Validate code with Web linters
ReSharper integrates with web code quality tools (also known as linters) — JSLint, ESLint, and TSLint — to help you detect and fix even more problems in your code.
Linters are designed as command-line tools, so normally each time you want to validate your code, you need to go to the console, run a command line, and then dig through its text output.
With ReSharper it is different. When a linter is installed and enabled in ReSharper settings, the linter code rules are used together with ReSharper's own code inspections, and all code issues detected by linters are highlighted right in the editor in design-time.
The table below shows in which contexts different linters are supported.
JavaScript | JS code in HTML | JS code in ASPX | TypeScript | JSON | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
JSLint | |||||
ESLint | |||||
TSLint |
Enable web linter validation in the editor
Install Node.js interpreter. The easiest way to do so is to install the Node.js Tools for Visual Studio.
In most cases, ReSharper will find the Node.js interpreter automatically. If it is installed in an uncommon location, specify it on the page of ReSharper options Alt+R, O
Install the desired linter packages in your project.
Open the desired linter options pages under and enable the linter.
If there is node_modules folder in your project, ReSharper will find linter packages automatically. But you can also specify a custom linter folder.
If you use ESLint or TSLint, ReSharper will take all rules and settings from linter configuration files. By default, these files are found automatically but you can also specify a custom configuration file.
If the automatic search is enabled and the linter does not work, make sure that the configuration files are in the current directory and/or its parent directories, or in the user home directory:
For ESLint: .eslintrc.* file or an
eslintConfigfield in a package.json.For TSLint: tslint.json, tslint.yaml, or tslint.yml.
You can also pass any additional command-line options separated with spaces (see command line options reference for JSLint, ESLint, and TSLint).
Note that some options, which affect how the linter is executed cannot be applied. For example,
--fixwill be ignored because ReSharper provides its own way to apply the linter fixes.If you use TSLint, ReSharper will enable the linter in TypeScript and JavaScript code by default. To use it in TypeScript code only, clear the corresponding checkbox.
When linter support is set up, you will see code issues detected by the linter highlighted in the editor according the severity level (error level) of the corresponding rule:
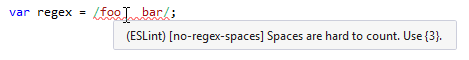
If the linter provides a fix for a rule, you will be able to apply it right from the Alt+Enter menu:
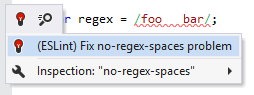
You can also choose from the Alt+Enter menu — this will write the new severity level (error level) for the corresponding rule right in the linter configuration file.
This feature is supported in the following languages and technologies: