Create and run your first Ruby project
This tutorial will show you how to create and run the simple interactive Ruby program in RubyMine.
Before starting this tutorial, download and install the Ruby distribution for your platform.
We'll perform all steps using RubyMine installed on macOS.
Create an empty application
To create a Ruby program from scratch, do the following:
Run RubyMine and click New Project on the Welcome Screen.

In the New Project dialog, make sure that Empty Project is selected on the left pane. Then, specify the following settings:

Name: specify a name for the project.
Location: specify a path to the directory in which you want to create the project. By default, RubyMine creates a directory with the same name as the project.
Ruby SDK: select a required Ruby interpreter installed on your system.
Click Create to continue.
Create a Ruby file
After creating a project, you will see its structure in the Project tool window on the left. To add a Ruby file, do the following:
Select a project root in the Project tool window and press Alt+Insert.
In the invoked popup, select Ruby File/Class and press Enter.

In the invoked popup, specify a script name (script in our case) and click OK.

In the editor, insert the following code:
puts "Please enter your name" name = gets.chomp puts "Hello, #{name}! I'm Ruby!"
Run an application
To run the created script, do the following:
Press Ctrl twice and type the following command:
ruby script.rbPress Enter.

In the Run tool window, type any name and press Enter to see a program's response.

Run/debug configurations
After you run a Ruby script, RubyMine automatically creates a special profile - a run/debug configuration. Such a profile is used for running, debugging and testing applications, and specifies the script name, working directory, actions to be performed before launch, and so on.
To edit a configuration, go to the dropdown on the top of the editor and click Edit Configurations.
In the invoked Run/Debug Configurations dialog, you can specify the settings required to launch your script.
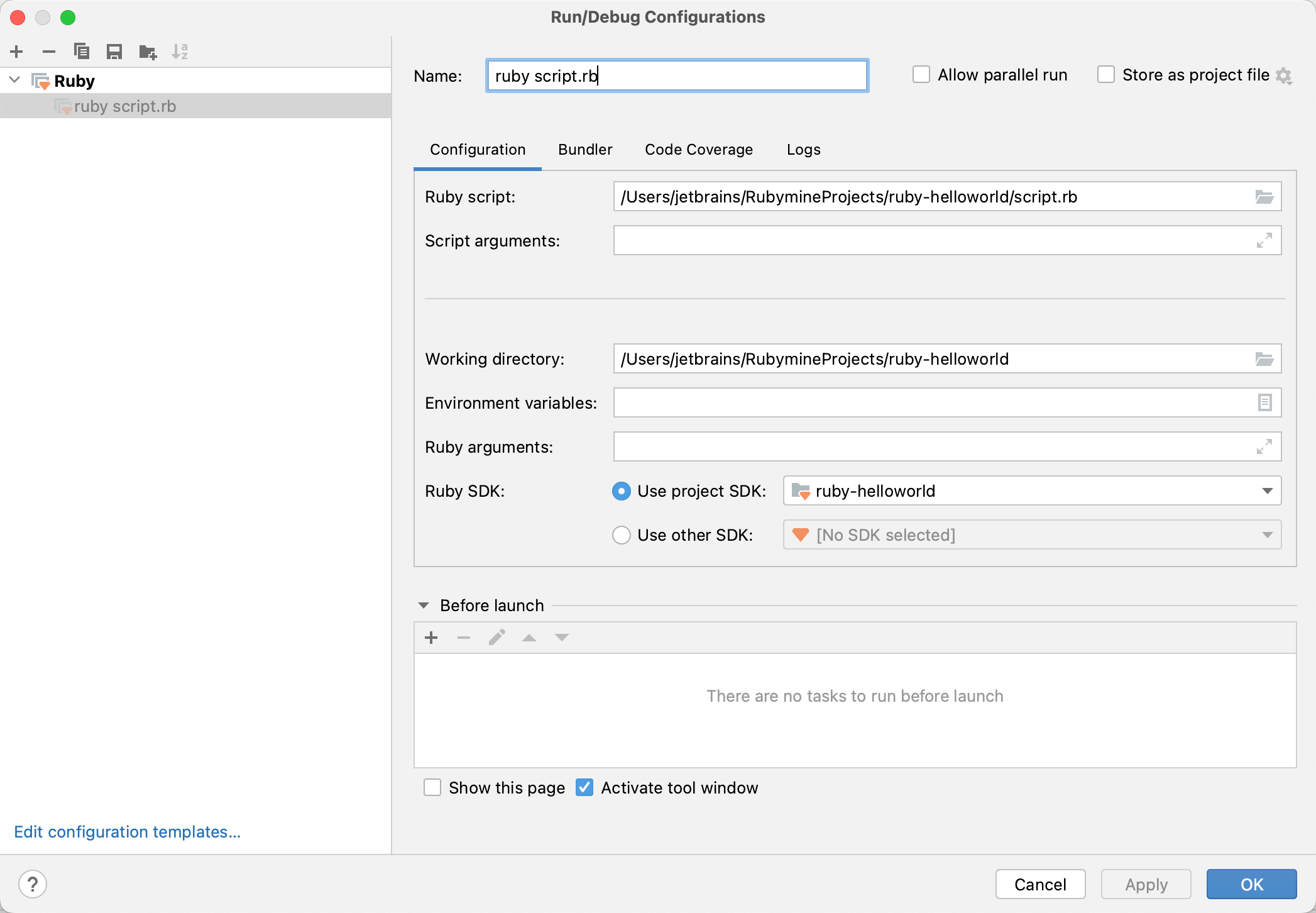
See Working with Run/Debug Configurations for more details.