Security model
When your work includes accessing remote servers you want to be sure that the connection between your local machine and the backend is secured and any data going back and forth is well encrypted.
The remote development security model lets you control almost all the security aspects of your work.
There are IDE components running both on the server-side and on the client-side. Any information loaded by the backend may be forwarded to the client without further user interaction, and any information provided to the client may be forwarded to the server-side process without further user interaction as well.
note
Even though in many cases JetBrains will inform the user and ask for permission, there may be cases such as GitHub authorization where forwarding takes place in the background.
The communication between JetBrains Client and the IDE backend is end-to-end encrypted with the 1.3 TLS even if performed in a secure SSH tunnel. JetBrains uses TLS 1.3 and on top of that, the SSH security connection is used.
Since in Remote Development there is no trust hierarchy from root certificates, the additional manual check is performed to ensure that there is no man-in-the-middle attack.
The regular connection link looks as follows:
tcp://0.0.0.0:5990#jt=71b0a870-e082-4e6b-aaf6-757398801cd2&p=IU&fp=17DC5CAB759FD8BB4298AF1116EA7D5E1F1D3C4D520CFC99748DBD0A88840B36&cb=223.2951&jb=17.0.4b535.2Upon the connection, a client checks that the fingerprint of a host certificate is exactly
fp. It verifies for the client that the host is correct (not hijacked by a third-party)Upon the connection, a host checks that the client provides a one-time connection token
jt. It denies connection for anyone on this port who does not know this token.
It is safe to transfer any authentication information via this connection or pass this connection data via public space. It is done the same way for Code With Me as well.
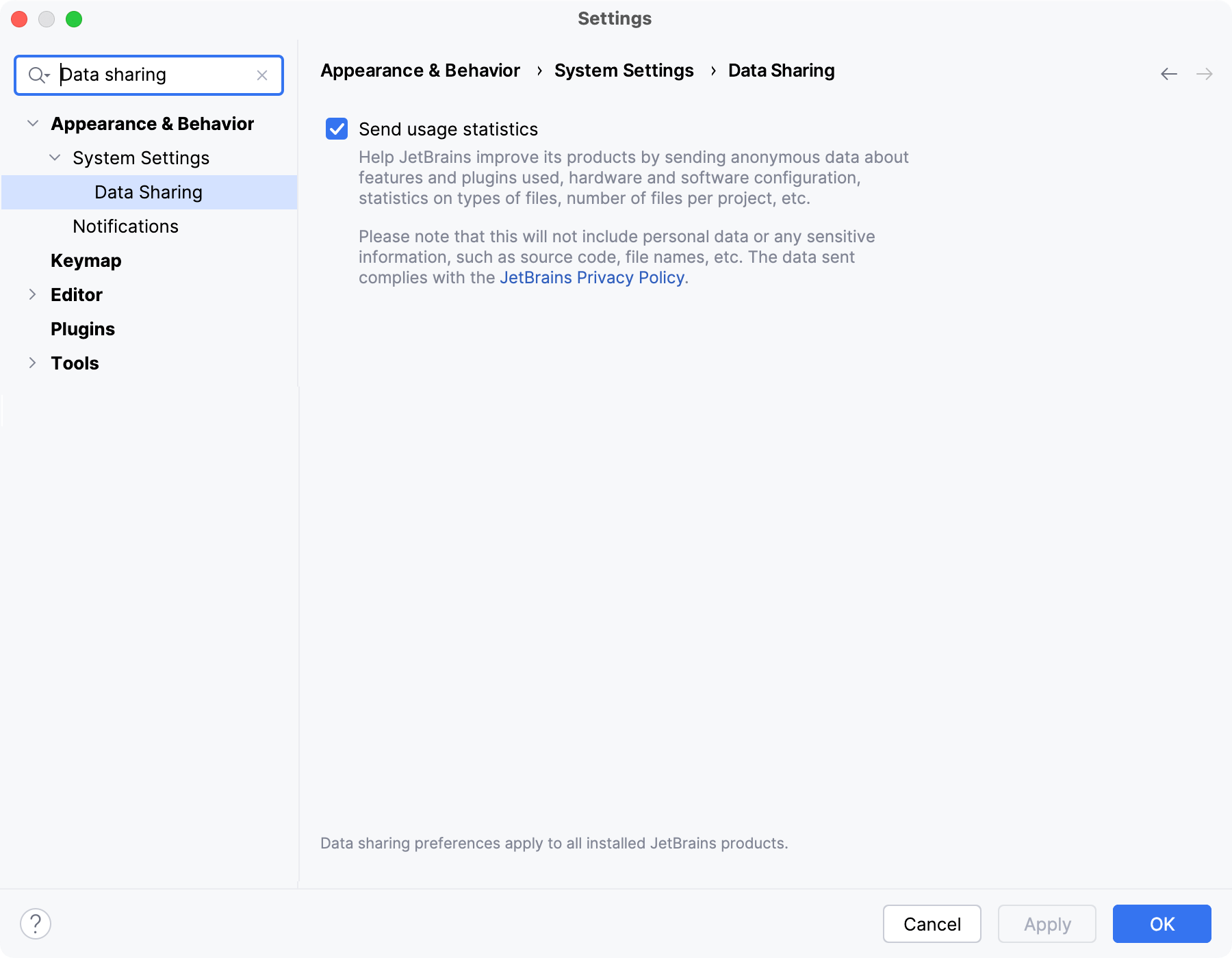
JetBrains collects statistics and logs with your permissions. By default, data sharing is disabled in all release versions and enabled in the Preview and Early Access Program (EAP) versions of IntelliJ IDEA.
tip
These preferences apply to all JetBrains IDE products you use, except JetBrains Fleet.
Select the Send usage statistics checkbox to allow JetBrains to collect anonymous statistics on the features and actions that you use when working with IntelliJ IDEA.
Select the Send usage statistics when using EAP versions checkbox to allow JetBrains to collect statistics on the features and actions that you use when working with IntelliJ IDEA.
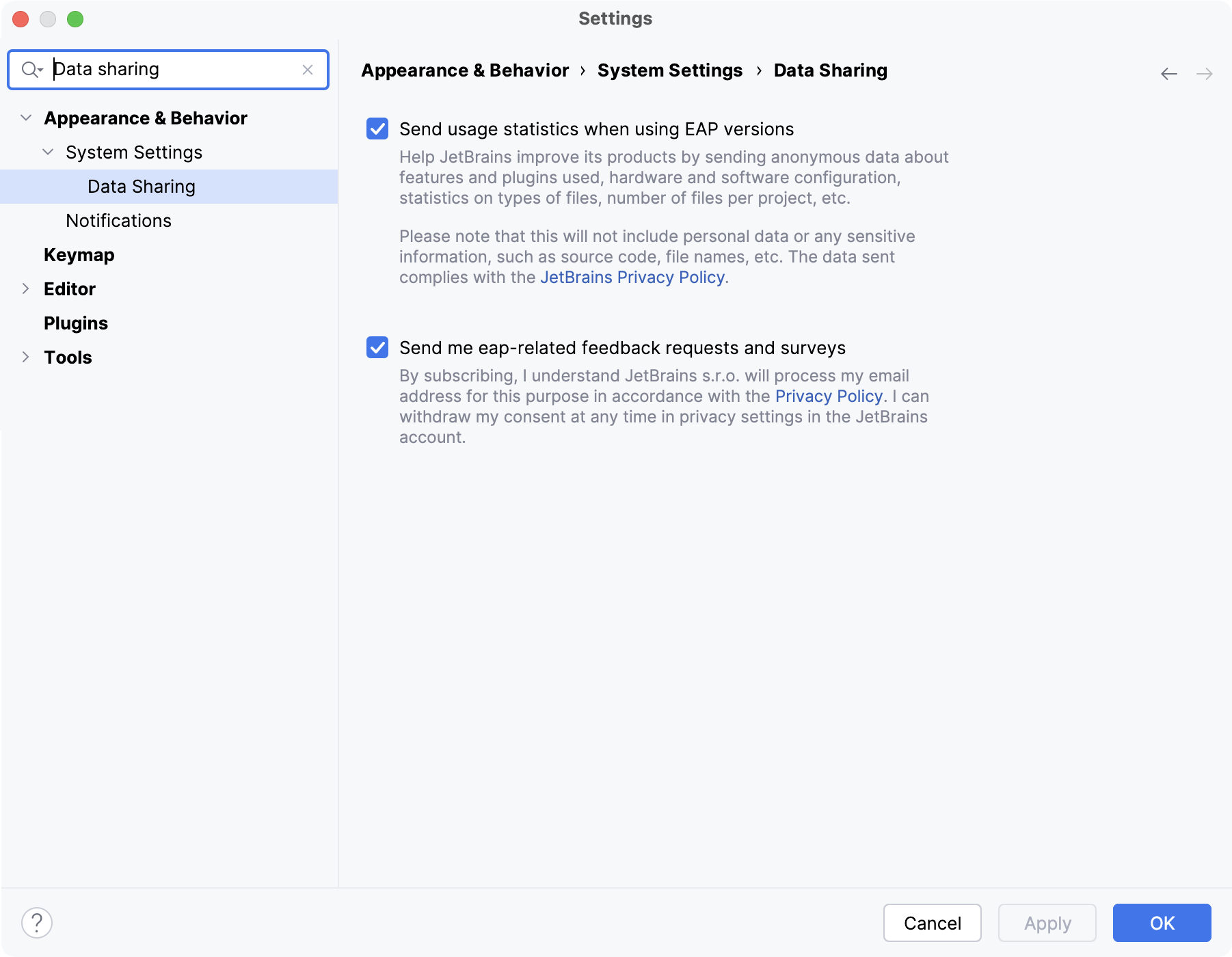
For more information about the collection and usage of this data, refer to data sharing settings.
When JetBrains asks you to collect and send logs, it also warns you that the logs might contain the sensitive data.
In the main menu, go to Help | Collect Logs and Diagnostic Data.
In the dialog that opens, click Show in Finder if you agree to send the data to JetBrains.

For the full information on JetBrains privacy policy, refer to JetBrains website.
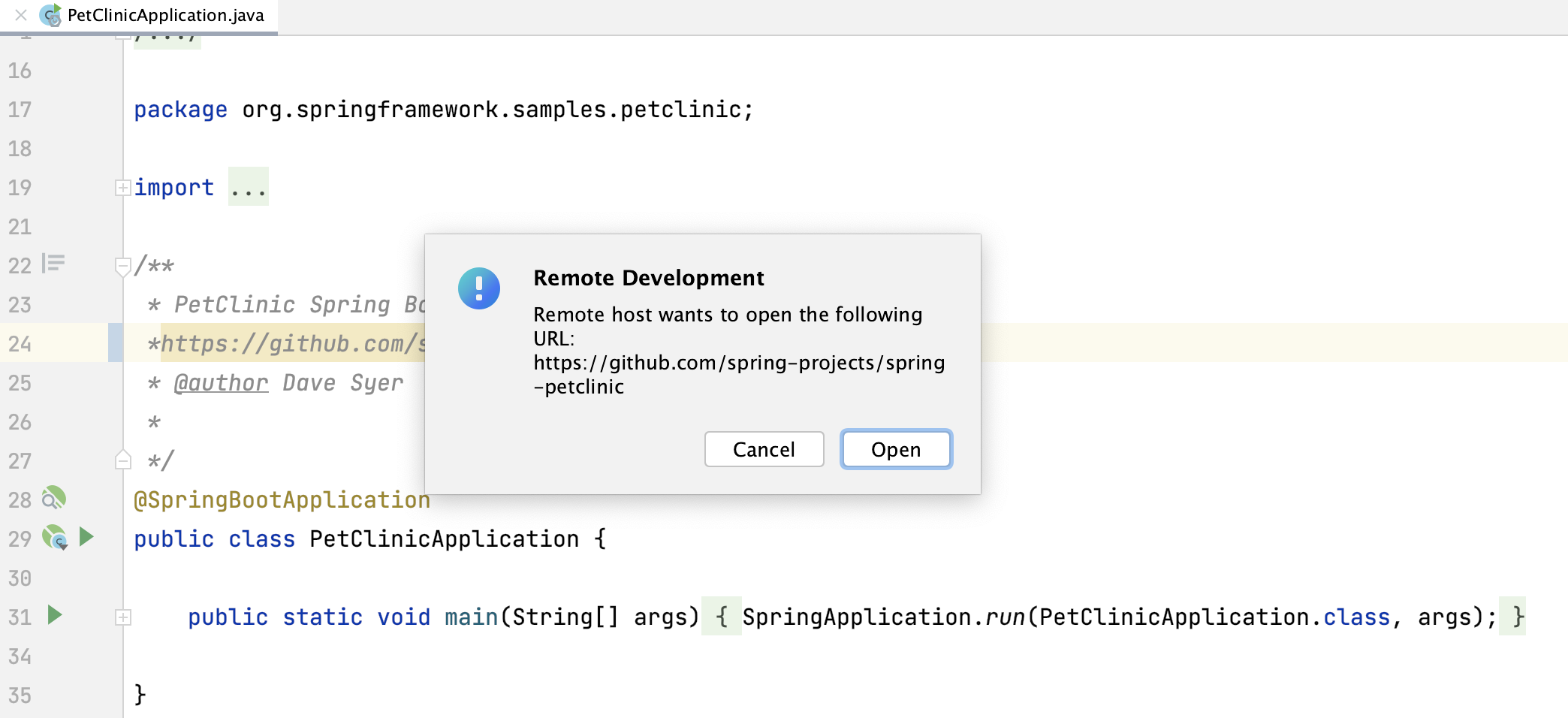
The IDE can require opening a browser for various features. Keep in mind that there is no browser on the server side. In this case, the request is redirected to JetBrains Client.
Before opening any arbitrary links on the client machine, JetBrains displays a confirmation dialog.
The Copy / Paste action sends the content of the clipboard only before the actual paste and allows the backend to change the clipboard only during the actual copying.
The SSH forwarding settings let you use SSH key forwarding to authenticate access to Git repositories from your remote server. Alternatively, you can use the SSH-agent helper to achieve the same result.
Press to open settings and then select Tools | SSH Forwarding.
From the options on the right, select Enable SSH agent Forwarding and click OK to save the changes.

You can access a port on the remote server by forwarding it to a local machine. It might be helpful for debugging purposes or bypassing a firewall.
note
You can use not only the Run tool window or backend control center for adding a port, but the terminal as well.
Start a remote session and open your project.
Run the application.
In the Run tool window, the application displays listening ports.

Click a port you want to forward and from the list of options, select Forward Port.

If you want to open the browser after forwarding, select Forward Port and open in browser.
As a result, the remote port is forwarded to the local machine.
Click the created port to check the result in the browser.

The forwarded port is also added to the backend control center.

You can add, delete, or edit ports through the backend control center.
Open your remote project.
On the main toolbar, click the name of the backend to open the backend control center window.
In the window that opens, on the Ports tab, click
to add the new port.
You can use
to delete a port. It will be also removed from the
forwardedPorts.xmlfile on the restart of the project.In the suggested field, type the port number and click Apply to save the changes.

The added port is saved in the
forwardedPorts.xmlfile.Restart your project to see the added port inside the
forwardedPorts.xmlfile.
Open your remote project.
On the main toolbar, click the name of the backend to open the backend control center window.
In the window that opens, on the Ports tab, select a port you want to remove and click
.
The port will be also removed from the
forwardedPorts.xmlfile on the restart of the project.
In the window that opens, on the Ports tab, click
to add the new port.
In the suggested field, type the port number and before you click Apply to save the changes, change the port number by clicking the port address field.

You should note the following:
If you stop forwarding the port, and the port is not used in other open projects, it is removed from the
forwardedPorts.xmlfile.When you close your application, the port forwarding stops. When the project is reopened, the ports are loaded from the
forwardedPorts.xmlfile (per project), forwarded, and displayed in the necessary locations.
For security reasons, you can disable port forwarding settings for a specific user or for the whole system.
note
This process can be applied to the Code With Me settings as well.
The changes should be made on the host IDE side.
For the user-specific settings, create a text file in the following directory:
/Users/UserName/Library/Application Support/JetBrains/portForwarding/enabledFor the system-wide settings, create a text file in the following directory:
/Library/Application Support/JetBrains/portForwarding/enabledFor the user-specific settings, create a text file in the following directory:
$HOME/.config/JetBrains/portForwarding/enabledFor the system-wide settings, create a text file in the following directory:
/etc/xdg/JetBrains/portForwarding/enabledFor the user-specific settings, use the following registry key:
HKEY_CURRENT_USERFor system-wide settings, use the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINEIn the SOFTWARE\JetBrains\portForwarding directory create a key enabled with value of this setting.
For the security purpose, you can disable port forwarding (porForwarding) for a specific user or for the whole system entirely using the OsRegistryConfigProvider OS registry. The location of the registry depends on your OS.
For the user-specific settings, create a text file in the following directory:
/Users/UserName/Library/Application Support/JetBrains/portForwarding/enabledFor the system-wide settings, create a text file in the following directory:
/Library/Application Support/JetBrains/portForwarding/enabledFor the user-specific settings, create a text file in the following directory:
$HOME/.config/JetBrains/portForwarding/enabledFor the system-wide settings, create a text file in the following directory:
/etc/xdg/JetBrains/portForwarding/enabledFor the user-specific settings, use the following registry key:
HKEY_CURRENT_USERFor system-wide settings, use the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINEIn the SOFTWARE\JetBrains\portForwarding directory create a key enabled with value of this setting.
If the key is absent, the setting is considered true by default.
You can configure reverse port forwarding to initiate a connection from a remote machine to a local one. This is useful, for example, if you are developing an application on a mobile device or working on a remotely located application that requires access to the database on your local machine.
There are some potential security risks that you need to consider and mitigate when using reverse port forwarding:
Open your remote project.
Open the backend control center.
In the window that opens, click the Ports tab, then click
to add a new port and select Local to Remote.

In the port's field, add the port number you need and click Apply.

In the dialog that appears, ensure that you trust the remote server requesting the port forwarding and click Allow.


You can redefine where to store the JetBrains Client's folder and files after the download.
For the user-specific settings, create a text file in the following directory:
/Users/UserName/Library/Application Support/JetBrains/JetBrainsClient/downloadDestinationThe content of the file is path/to/directory.
For the system-wide settings, create a text file in the following directory:
/Library/Application Support/JetBrains/JetBrainsClient/downloadDestinationThe content of the file is path/to/directory.
For the user-specific settings, create a text file in the following directory:
$HOME/.config/JetBrains/JetBrainsClient/downloadDestinationThe content of the file is path/to/directory.
For the system-wide settings, create a text file in the following directory:
/etc/xdg/JetBrains/JetBrainsClient/downloadDestination with content path/to/directoryThe content of the file is path/to/directory.
For the user-specific settings, use the HKEY_CURRENT_USER registry.
For the system-wide settings, use the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE registry.
In SOFTWARE\\JetBrains\\JetBrainsClient create a key downloadDestination with the value containing path/to/directory.