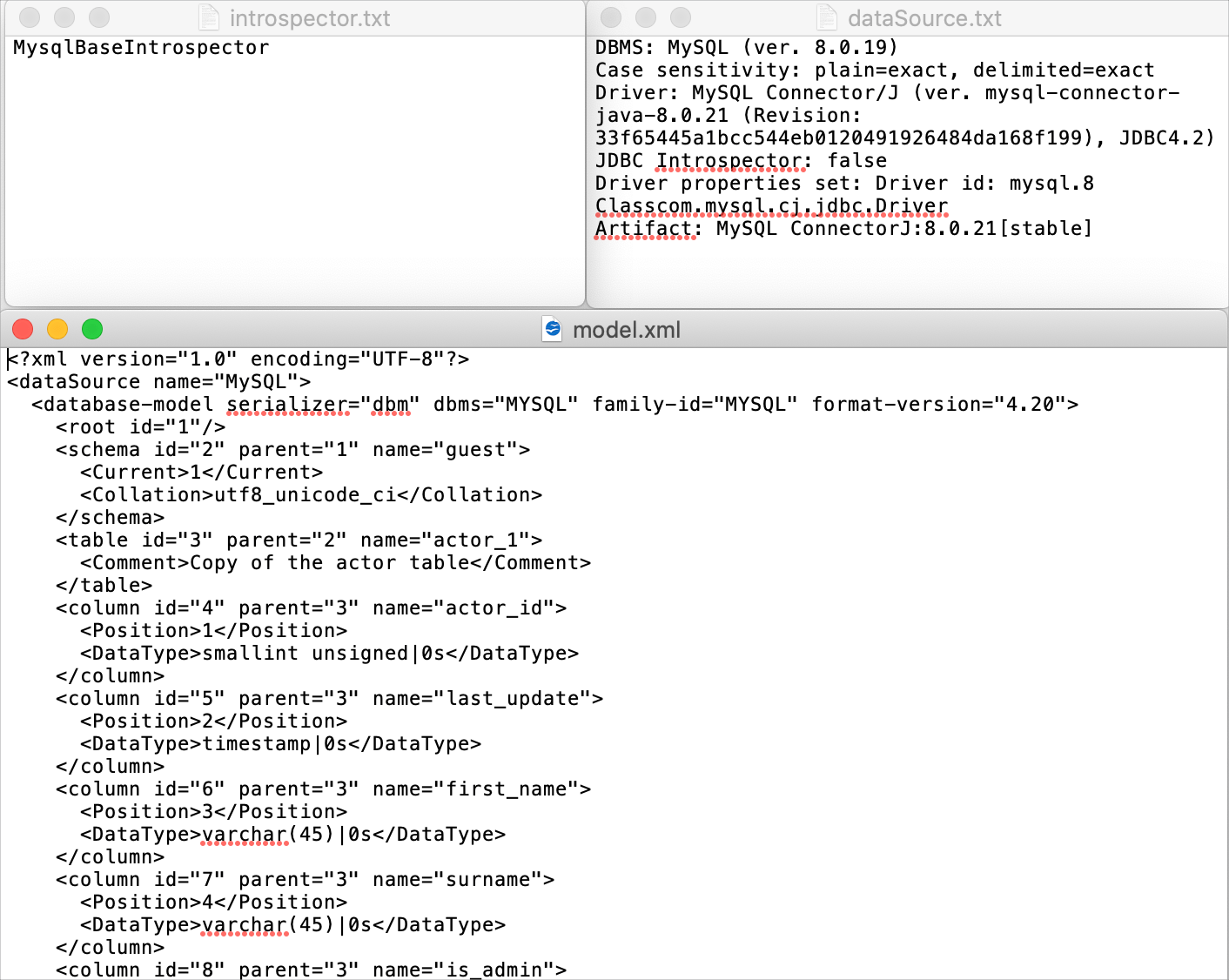 | Data sources and their elements. | ||
Ctrl+Shift+F5 | Delete the data source information from cache and load it again. This action is available on the data source node only. | Data source nodes. | |
Delete the information that PyCharm has accumulated about your database. This action is available on the data source node only. Use this command when you experience issues like wrong display of data structures or errors during synchronization. To check if this has eliminated the problem, use the Synchronize command. | Data source nodes. |
View options
The view options, generally, define what is shown in the tool window and how. To view or change these options, click on the title bar.
Option | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Group Data Sources | Displays folders for data sources if you created any.
| ||||
Group Server and Database Objects | Displays folders for server and database objects. This setting concerns users, roles, tablespaces, modules, foreign data wrappers and other rarely-used objects.
| ||||
Group Schema Objects | Defines how schema elements are shown. When on, there are separate nodes for tables, views and stored routines (shown as folders). Tables, views and routines (procedures and functions) are shown as elements of the corresponding groups.  When off, there is no explicit grouping for tables, views, and routines. Tables and views are followed by procedures and functions.  | ||||
Group Object Elements | This option defines how table elements are shown. When on, there are separate nodes for columns, indexes, primary and foreign key constraints, and triggers (shown as folders). The elements appear in the corresponding groups.  When off, there is no such grouping and, generally, only columns are shown for tables.  | ||||
Show All Namespaces | Show all databases and schemes even if they are not selected for introspection. When the Show All Namespaces option is disabled, databases that are not selected for introspection do not appear in the Database tool window.  When the Show All Namespaces option is enabled, databases that are not selected for introspection are displayed in the Database tool window.  | ||||
Show Empty Groups | If the Group Schema Objects or Group Object Elements options are selected, you can select to show or hide the categories that contain no elements. The Show Empty Groups option is on:  The Show Empty Groups option is off:  | ||||
Show Intermediate Nodes | Shows or hides parent nodes only when you do not have other objects on the same level with a parent.
| ||||
Show Generated Objects | For Oracle, shows or hides auto-generated objects in the tree. It concerns the following objects:
| ||||
Separate Procedures and Functions | In Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, and PostgreSQL, separates procedures and functions into different folders.  | ||||
Alphabetically | Order database objects alphabetically. When the option is disabled, natural sort order is applied.
| ||||
Place Constraints and Similar Objects under Schema | Display nodes for object names that exist in a schema namespace. For example, nodes for keys, CHECK constraints, indexes, triggers, rules, and other objects. You can use this option in the following situations:
| ||||
Show Toolbar | Display the toolbar in the Database tool window. |
The rest of the options are common for all the tool windows, see Tool window view modes.
Icons for data sources and their elements
Icon | Description |
|---|---|
Access Method | |
Aggregate | |
Alias Type | |
Argument | |
Body | |
Check | |
Cluster | |
Collation | |
Collection Type | |
Column. For more information about column icon combinations, see Possible icon combinations for columns. | |
| Data File |
Database | |
Read-only status | |
DDL data source | |
Default | |
Exception | |
Extension | |
External Schema | |
Foreign Data Wrapper | |
Foreign Key | |
Foreign Table | |
Index | |
Key | |
Materialized Log | |
Materialized View | |
Object Attribute | |
Object Type | |
Operator | |
Package | |
| Projection |
Read-only data sources | |
Role | |
Routine | |
Rule | |
Scheduled Event | |
Schema | |
Sequence | |
Server | |
Stored procedure or function | |
Synonym | |
Table | |
Table Type | |
| Tablespace |
Trigger | |
User | |
User Mapping | |
Variable | |
View | |
Virtual Table |
Possible icon combinations for columns
Icon | Foreign key | Primary key | Indexed | NOT NULL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Title bar context menu and buttons
You can right-click the window title bar and use the context menu to configure its viewing mode, associate the window with a different tool window bar, or resize and hide the window.
You can also use the toolbar buttons:
Item | Shortcut | Description |
|---|---|---|
Ctrl+NumPad - | Collapse all expanded nodes in the current view. | |
Shift+Escape | Hide the tool window . To hide all the tool windows, press Ctrl+Shift+F12. |









