Connect to Oracle Cloud by using wallets
For full information about Oracle, refer to the official documentation.
To download Oracle database software, refer to the official software downloads.
For more versions of Oracle JDBC driver, refer to the official JDBC driver downloads.
Oracle Wallet is a set of files that stores all the user credentials such as certificates, certificate requests, and private keys. You can create a wallet by using the Oracle tooling or ask your Oracle server administrator to generate the wallet. For more information about wallets, see Creating and Managing Oracle Wallet and Download Client Credentials (Wallets) at docs.oracle.com.
Oracle Instant Client (OCI) packages: Basic Package, SQL*Plus Package, JDBC Supplement Package. Download packages for your operating system from the Oracle Instant Client Downloads page at oracle.com.
oraclepki.jar: download the JAR file from Oracle Database 12.2.0.1 JDBC Driver & UCP Downloads page at oracle.com.
Running Oracle Cloud instance with access permissions for your user.
Configured tnsnames.ora file.
Oracle wallet
From the Oracle Instant Client Downloads page at oracle.com, download the following packages for your operating system:
Basic Package
SQL*Plus Package
JDBC Supplement Package
Also, download oraclepki.jar from Oracle Database 12.2.0.1 JDBC Driver & UCP Downloads page at oracle.com.
Prepare a ZIP archive with wallet files. For more details about downloading a wallet, see Download Client Credentials (Wallets) at docs.oracle.com.
Create a directory (for example, ~
/Oracle )./instantclient_19_8/ Extract all packages to the created directory.
Move oraclepki.jar to the created directory.
Extract a ZIP archive with wallet files to the wallet directory inside the network directory. The path to wallet files might look as follows: ~
/Oracle ./instantclient_19_8 /network /wallet 
This procedure is optional, but it might further simplify operations with OCI.
Add the following environment variables:
macOSWindowsexport ORACLE_HOME=~/Oracle/instantclient_19_8export TNS_ADMIN=$ORACLE_HOME/network/adminexport NLS_LANG=English_America.UTF8export PATH=$PATH:$ORACLE_HOMEset ORACLE_HOME=C:\Oracle\instantclient_19_8set TNS_ADMIN=%ORACLE_HOME%\network\adminset NLS_LANG=English_America.UTF8set PATH=%PATH%:%ORACLE_HOME%
note
For this step, you must have a ZIP archive with wallet files. For more details about downloading a wallet, see Download Client Credentials (Wallets) at docs.oracle.com.
An archive with wallet files includes tnsnames.ora and sqlnet.ora files.
In the directory that you created on Step 1, create the network directory. Inside the network directory, create the admin directory. The overall path should look as follows: ~
/Oracle ./instantclient_19_8 /network /admin Copy tnsnames.ora and sqlnet.ora files to the admin directory.
Open the sqlnet.ora file from the admin directory in the text editor.
Change the value of the
DIRECTORYattribute to the path to your wallet. For example, the path for this tutorial looks as follows:WALLET_LOCATION = (SOURCE = (METHOD = file) (METHOD_DATA = (DIRECTORY="/Users/jetbrains/Oracle/instantclient_19_8/network/wallet"))) SSL_SERVER_DN_MATCH=yesConsider the following screenshot of the admin directory and configuration files.

Open data source properties. You can open data source properties by using one of the following options:
In the Database tool window ( View | Tool Windows | Database) , click the Data Source Properties icon
.
Press .
In the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Drivers tab.
In the list of drivers, right-click the Oracle driver and select Duplicate.
Change the name of the duplicated Oracle driver (for example, Oracle [Cloud]).
In the Driver Files pane, click the Add icon (
) and select Custom JARs….
In the file browser, navigate to the directory of the Instant Client that you created previously (for example, ~
/Oracle )./instantclient_19_8 In the directory, select the following files: ojdbc8.jar, orai18n.jar, and oraclepki.jar.
Click Open.
In the Driver Files pane, click the Add icon (
) and select Native Library Path….
In the file browser, navigate to the directory of the Instant Client created previously (for example, ~
/Oracle ) and click Open./instantclient_19_8 
To connect to the database, create a data source that will store your connection details. You can do this using one of the following ways:
From the main menu, navigate to File | New | Data Source and select Oracle.
In the Database tool window ( View | Tool Windows | Database) , click the New icon (
) in the toolbar. Navigate to Data Source and select Oracle.

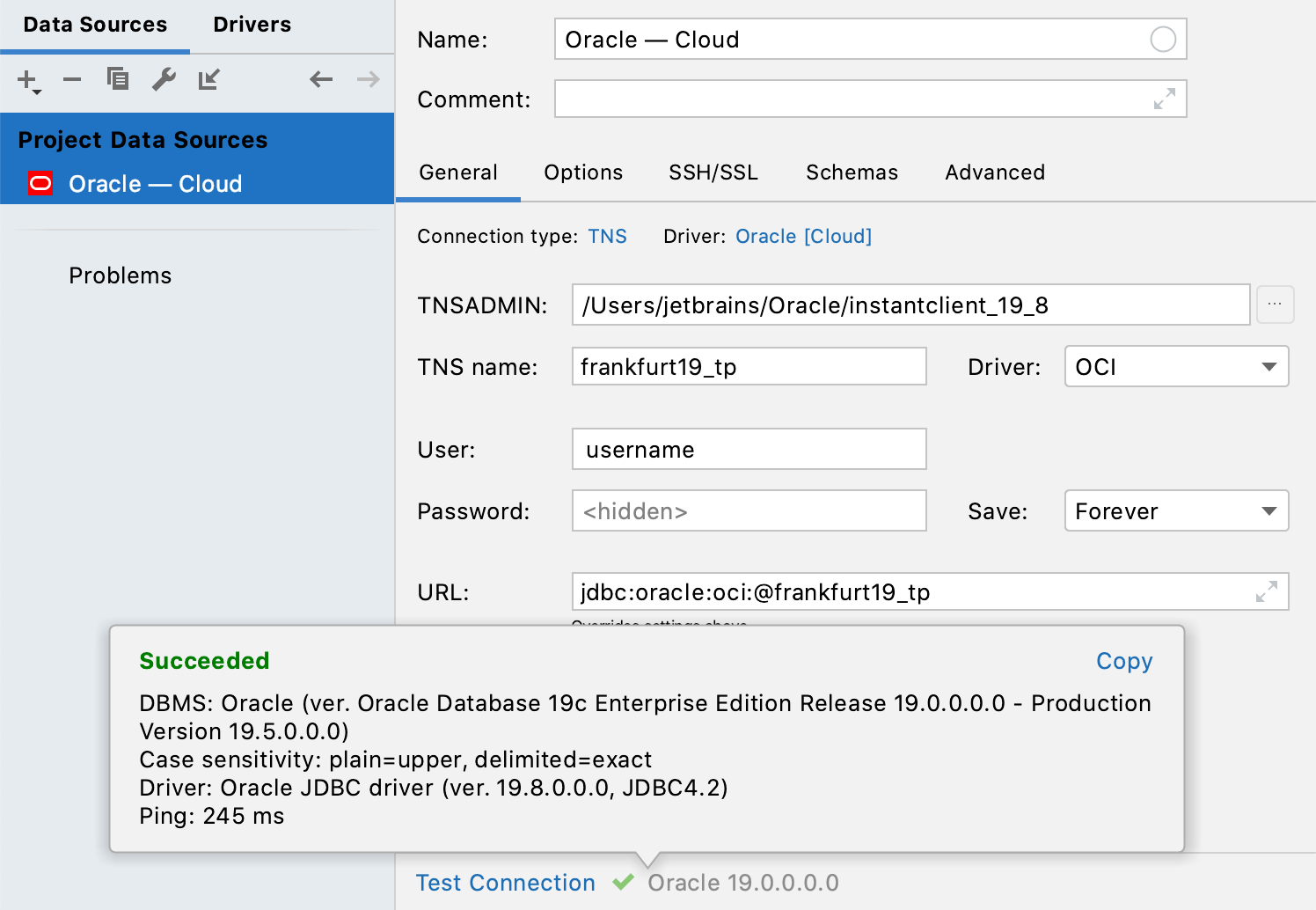
From the Connection type list, select TNS.
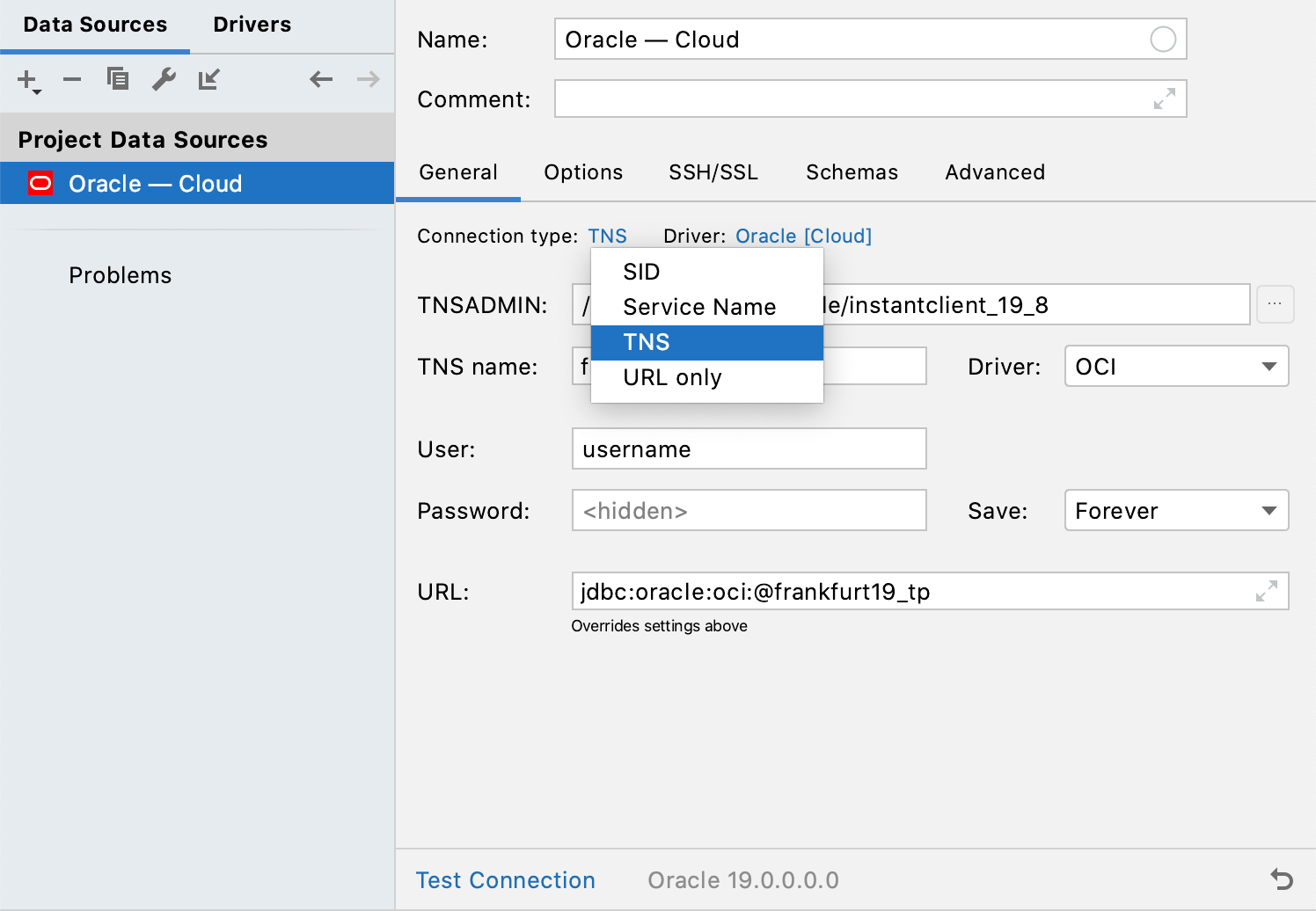
From the Driver list, select OCI.

Click the Driver link and select the driver entry that you created on Step 1.

In the TNSADMIN field, click the browse button and navigate to the directory with the Instant Client (in our case, ~
/Oracle )./instantclient_19_8/ In the TNS name field, specify what service name to use (see a value of an alias in tnsnames.ora).
Specify credentials for the Oracle user.
Ensure that the connection to the database can be established using the provided details. To do that, click the Test Connection link at the bottom of the connection details area.

In case of any connection issues, refer to the Cannot connect to a database page.
(Optional) By default, only the default schema is introspected and available to work with. If you also want to work with other schemas, in the Schemas tab, select them for the introspection.

Click OK to create the data source.
Find your new data source in the Database tool window () .
To learn more about the Database tool window, see the corresponding reference topic.
tip
To see more schemas under your new data source node, click the N of M button and select the ones you need. GoLand will introspect and show them.

To learn how to work with database objects in GoLand, see Database objects.
To write and run queries, open the default query console by clicking the data source and pressing .
To view data of a database object, open Data Editor and Viewer by double-clicking the object.