ReSharper C++ Features
ReSharper C++ makes Visual Studio a better IDE for C++ developers, providing on-the-fly code analysis, quick-fixes, powerful search and navigation, smart code completion, refactorings, a variety of code generation options and other features to help increase your everyday productivity.
Code Analysis
ReSharper C++ starts analyzing code as soon as you open your project in Visual Studio editor, and keeps reanalyzing files as you edit them, detecting errors and possible problems before you even compile.



Quick-fixes
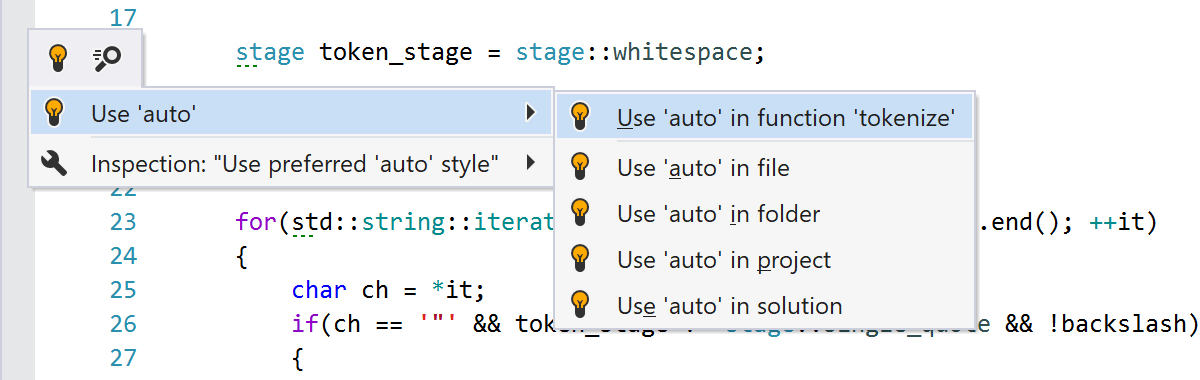
40+ quick-fixes are available to instantly solve many of the detected code issues. Whenever you see a light bulb to the left of your code, press Alt+Enter to apply a suggested quick-fix.
For example, when an uninitialized variable is detected, you can immediately initialize it with
the default value. Other quick-fixes let you add missing
#include directives,
or remove redundant qualifiers in a particular statement, or in a larger scope such as a file or
even the entire solution.

Create from usage
Another benefit of quick-fixes is that you can start using classes, methods, variables, properties and fields before you declare them. When ReSharper C++ detects an undeclared symbol, it suggests quick-fixes to generate the corresponding symbol declaration based on its usage.

Find code issues
For any given scope such as a file, project or solution, you can tell ReSharper C++ to display all code issues that it detects in a dedicated tool window.
Find Code Issues works in the background, which lets you keep editing or navigating your code while ReSharper C++ runs its analysis and populates the Inspection Results tool window.
As soon as results are ready, you can group them by various criteria and search to find specific types of issues. You can also save and load reports of Find Code Issues results.

C++ code analysis from the command line
ReSharper C++ code inspections are also available via InspectCode, a free command line tool that allows running ReSharper inspections outside of Visual Studio.
To use InspectCode, please download and unzip the command line tools package and run InspectCode.exe with your solution file as a parameter. To learn more about using InspectCode, please read this article.

Clang-Tidy
ReSharper C++ integrates seamlessly with Clang-Tidy, a powerful open-source code analysis tool based on the Clang compiler. The integration provides code checks and the quick-fixes.
Syntax Style
ReSharper C++ includes a collection of syntax style settings that you can use to make ReSharper follow your chosen code style and enforce it throughout your entire codebase.
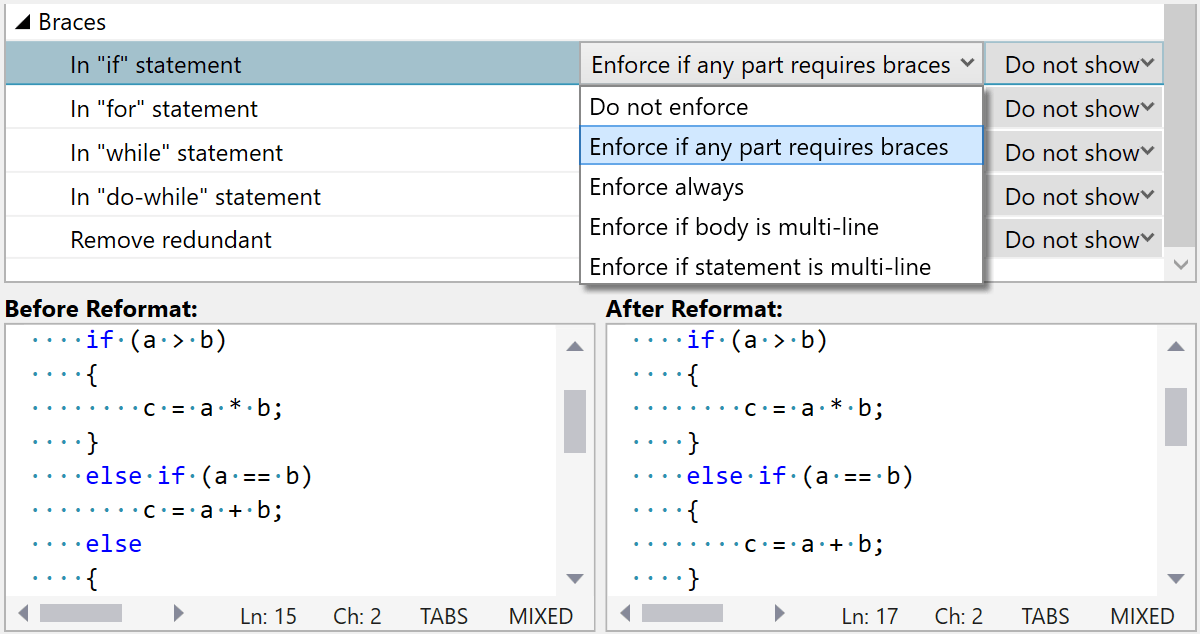
You can customize your syntax style preferences on the Code Editing | C++ | Syntax Style page. The selected option value will be used both for code generation and for code style enforcement.
ReSharper C++ will highlight style violations and offer you quick-fixes to help eliminate them. All syntax style quick-fixes can be applied in scope, including in local scopes like function bodies or class definitions.
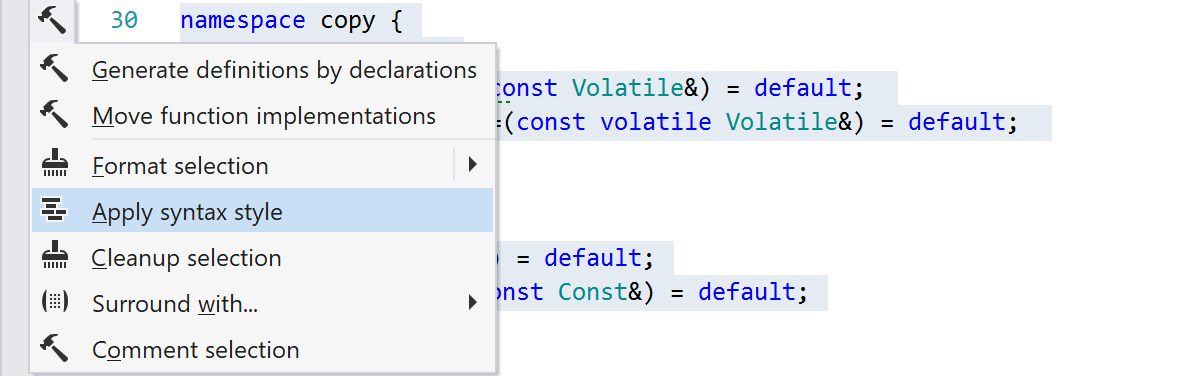
To enforce the chosen syntax style, you can use code cleanup or the dedicated Apply Syntax Style action, which will fix syntax style issues in the selection, the entire current file, or a set of files depending on the current context.
Refactorings
ReSharper C++ provides several full-scale, mainstream refactorings such as Rename, Extract Method and Change Signature. In addition, it offers dozens of context actions, which are local code transformations available with a single shortcut.

Rename
Modifying the name of a class or macro can cause many problems when performed manually. That's why, when you invoke the Rename refactoring, ReSharper C++ takes care of all the necessary checks.
Either all modifications are performed automatically, or you're shown a list of conflicts that you can resolve manually to be sure that only necessary and appropriate changes are made.
Along with actual code symbols that you apply it to, the Rename refactoring can
rename related files (both the source file and the header file) and related text in comments
and documentation, as well as update usages in #include directives.

Extract Method
The Extract Method refactoring helps you create a new method based on a selected code fragment. ReSharper analyses the selected block of code and detects variables that can be converted into method parameters or represent its return value.

Change Signature
The Change Signature refactoring allows you to apply one or more changes to the signature of a function. All usages, implementations, and overrides of the function will be updated accordingly.

Introduce Variable and Inline Variable
The Introduce Variable refactoring allows you to create a new local variable based on a selected expression, initialize it with the expression, and finally replace all occurrences of the expression in the code with references to the newly introduced variable.
Conversely, Inline Variable replaces all occurrences of a given variable or local constant with its initializer.

Introduce Field
The Introduce Field refactoring helps create a new field based on a selected expression, assign the original expression to the field in its own initializer or in the constructor, and replace occurrences.


Introduce Namespace Alias
The Introduce Namespace Alias refactoring helps define shortcut names for deeply nested namespaces.
As soon as you invoke the refactoring, it suggests defining a scope that you want to introduce a namespace alias for.

Introduce typedef and Inline typedef
The Introduce typedef refactoring allows you to quickly create a
typedef for the selected data
type and replace this data type and all its occurrences with the newly created typedef.
The Inline typedef refactoring does the inverse: it replaces an existing
typedef with the actual data type.



Context actions
In addition to refactorings, ReSharper C++ provides a set of context actions: local code transformations that usually help switch between alternative syntax options. Similar to quick-fixes, they are made available when you press Alt+Enter.
For example, you can quickly replace
auto with explicit type or replace type with
auto. Other context actions help merge nested if statements,
generate missing
case statements when switching over an enum, substitute a macro
call or typedef etc.
Coding Assistance
ReSharper C++ extends Visual Studio's ways of highlighting syntax and matching structural pieces of code, provides its own implementation of code completion, and helps visualize available documentation for any C++ symbol.

Syntax and structure highlighting
ReSharper C++ recognizes *.c, *.cc, *.cxx, *.cpp, *.h, and *.hpp files in your solution, and highlights source code in these files according to a color scheme that you can modify at any time.
In addition, ReSharper C++ highlights various matching items when you place the caret at one
item in a pair, be it matching delimiters,
macros or a format specifier and argument in a printf function call.
When you put the caret on one of exit points from a function, loop or a
switch
statement (return,
throw, break
etc.), ReSharper C++ will now automatically highlight all other
function or loop
exits.

Code completion
In C++ files, you can use code completion when writing your code, which sometimes suggests code generation options among other choices.
Code completion can even suggest symbols that are not
yet included in the current file. When you select a symbol like this in the completion list,
the corresponding #include directive is added automatically.


Documentation summary
Quick Documentation pop-up displays documentation based on Doxygen comment blocks without forcing you to navigate to a symbol's definition: just hit Ctrl+Shift+F1 in the default keymap.
Even if there is no Doxygen documentation available for a symbol, Quick Documentation will show the symbol's signature.
ReSharper C++ can also display rich, syntax highlighted tooltips for C++ code elements. The tooltips will display function and variable types, as well as documentation.
C#-style XML documentation comments are also sometimes used for C++ symbols. ReSharper C++ correctly displays them in the Quick Documentation pop-up and in the quick info tooltip.

C++/CLI support
C++/CLI is a set of C++ language extensions by Microsoft for easy interoperability between managed and native code. With extensive support for both managed languages and C++, it is only natural for ReSharper to offer help with writing code in C++/CLI too.
Within C++/CLI code you can access all the same refactorings and intention actions as in pure C++ code. There is also an ability to navigate between C# and C++/CLI worlds.
Navigation and Search
With ReSharper C++, finding your way through the source code gets a lot easier. Just search for declarations, members, method calls, or members of an inheritance hierarchy with simple shortcuts.

Contextual navigation
For all symbols that have separate declarations and definitions, ReSharper C++ displays the
Navigate to declaration/definition
icon on the left (![]() ).
Click the icon or press
Ctrl+B to quickly switch between the declaration and the
corresponding definition.
).
Click the icon or press
Ctrl+B to quickly switch between the declaration and the
corresponding definition.
Other context-sensitive navigation options in ReSharper C++ include navigating from a selected symbol to its usages, base or derived symbols.

Go to anything
ReSharper C++ offers a set of context-insensitive navigation commands including Go to File, Go to Symbol, Go to File Member and Go to Everything.
All these commands support lowerCamelCase-based search and filtering by path. For example, entering
fc movie in the
Go to Everything pop-up returns the
list of files and file members that have the string
movie in their names and that belong to either FollowerC project
or FollowerConstants namespace (both matching fc).


Visualize hierarchies
ReSharper C++ can give you an overview of the inheritance hierarchy that any given type is a part of. You can see both base types and inheritors of the selected type and navigate to any of them in one click.
In addition, ReSharper C++ comes with a hierarchy view that serves to visualize and help you
figure out dependencies introduced via #include directives.

Find usages
Use Find Usages to search for all references of a specific symbol in the C++ code of your solution.
As soon as search is completed, found occurrences are displayed in a tool window with grouping and filtering options, as well as a preview pane.

File structure
With ReSharper C++, you can view the structure of the current document using the File Structure window, which greatly simplifies navigation in large files.
As you switch to another editor tab, the tool window displays the structure of the corresponding file.

To-do Explorer
The To-do Explorer tool window lets you view, group and filter comments that contain one of the 3 default to-do patterns (Bug, Todo and Not Implemented) and any custom patterns that you might want to set up.
If you use the full ReSharper Ultimate license and you have a multilingual solution, the To-do Explorer will gather to-do items from all supported languages: C#, VB.NET, C++, JavaScript, XAML, HTML etc.
Code Generation
ReSharper C++ provides a variety of ways to generate boilerplate code. In addition to declaring and defining symbols based on their existing usages, it can create type members, surrounding code blocks, and any code snippets that you commonly need in your code base.

Generate common code
ReSharper C++ offers a quick way to generate missing members, overriding members, equality or relational operators, definitions based on existing declarations, hash and swap functions and constructors.
Just press Alt+Ins in the text editor to invoke the Generate menu and see all available options.

Code and file templates
ReSharper C++ comes with 29 customizable templates. Some of them are regular code snippets, others are specifically used to wrap around code selections.
You can use and create file templates as well. Pressing Ctrl+Alt+Ins helps you quickly add a class to the project you're working on.
Code Style Assistance
With ReSharper C++, code formatter learns from your existing code, and your formatting and code style preferences can be shared with your team members.

Code formatter
ReSharper C++ allows you to configure and apply code formatting rules that you prefer to use when working on a specific solution.
As an alternative to digging through all available code formatting options, you can select a block of code and configure only those that are applicable to this particular block.

Code style settings
To ensure a consistent code style across the entire team, you can save your formatting and naming preferences to a settings file and share it among your teammates.
ReSharper C++ also lets you define other parts of a team coding standard, such as the order
of modifiers and the preferred value for pointer initializers.
For example, you can specify 0, nullptr or NULL
as the preferred initializer style, and ReSharper C++ will respect your choice when it
generates new initializers for you.
Use ReSharper Options | Code Editing | C++ | Naming Style to select one of the predefined C++ naming styles: STL, Google, LLVM, CamelCase, or Microsoft.

Detect formatting settings
Often it's much easier to customize formatting settings by simply detecting them from the existing code. Use ReSharper | Edit | Detect formatting settings menu to have ReSharper detect code formatting settings. You'll get the tool window with the detected values, which can be reviewed and applied to the ReSharper settings on your machine. Or, you can save them to a team-shared settings layer so that other developers on your team will have the same code formatting configuration when opening the current solution.
Unit Testing
A Visual Studio-integrated unit test runner supports Google Test, Boost.Test, Catch and Doctest frameworks.



Unit test runner
ReSharper C++ comes with a unit test runner in Visual Studio that supports Google Test, Boost.Test, Catch and Doctest frameworks.
You can run and debug unit tests, as well as add tests to different sessions, right from the text editor, via the Alt+Enter contextual menu.
ReSharper C++ provides Unit Test Explorer and Unit Test Sessions tool windows to view, group, filter and run unit tests, as well as to create and manage unit test sessions.
Unreal Engine
If you are making games based on Unreal Engine, benefit from the specific Unreal Engine support in ReSharper C++.

UE naming convention
ReSharper C++ accommodates UE naming convention across all its actions, including Introduce Variable and Rename refactorings, code generation for getters and setters, and many others. It also keeps an eye on the names you use across your code base. It highlights any inconsistencies with the UE naming convention by running Inconsistent UE naming inspections.

UE code analysis
A few code analysis checks are also available for UE-based code, especially targeting the missing or incorrectly set UE reflection macros:
- UCLASS declaration must publicly inherit UObject or class derived from it.
- Class marked by UCLASS must inherit only one class derived from UObject or UObject directly.
- UCLASS must be a class / USTRUCT must be a struct.
- UInterface must be empty.
- Missing UCLASS / UINTERFACE / USTRUCT macro call in UE class / interface / struct declaration.
- UE classes can not be declared inside another class.
- UPROPERTY / UFUNCTION macro call before declaration has no effect.
- Objects stored in non-uproperty member can be garbage collected at any time.

UnrealHeaderTool
ReSharper C++ provides seamless integration with UnrealHeaderTool to help you catch more issues with Unreal Engine class metadata right in the editor. When working with an Unreal Engine project, ReSharper C++ automatically runs UnrealHeaderTool on the file you’re editing and displays any errors or warnings, just like with other inspections. Watch the UnrealHeaderTool integration in action.

Code completion for reflection specifiers
To help you easily work with Unreal Engine reflection macros, ReSharper C++ offers completion for reflection specifiers inside reflection macros.

Code documentation for reflection specifiers
Built-in documentation for UE reflection specifiers is shown in the Quick Documentation popup (Ctrl+Q) when the caret is located on a specifier.

Support for UE Remote Procedure Calls
ReSharper C++ identifies
RPCs by
Client, Server, or NetMulticast keywords in the
UFUNCTION declaration statement. For such functions, ReSharper C++ is aware that an
_Implementation function should be generated, as well as a
_Validate function if
WithValidation is set. It can generate both if both are missing, or only one if only one is missing.
When navigating to a definition, both functions (_Validate and
_Implementation) will be suggested. Alternatively, these options are available in the
Alt+Enter menu too, as “Related UE functions”.

Auto-import and the generated headers
When you use a symbol that’s not available in the current scope, ReSharper C++ highlights it in red and suggests adding the missing
#include when possible. When the
#include is missing from a header file, it will be inserted before the
.generated.h, which should be the last one in the list of includes. The incorrectly placed
#include is highlighted by the corresponding inspection.
Rename refactoring in Unreal Engine projects updates the corresponding
.generated.h include directive and related files with the A,
F, E, T, S, and U prefixes.

Code generation
The “new” postfix template for UCLASSes expands to a proper factory function call
(which will register the created object in the garbage collector).
Live templates with the corresponding names are available to help
you quickly generate USTRUCT/UCLASS/UENUM/UENUMCLASS.

USF files
The Unreal Engine USF files are based on HLSL and contain the multi-platform shader code. These files usually include virtual file paths, and ReSharper C++ can work with them and support all the usual actions.

SpatialOS GDK
The SpatialOS Game Development Kit is an Unreal Engine 4 fork that helps you run and manage online games in the cloud. ReSharper C++ recognizes CrossServer, SpatialType, NonSpatialType, and other SpatialOS specifiers. Learn more.
HLSL

ReSharper C++ provides initial support for HLSL, the High-Level Shading Language. ReSharper C++ highlights HLSL code according to your default color scheme and displays inlay hints and tooltips for code elements with type information and documentation. You can also search for and quickly navigate to structs, functions, or parameters in your entire solution, referenced files, and standard libraries. And to perfect the HLSL experience, ReSharper C++ offers you smart code completion, auto-inserting matching delimiters, and more.

The full power of ReSharper's control-flow analysis comes to HLSL shader files, including warnings about unreachable code, uninitialized variables, redundant control flow jumps and conditional branches, and much more.