HTTP Handlers
Managing Web Requests - The HTTP Handler Approach.
This marks the final segment of the tutorial, centering on configuring routes and employing HTTP handlers.
Server
We will be creating a new server instance.
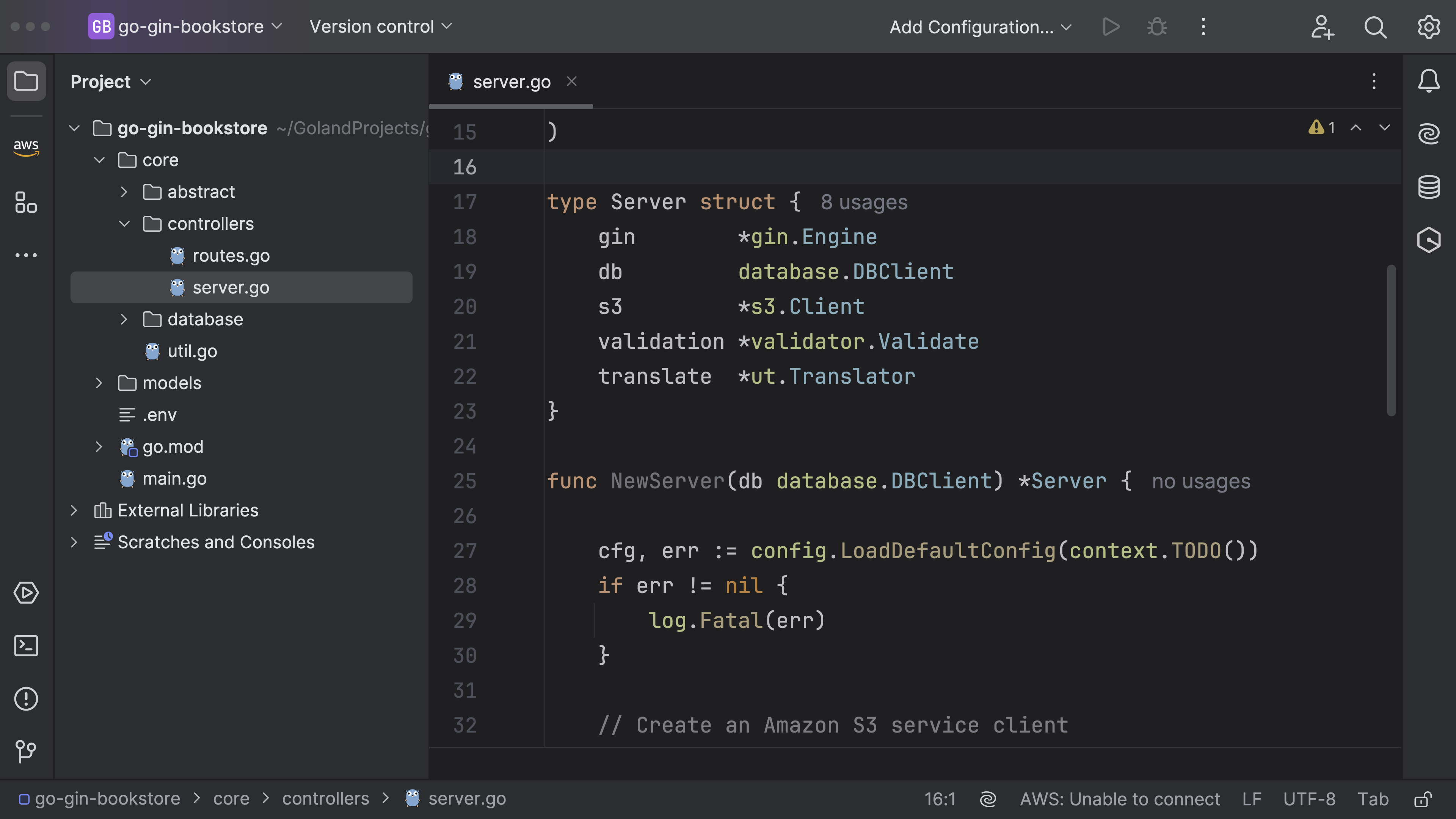
Let me first breakdown the Server struct.
ginfor HTTP services.dbpackage for handling database operations.s3which is a client for interacting with Amazon S3.validatorfor data validation tasks.ut(which seems to be universal-translator package) for localization.
Firstly, a Server struct is defined that encapsulates services and clients needed by the server.
Then, a NewServer function is provided to bootstrap a new instance of Server. It loads default configuration, creates an S3 client, sets a default Gin engine, and a new validator. It also registers translations and attaches endpoints to the server. Start method on the server is for starting the gin server at specified port (8080 in this case). If there is an error when running the server, it will log the error and return it. registerTranslation function generates a translator for a given validator. Here, english translations are registered. endpoints is a method on server which calls helper functions (bookRoute, authorRoute, customerRoute, reviewRoute) to attach various routes (endpoints) to the server. Each of these routing functions configures a series of HTTP endpoints pertaining to individual topics (like books, authors, customers, reviews). For example, bookRoute configures endpoints for creating, listing, updating, and deleting books as well as uploading book cover.
controllers/server.go
type Server struct {
gin *gin.Engine
db database.DBClient
s3 *s3.Client
validation *validator.Validate
translate *ut.Translator
}
func NewServer(db database.DBClient) *Server {
cfg, err := config.LoadDefaultConfig(context.TODO())
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Create an Amazon S3 service client
client := s3.NewFromConfig(cfg)
newValidator := validator.New()
server := &Server{
gin: gin.Default(),
db: db,
s3: client,
validation: newValidator,
translate: registerTranslation(newValidator),
}
server.endpoints()
return server
}
func (s *Server) Start() error {
slog.Info("serving at port 8080")
err := s.gin.Run(":8080")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Server Issue: %s", err)
return err
}
return nil
}
func registerTranslation(validation *validator.Validate) *ut.Translator {
// Create a new instance of the universal translator
uni := ut.New(en.New())
trans, _ := uni.GetTranslator("en")
// Register translations for English
if err := entranslations.RegisterDefaultTranslations(validation, trans); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
return &trans
}
Routes
Next, we will create a common route, and name it routes.go.
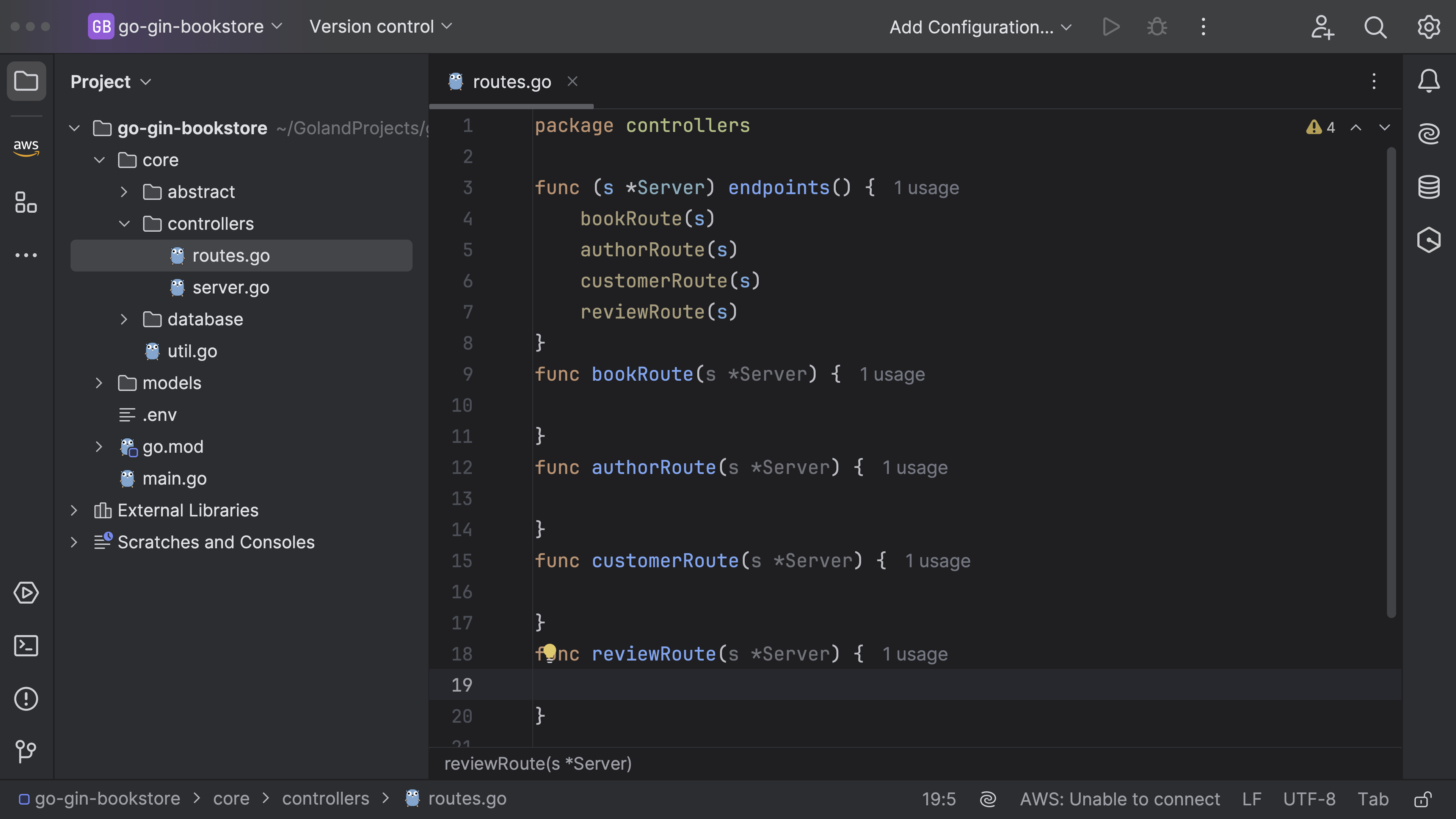
controllers/routes.go
package controllers
func (s *Server) endpoints() {
bookRoute(s)
authorRoute(s)
customerRoute(s)
reviewRoute(s)
}
func bookRoute(s *Server) {
}
func authorRoute(s *Server) {
}
func customerRoute(s *Server) {
}
func reviewRoute(s *Server) {
}
This function is a method of Server type that initializes the HTTP routes for the web server. Each function (bookRoute, authorRoute, etc.) is passed a pointer to the Server instance and sets up routes related to a specific entity (e.g., books, authors, customers, reviews). Currently, the function is empty, we will come back to this later to update it.
Update main.go
Let's return to main.go and update the functionality.
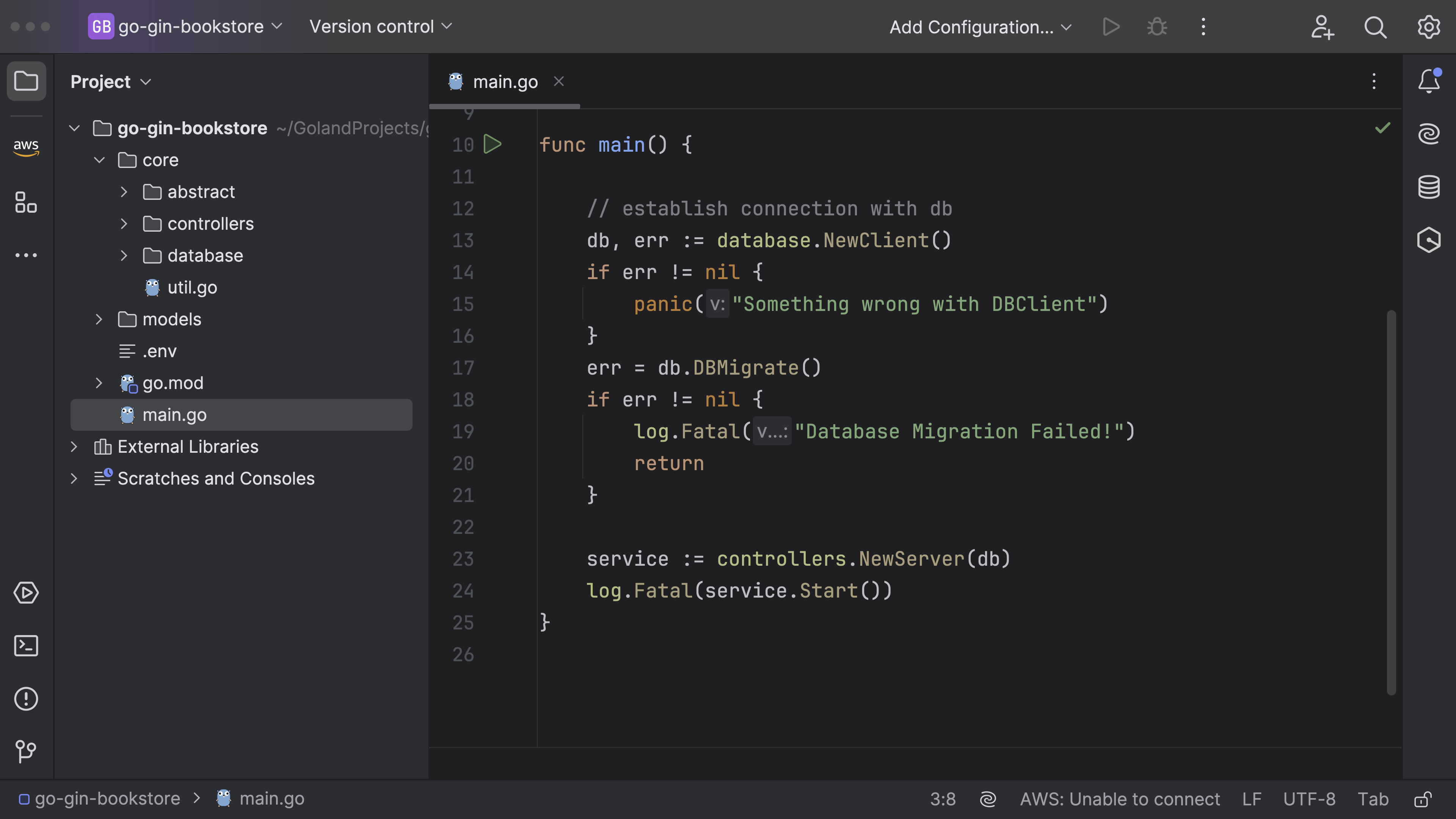
Within the main function, the initial lines are creating a new connection to a database using a function NewClient() that belongs to a package named database. The NewClient() function returns two values, db which is the initialized database client, and err which is an error object in case any error occurs during the execution of the NewClient() function.
db, err := database.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic("Something wrong with DBClient")
}
Next, the script tries to perform a database migration using a method called DBMigrate(). If you remember, we haven't implemented this function. Let's do it.
err = db.DBMigrate()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("Database Migration Failed!")
return
}
Move to database/db.go
Update the function.
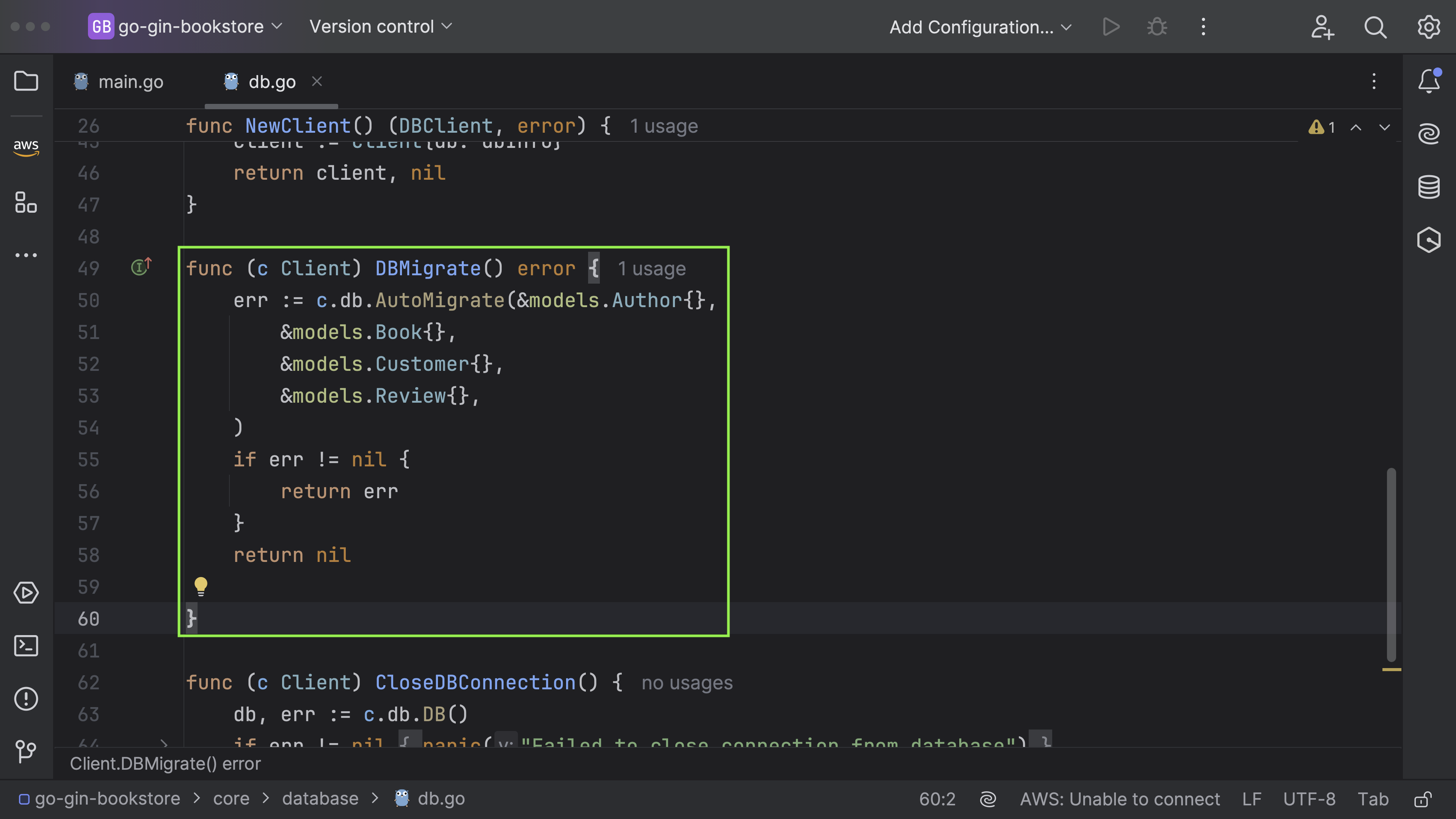
func (c Client) DBMigrate() error {
err := c.db.AutoMigrate(&models.Author{},
&models.Book{},
&models.Customer{},
&models.Review{},
)
if err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
The AutoMigrate function takes pointers to model structures as parameters. In this case, pointers to Author, Book, Customer and Review are passed.
It updates the database schema automatically with matching the tables to the provided models (Author, Book, Customer, Review). This is typically used when models are added or modified in the program, to keep the database in synchronization. This function utilizes the AutoMigrate method from the gorm library which is a popular ORM (Object-Relational Mapper) tool in Go. Post migration, the code sets up a new server (some form of routing, etc., defined within controllers.NewServer(db)), passing our database client db to this new server.
service := controllers.NewServer(db)
log.Fatal(service.Start())
Finally, it attempts to start this server with service.Start(). If there's an error in starting the service, it logs a fatal error, indicating service start failure.
Note: "AutoMigrate" is excellent for crafting prototypes; however, it should be employed with care in production environments.
Controllers
Let's begin focusing on the primary aspect: the HTTP Handlers.
Book
controllers/book.go
package database
import (
"context"
"errors"
"fmt"
"go-gin-bookstore/models"
"gorm.io/gorm"
"log/slog"
)
func (c Client) AddBook(ctx context.Context, bookParams models.DateParser) (*models.BookParams, error) {
var maxID int
if result := c.db.Model(&models.Book{}).Select("COALESCE(MAX(id), 0)").Scan(&maxID); result.Error != nil {
return nil, errors.New("something went wrong")
}
var Book models.Book
switch params := bookParams.(type) {
case *models.BookParams:
Book.ID = uint(maxID) + 1
Book.Title = params.Title
Book.ISBN = params.ISBN
Book.PublicationDate, _ = bookParams.ParsePublicationDate()
params.Id = int64(Book.ID)
result := c.db.WithContext(ctx).Create(&Book)
if result.Error != nil {
slog.Error(result.Error.Error())
return nil, errors.New("unable to register book")
}
return params, nil
default:
fmt.Printf("Type of bookParams: %T\n", bookParams)
return nil, errors.New("unsupported Type")
}
}
func (c Client) ListBooks(ctx context.Context) ([]models.Book, error) {
var books []models.Book
result := c.db.WithContext(ctx).Find(&books)
return books, result.Error
}
func (c Client) UpdateBook(_ context.Context, updateBookParams models.DateParser, bookId int64) (bool, error) {
var bookInfo = models.Book{Id: bookId}
if err := c.db.First(&bookInfo).Error; err != nil {
if errors.Is(err, gorm.ErrRecordNotFound) {
return false, errors.New("there is no book associated with this ID")
}
}
switch params := updateBookParams.(type) {
case models.UpdateBookParams:
parsedDate, _ := params.ParsePublicationDate()
c.db.Save(&models.Book{Id: bookId, Title: params.Title, ISBN: params.ISBN, PublicationDate: parsedDate})
}
return true, nil
}
func (c Client) DeleteBook(_ context.Context, bookId int64) error {
var bookInfo = models.Book{Id: bookId}
if err := c.db.First(&bookInfo).Error; err != nil {
if errors.Is(err, gorm.ErrRecordNotFound) {
return errors.New("there is no book associated with this ID")
}
}
// Delete Book (Hard delete)
c.db.Unscoped().Delete(&bookInfo)
return nil
}
func (c Client) UpdateBookCover(_ context.Context, bookId int64, bookImageURL string) (bool, error) {
var bookInfo = models.Book{Id: bookId}
if err := c.db.First(&bookInfo).Error; err != nil {
if errors.Is(err, gorm.ErrRecordNotFound) {
return false, errors.New("there is no book associated with this ID")
}
}
//Update ImageURL
c.db.Model(&bookInfo).Updates(models.Book{Image: bookImageURL})
return true, nil
}
Let's break it down.
Create a new book
The CreateBook function is an HTTP handler that creates a new book record in a database. It uses Gin for handling HTTP requests.
Briefly, it works as follows:
- CreateBook attempts to parse incoming JSON data into a
BookParamsstructure. If it fails, an HTTP 400 (Bad Request) error is returned, identifying an error in request format. - The function then validates whether the
PublicationDateinside theBookParamscan be parsed without error. If there is an error, it responds with an HTTP 400 error, indicating that the providedPublicationDateis invalid. - Assuming that all information is valid, it attempts to add the new book record to the database using the
AddBookmethod. If a problem arises during this process, it triggers a panic, effectively halting the server. - On successful creation of the book record, the function responds with an HTTP 200 status code and the newly created book record in JSON format.
func (s *Server) CreateBook(c *gin.Context) {
var book models.BookParams
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&book); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
if _, err := book.ParsePublicationDate(); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": "Invalid PublicationDate"})
return
}
addBook, err := s.db.AddBook(c, &book)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("err", err.Error())
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, addBook)
}
Listing books
This function tries to list all the books and if successful, it returns the list as JSON in the response, otherwise it returns an error in JSON format with HTTP status 400.
func (s *Server) ListBook(c *gin.Context) {
listBooks, err := s.db.ListBooks(c)
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, listBooks)
}
Updating a book
The UpdateBook function is used to update a particular book based on book id. It performs several operations including retrieving the book's id from the URL parameters, parsing and validatingthe JSON body of the incoming request, checking the validity of the publication date, and updating the book's details in the database.
func (s *Server) UpdateBook(c *gin.Context) {
var book models.UpdateBookParams
bookId := c.Param("id")
parseBookId, err := strconv.ParseInt(bookId, 10, 64)
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": "bookId is invalid"})
return
}
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&book); err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": "Check the data you are passing."})
return
}
if _, err := book.ParsePublicationDate(); err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": "Invalid PublicationDate"})
return
}
updateBook, err := s.db.UpdateBook(c, book, parseBookId)
if err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
if updateBook {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"status": true, "message": "Book Updated!"})
return
}
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"status": false, "message": "Something went wrong."})
}
Deleting a book
The DeleteBook function is going to delete a book from the database. It fetches the id parameter from the URL, and attempts to delete the corresponding book. Depending on the success of these operations, it sends appropriate HTTP responses.
func (s *Server) DeleteBook(c *gin.Context) {
bookId := c.Param("id")
parseBookId, err := strconv.ParseInt(bookId, 10, 64)
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": "bookId is invalid"})
return
}
if err = s.db.DeleteBook(c, parseBookId); err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"status": true, "message": "book deleted"})
}
Updating Book Cover
This function UploadBookCover is responsible for uploading the cover image of the book and updating its reference URL in the database.
func (s *Server) UploadBookCover(c *gin.Context) {
bookId := c.Param("id")
parseBookId, err := strconv.ParseInt(bookId, 10, 64)
if err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": "bookId is invalid"})
return
}
fileHeader, err := c.FormFile("file")
if err != nil {
c.String(http.StatusBadRequest, fmt.Sprintf("Error while getting file: %s", err.Error()))
return
}
file, err := fileHeader.Open()
if err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, fmt.Sprintf("Error opening file: %s", err.Error()))
return
}
defer file.Close()
// Create an uploader passing it the client
uploader := manager.NewUploader(s.s3)
uploadResult, err := uploader.Upload(c, &s3.PutObjectInput{
Bucket: aws.String(os.Getenv("S3_BUCKET")),
Key: aws.String(fileHeader.Filename),
Body: file,
//ACL: "public-read",
})
if err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
//Update URL in DB
_, err = s.db.UpdateBookCover(c, parseBookId, uploadResult.Location)
if err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": "Something went wrong."})
}
c.JSON(200, gin.H{"status": true, "message": "Image Updated Successfully!"})
}
- NOTE: Ensure that you possess an AWS account and that you've created both your access key ID and secret access key.
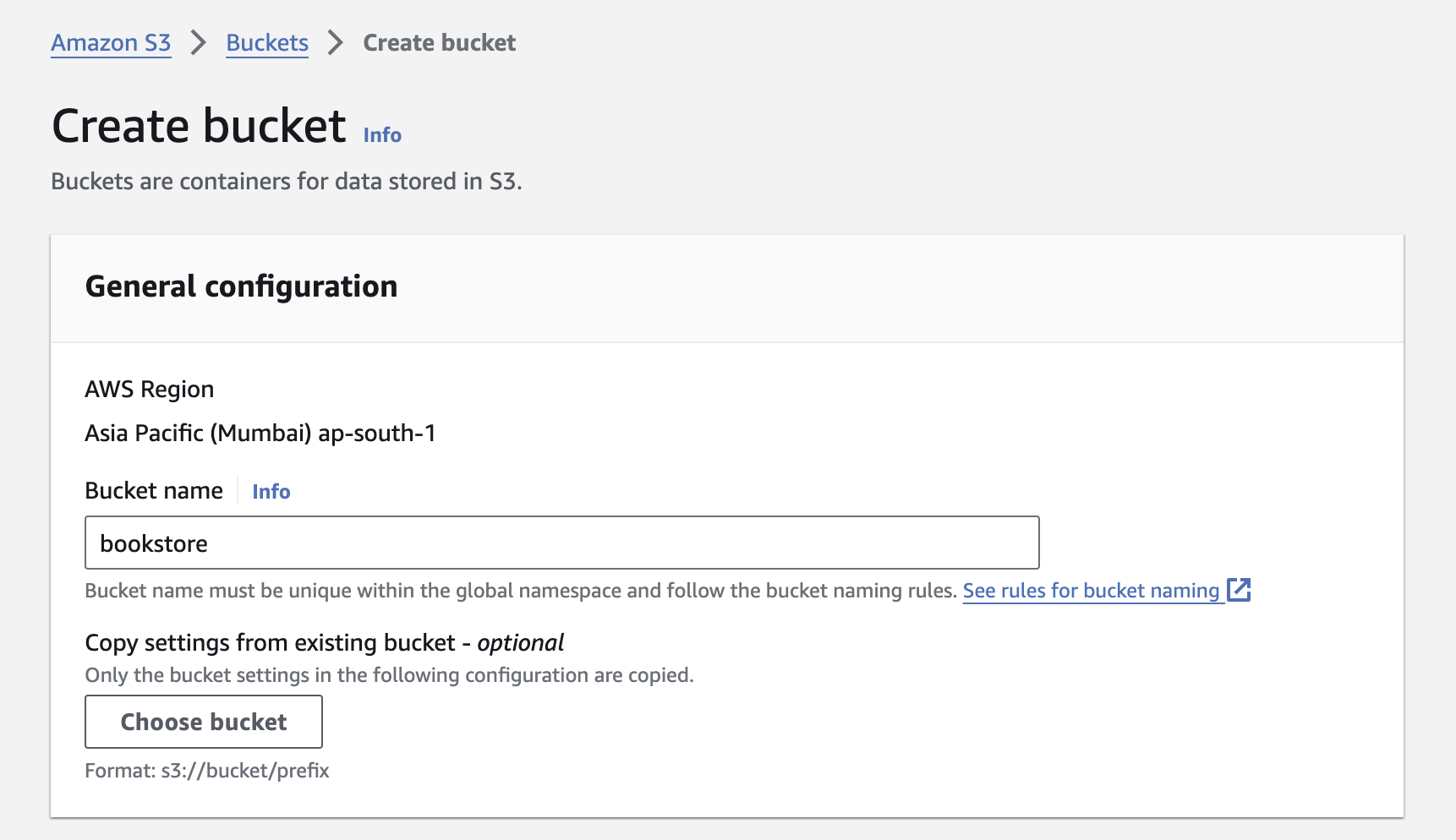
Note You need to create an S3 Bucket in AWS and make sure to update
S3_BUCKETenvironment variable in.envfile.
Author
controllers/author.go
package controllers
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"go-gin-bookstore/models"
"net/http"
)
func (s *Server) CreateAuthor(c *gin.Context) {
var author models.Author
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&author); err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
addAuthor, err := s.db.AddAuthor(c, author)
if err != nil {
panic("err")
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, addAuthor)
}
func (s *Server) LinkBook(c *gin.Context) {
var authorBook models.AuthorBook
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&authorBook); err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
linkBook, err := s.db.LinkAuthorBook(c, authorBook)
if err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
}
if linkBook {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"status": true, "message": "Book has been successfully linked!"})
return
} else {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"status": false, "message": "Something went wrong."})
}
}
func (s *Server) ListAuthors(c *gin.Context) {
listAuthors, err := s.db.ListAuthors(c)
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, listAuthors)
}
Let's break it down.
Create Author
The CreateAuthor function is an HTTP handler that creates a new author in the database.
func (s *Server) CreateAuthor(c *gin.Context) {
var author models.Author
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&author); err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
addAuthor, err := s.db.AddAuthor(c, author)
if err != nil {
panic("err")
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, addAuthor)
}
Linking Book
This function is trying to create relationship between Author and Book.
func (s *Server) LinkBook(c *gin.Context) {
var authorBook models.AuthorBook
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&authorBook); err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
linkBook, err := s.db.LinkAuthorBook(c, authorBook)
if err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
}
if linkBook {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"status": true, "message": "Book has been successfully linked!"})
return
} else {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"status": false, "message": "Something went wrong."})
}
}
Listing Authors
In this function we are trying to list down all the authors present in the database.
func (s *Server) ListAuthors(c *gin.Context) {
listAuthors, err := s.db.ListAuthors(c)
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, listAuthors)
}
Customer
controllers/customer.go
package controllers
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"go-gin-bookstore/models"
"log/slog"
"net/http"
"strconv"
)
func getAndValidateCustomer(c *gin.Context, customer interface{}) (int64, bool) {
customerID, ok := parseCustomerId(c)
if !ok {
return 0, false
}
if !bindCustomerData(c, customer) {
return 0, false
}
return customerID, true
}
func parseCustomerId(c *gin.Context) (int64, bool) {
customerId := c.Param("id")
parseCusId, err := strconv.ParseInt(customerId, 10, 64)
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": "customerId is invalid"})
}
return parseCusId, err == nil
}
func bindCustomerData(c *gin.Context, customer interface{}) bool {
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(customer); err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": "Check the data you are passing."})
return false
}
return true
}
func (s *Server) CreateCustomer(c *gin.Context) {
customer := models.Customer{}
if !bindCustomerData(c, &customer) {
return
}
addCustomer, err := s.db.AddCustomer(c, customer)
if err != nil {
slog.Error(err.Error())
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": "Something went wrong"})
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, addCustomer)
}
func (s *Server) UpdateCustomer(c *gin.Context) {
customer := models.CustomerParams{}
customerID, ok := getAndValidateCustomer(c, &customer)
if !ok {
return
}
updateCustomer, err := s.db.UpdateCustomer(c, customer, customerID)
if err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
if updateCustomer {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"status": true, "message": "Customer Information Updated!"})
return
}
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"status": false, "message": "Something went wrong."})
}
func (s *Server) DeleteCustomer(c *gin.Context) {
customerID, ok := parseCustomerId(c)
if !ok {
return
}
if err := s.db.DeleteCustomer(c, customerID); err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"status": true, "message": "customer deleted"})
}
Let's take a closer look at each function one by one.
Add Customer
In this function we are trying to create a new customer. It uses the bindCustomerData function to parse the customer data from the JSON provided. If bindCustomerData returns false, it will exit the function. After that, it tries to add the customer using s.db.AddCustomer(c, customer) and checks for errors. If an error occurs, logs the error and responds with an HTTP 500 error status code and a JSON message to the client. If there are no errors, it will respond with an HTTP 200 status code and the newly created customer in the response.
func bindCustomerData(c *gin.Context, customer interface{}) bool {
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(customer); err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": "Check the data you are passing."})
return false
}
return true
}
func (s *Server) CreateCustomer(c *gin.Context) {
customer := models.Customer{}
if !bindCustomerData(c, &customer) {
return
}
addCustomer, err := s.db.AddCustomer(c, customer)
if err != nil {
slog.Error(err.Error())
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": "Something went wrong"})
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, addCustomer)
}
Update Customer
This function is responsible for updating the details of the customer. At the start, it creates an instance of CustomerParams model, which is then filled by the getAndValidateCustomer function. If the validation fails to get the customer details, the function ends immediately. If the validation is successful, the function attempts to update the customer's data in the database using the UpdateCustomer method. If an error is encountered while updating the customer information, the function responds with an HTTP status 400 (Bad Request) and sends a JSON object containing the error details.
On successful update, it sends an HTTP status 200 (OK) and sends a JSON message indicating the success of the operation. However, if the update isn't successful for some other reason, the function aborts the process and sends an HTTP status 500 (Internal Server Error) along with a JSON indicating that an error occurred.
func getAndValidateCustomer(c *gin.Context, customer interface{}) (int64, bool) {
customerID, ok := parseCustomerId(c)
if !ok {
return 0, false
}
if !bindCustomerData(c, customer) {
return 0, false
}
return customerID, true
}
func (s *Server) UpdateCustomer(c *gin.Context) {
customer := models.CustomerParams{}
customerID, ok := getAndValidateCustomer(c, &customer)
if !ok {
return
}
updateCustomer, err := s.db.UpdateCustomer(c, customer, customerID)
if err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
if updateCustomer {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"status": true, "message": "Customer Information Updated!"})
return
}
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"status": false, "message": "Something went wrong."})
}
Delete Customer
This method is designed to delete a customer's record from a database. It begins by trying to parse a customer ID from the context. If it can't parse the ID, the operation halts and returns. If the ID is parsed successfully, the function then attempts to delete that customer from the database.
func (s *Server) DeleteCustomer(c *gin.Context) {
customerID, ok := parseCustomerId(c)
if !ok {
return
}
if err := s.db.DeleteCustomer(c, customerID); err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"status": true, "message": "customer deleted"})
}
Review
controllers/review.go
package controllers
import (
"errors"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/go-playground/validator/v10"
"go-gin-bookstore/core"
"go-gin-bookstore/models"
"net/http"
"strconv"
)
func (s *Server) CreateReview(c *gin.Context) {
var review models.ReviewParams
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&review); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
// Validate the struct
if err := s.validation.Struct(&review); err != nil {
// Collect validation errors
var errs []string
for _, err := range err.(validator.ValidationErrors) {
// Translate validation error messages using the default translator
errs = append(errs, err.Translate(*s.translate))
}
// Prepare JSON response
jsonResponse := map[string]interface{}{
"success": false,
"errors": errs,
}
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, jsonResponse)
return
}
_, err := s.db.AddReview(c, review)
if err != nil {
// Check if the error is of type notFoundError
var notFoundErr *core.NotFoundError
if errors.As(err, ¬FoundErr) {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusNotFound,
gin.H{"status": notFoundErr.Code, "message": notFoundErr.Message})
return
} else {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": "Something went wrong"})
return
}
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, map[string]string{"message": "Review successfully added."})
}
func (s *Server) ListReviewByBook(c *gin.Context) {
bookId := c.Param("id")
parseBookId, err := strconv.ParseInt(bookId, 10, 64)
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": "bookId is invalid"})
return
}
bookReviews, err := s.db.ListReview(c, parseBookId)
if err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": "Something went wrong"})
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, bookReviews)
}
Create Review
It is intended to create a review information based on the incoming request. First, it attempts to bind the incoming request JSON data to the ReviewParams model. The ReviewParams struct is capturing CustomerID, BookID, Rating and Comment.
func (s *Server) CreateReview(c *gin.Context) {
var review models.ReviewParams
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&review); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
// Validate the struct
if err := s.validation.Struct(&review); err != nil {
// Collect validation errors
var errs []string
for _, err := range err.(validator.ValidationErrors) {
// Translate validation error messages using the default translator
errs = append(errs, err.Translate(*s.translate))
}
// Prepare JSON response
jsonResponse := map[string]interface{}{
"success": false,
"errors": errs,
}
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, jsonResponse)
return
}
_, err := s.db.AddReview(c, review)
if err != nil {
// Check if the error is of type notFoundError
var notFoundErr *core.NotFoundError
if errors.As(err, ¬FoundErr) {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusNotFound,
gin.H{"status": notFoundErr.Code, "message": notFoundErr.Message})
return
} else {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": "Something went wrong"})
return
}
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, map[string]string{"message": "Review successfully added."})
}
Listing all reviews
In the function we are trying to get all the book reviews based on book id.
func (s *Server) ListReviewByBook(c *gin.Context) {
bookId := c.Param("id")
parseBookId, err := strconv.ParseInt(bookId, 10, 64)
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": "bookId is invalid"})
return
}
bookReviews, err := s.db.ListReview(c, parseBookId)
if err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": "Something went wrong"})
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, bookReviews)
}
Once, everything is done make sure to update the routes.
controllers/routes.go
package controllers
func (s *Server) endpoints() {
bookRoute(s)
authorRoute(s)
customerRoute(s)
reviewRoute(s)
}
func bookRoute(s *Server) {
s.gin.POST("/book", s.CreateBook)
s.gin.GET("/book", s.ListBook)
s.gin.PUT("/book/:id", s.UpdateBook)
s.gin.DELETE("/book/:id", s.DeleteBook)
s.gin.POST("/book/cover/:id", s.UploadBookCover)
}
func authorRoute(s *Server) {
s.gin.GET("/authors", s.ListAuthors)
s.gin.POST("/author", s.CreateAuthor)
s.gin.POST("/author/book/link", s.LinkBook)
}
func customerRoute(s *Server) {
s.gin.POST("/customer", s.CreateCustomer)
s.gin.PUT("/customer/:id", s.UpdateCustomer)
s.gin.DELETE("/customer/:id", s.DeleteCustomer)
}
func reviewRoute(s *Server) {
s.gin.POST("/review", s.CreateReview)
s.gin.GET("/review/book/:id", s.ListReviewByBook)
}
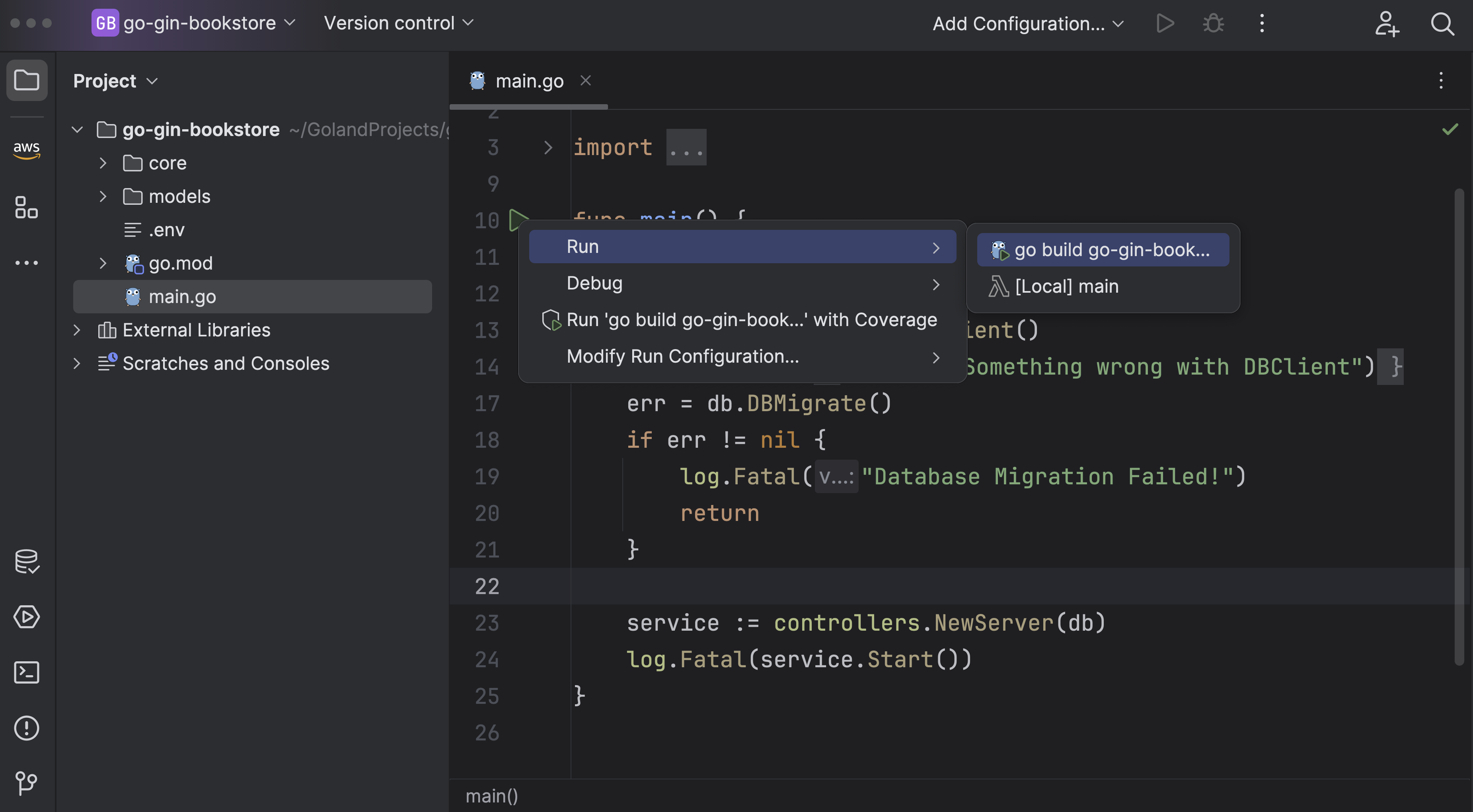
Let's start the application by running the following command in the terminal or an easy way through GoLand:
go run main.go
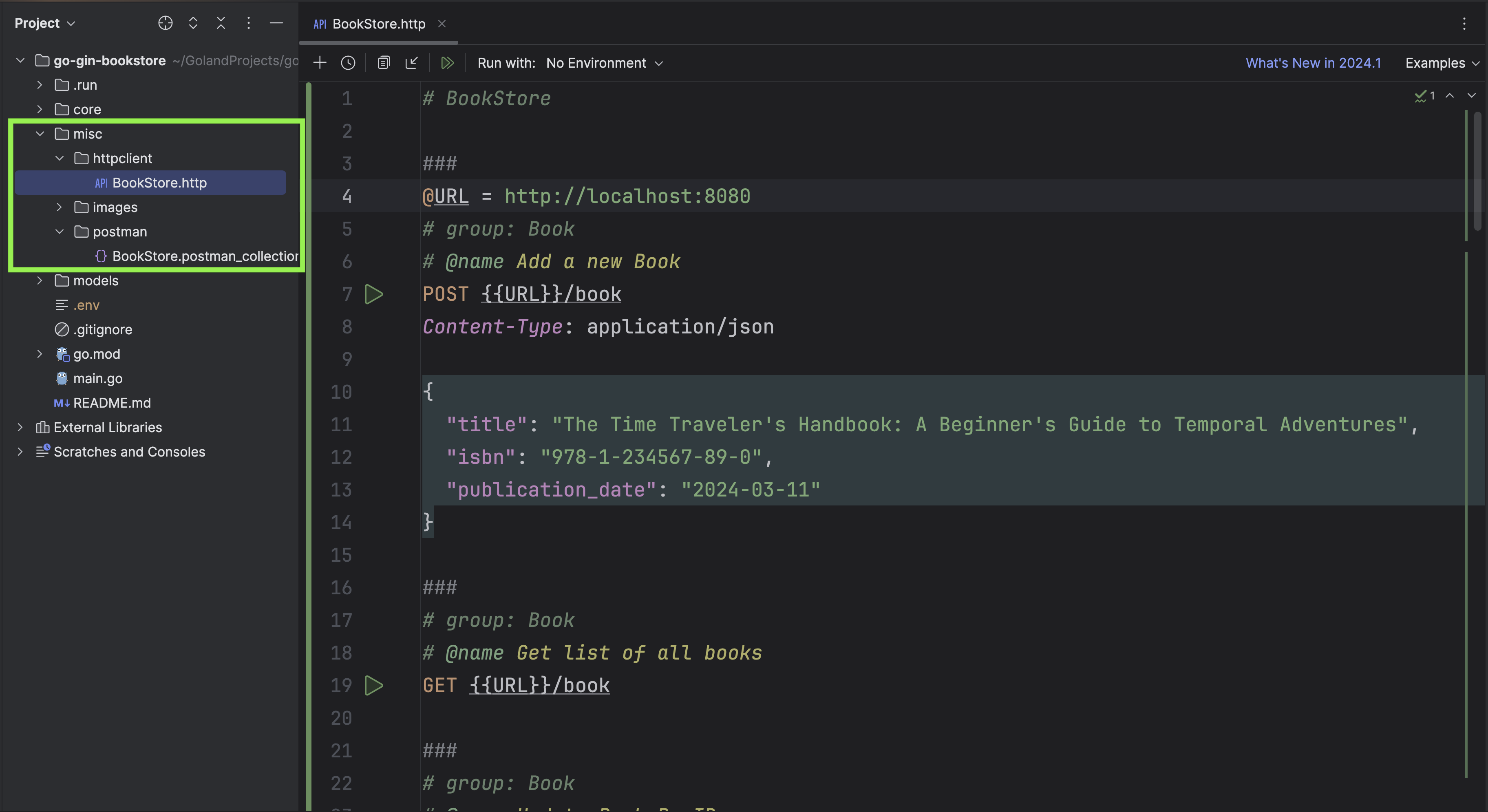
Now open HTTP Client to test your endpoints.
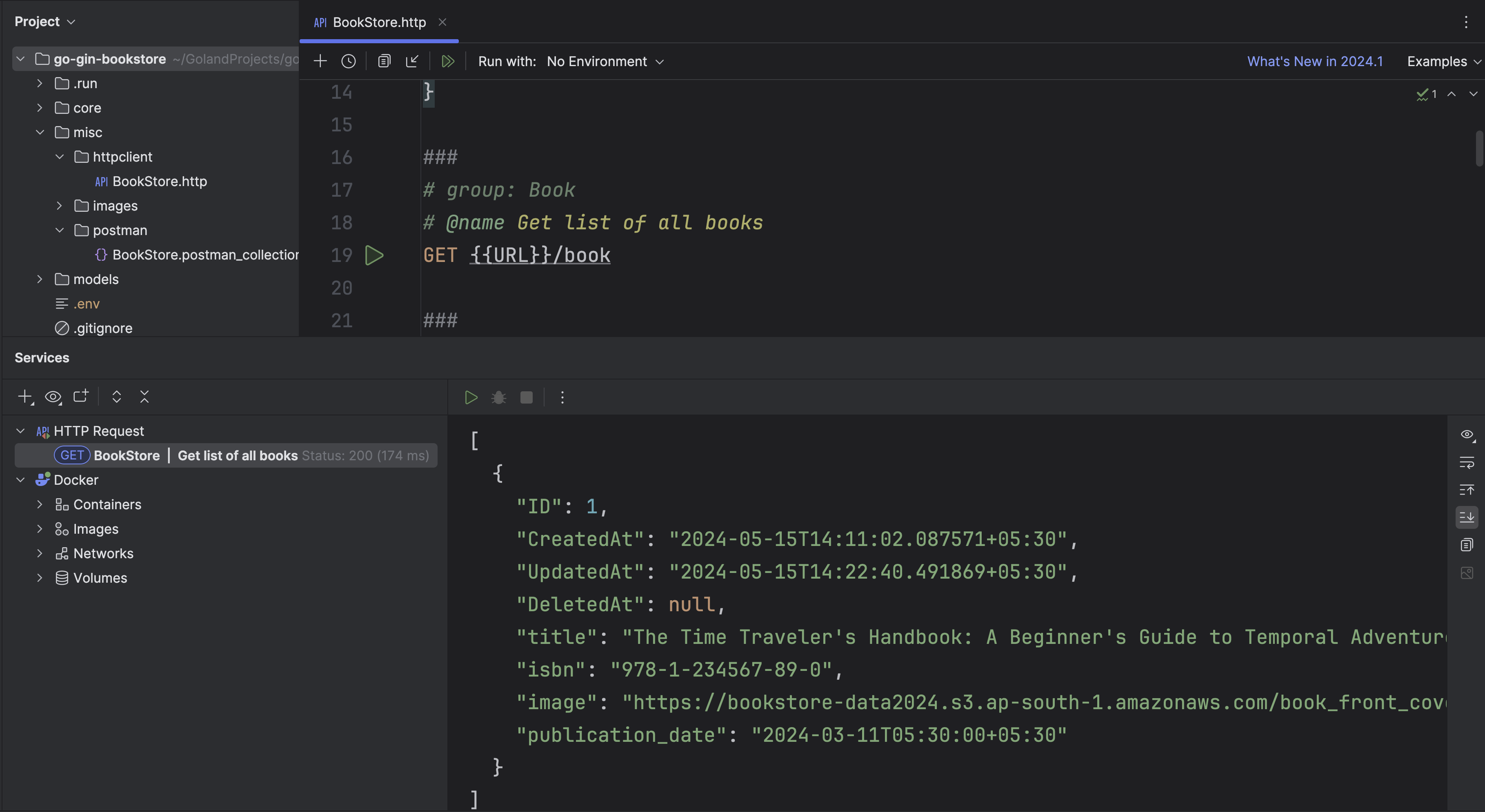
Congratulations on reaching this milestone! While the tutorial may have been extensive, I'm certain you've acquired valuable new knowledge. Now, take the next step and begin creating exciting applications with Go.
