Behat
With PhpStorm, you can practice behaviour-driven development by running scenarios using the Behat framework. Currently PhpStorm supports integration with Behat 3 and Behat 2 versions.
Native support of Behat in PhpStorm includes:
Recognition of and coding assistance for feature scenario files and PHP scenario definition files.
Gherkin syntax support in feature files:
Feature,Scenario,Given,When,Then,And, andButkeywords.Recognition of
@given,@when, and@thenannotations in definition files.Setting correspondence between scenarios and their definitions through regular expressions in accordance with the PCRE standard for Behat 2.4 and PCRE+ for Behat 3.0. Turnip expressions are also welcome.
Before you start
Make sure the PHP interpreter is configured in PhpStorm on the PHP page, as described in Configure local PHP interpreters and Configure remote PHP interpreters. Note that Behat 3 requires PHP 5.5 and later.
Download and install Behat
Before you start, make sure Composer is installed on your machine and initialized in the current project as described in Composer dependency manager.
Download Behat installation package manually
Download behat.phar from the Behat Downloads page and save it on your computer:
If you need full coding assistance in addition to the ability of running Behat tests, store behat.phar under the root of the project where Behat will be later used.
If you only need to run Behat tests and you do not need any coding assistance, you can save behat.phar outside the project.
Download and install Behat with Composer
Inside composer.json, add the
behat/behatdependency record to therequireorrequire-devsection. Press Ctrl+Space to get code completion for the package name and version.Do one of the following:
Click the Install shortcut link on top of the editor panel.
If the Non-installed Composer packages inspection is enabled, PhpStorm will highlight the declared dependencies that are not currently installed. Press Alt+Enter and select whether you want to install a specific dependency or all dependencies at once.
Click next to the package record in the composer.json editor gutter to jump to the corresponding Settings page and configure Behat manually.

Learn more about installing Behat from Behat Official website.
Integrate Behat with PhpStorm in a project
If you use a local PHP interpreter, PhpStorm performs initial Behat configuration automatically. In the case of remote PHP interpreters, manual Behat configuration is required.
Configure Behat automatically
Store the behat.yml or behat.yml.dist configuration file under the project root.
PhpStorm will create the local framework configuration on the Test Frameworks page and the Behat run/debug configuration.
Configure Behat manually
In the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S), go to .
On the Test Frameworks page that opens, click
in the central pane and choose the configuration type from the list:

In local configurations, the default project PHP interpreter is used, see Default project CLI interpreters for details.
To use Behat with a remote PHP interpreter, choose one of the configurations in the dialog that opens:

In the Behat Library area, specify the location of the Behat executable file or behat.phar archive.
Click
next to the Path to Behat directory or phar file field. PhpStorm detects the version of Behat and displays it below the field.
In the Test Runner area, appoint the configuration YML file to use for launching and executing scenarios.
By default, Behat looks for a behat.yml or behat.yml.dist configuration file in the project root folder. You can appoint a custom configuration file.
Clear the Default configuration file checkbox to have Behat use the behat.yml or behat.yml.dist configuration file from the project root folder. If no such file is found, test execution fails, therefore it may be more reliable to specify the configuration file explicitly.
Select the Default configuration file checkbox to specify your own YML configuration file. This file will be later used as default in all Behat run/debug configurations.
In the field, specify the location of the configuration file to use. Type the path manually or click
and choose the file in the dialog that opens.
Run and debug Behat tests
For information about writing Behat features, refer to the Behat Documentation.
Run or debug Behat tests
In the Project tool window, select the feature file to run your tests from and choose Run '<feature file>' or Debug '<feature file>' from the context menu of the selection:

PhpStorm generates a default run configuration and starts a run or debug test session with it.
Save an automatically generated default configuration
After a test session is over, choose Save <default_test_configuration_name> from the context menu of the file or folder.
Create a custom run/debug configuration
In the Project tool window, select the file or folder with the tests to run and choose Create run configuration from the context menu. Alternatively, choose from the main menu, then click
and choose Behat from the list.
In the Behat dialog that opens, specify the scenarios to run, choose the PHP interpreter to use, and customize its behavior by specifying the options and arguments to be passed to the PHP executable.
Monitor Behat test results
PhpStorm shows the tests execution results in the Test Runner tab of the Run tool window.
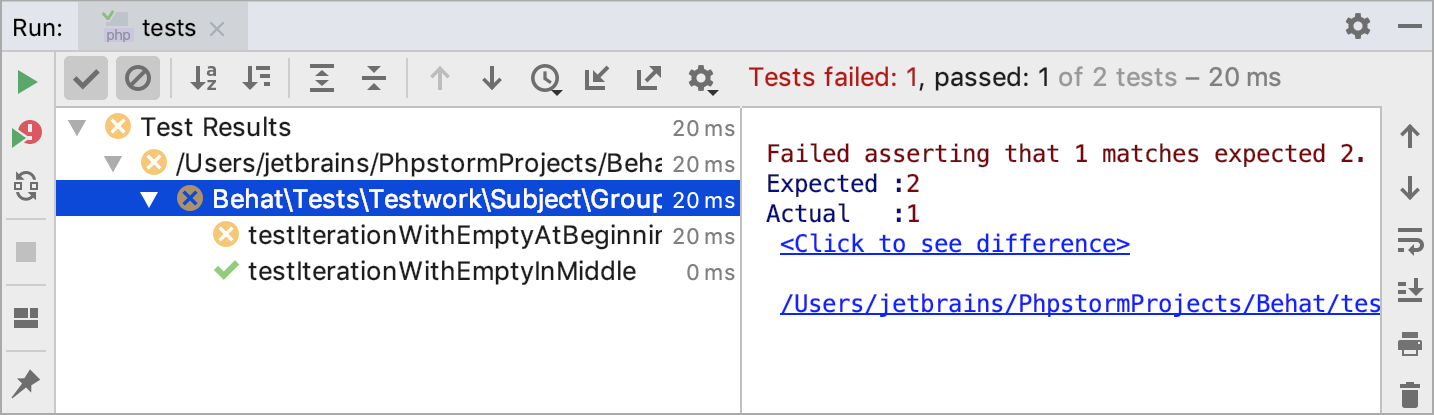
The tab is divided into 2 main areas:
The left-hand area lets you drill down through all unit tests to see the succeeded and failed ones. You can filter tests, export results, and use the context menu commands to run specific tests or navigate to the source code.
The right-hand area displays the raw Behat output.
Run Behat tests automatically
You can have PhpStorm re-run tests automatically when the affected code is changed. This option is configured per run/debug configuration and can be applied to a test, a test file, a folder, or a composite selection of tests, depending on the test scope specified in this run/debug configuration.
Run the tests.
On the Test Runner tab, press the
toggle button on the toolbar:

Optionally, click the
button and set the time delay for launching the tests upon the changes in the code:
