Migrate from NetBeans to PhpStorm
Switching from NetBeans to PhpStorm requires understanding some differences between the two IDEs. This section covers some PhpStorm-specific aspects.
Import a project to PhpStorm
Launch PhpStorm.
If the Welcome screen opens, click Open.
Otherwise, from the main menu, select .
In the dialog that opens, select the directory in which your sources, libraries, and other assets are located and click Open.
In the Open Project dialog that opens, click New Window.
PhpStorm will add the .idea directory to your project. This is used to store the PhpStorm project settings such as VCS settings, inspection profiles, or code styles. The NetBeans .nbproject directory will remain untouched, and you'll be able to use PhpStorm along with NetBeans.
See also, Importing Project from Existing Source Code.
User Interface
Projects
Just like in NetBeans, a project is used to group folders and files that represent a single unit. But if in NetBeans you work with all projects in the same window, in PhpStorm, you can also open each project in a separate window. And you can still open multiple projects in the same window by attaching new projects to the currently opened project. For more details, refer to Opening multiple projects.
Project groups
In NetBeans, a project group is a way to organize projects you are currently working on. Projects of the same group are opened in the same window; you can switch between projects groups without leaving the IDE.
You can encounter this term when you group your recent projects on the Welcome screen, but these groups do not appear on the Project tool window.
Options dialog
The equivalent of the NetBeans Options dialog is the (for Windows and Linux) or (for macOS) dialog. You can open it by pressing Ctrl+Alt+S. This dialog is used to control behavior and appearance of PhpStorm.
For more information, see Configuring the IDE.
Use NetBeans key bindings
PhpStorm includes several predefined keymaps, including NetBeans.
In the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S), select Keymap.
In the right-hand part of the dialog, under Keymap, select NetBeans.
If you want to customize some of the shortcuts of the predefined keymaps, refer to PhpStorm keyboard shortcuts.
Work with Projects
Most of the options available in the Project Properties dialog in NetBeans are available in in PhpStorm.
Run applications
In PhpStorm, you can run your application right from the editor by right-clicking and selecting Run from the context menu, and then selecting <script name>from the submenu.
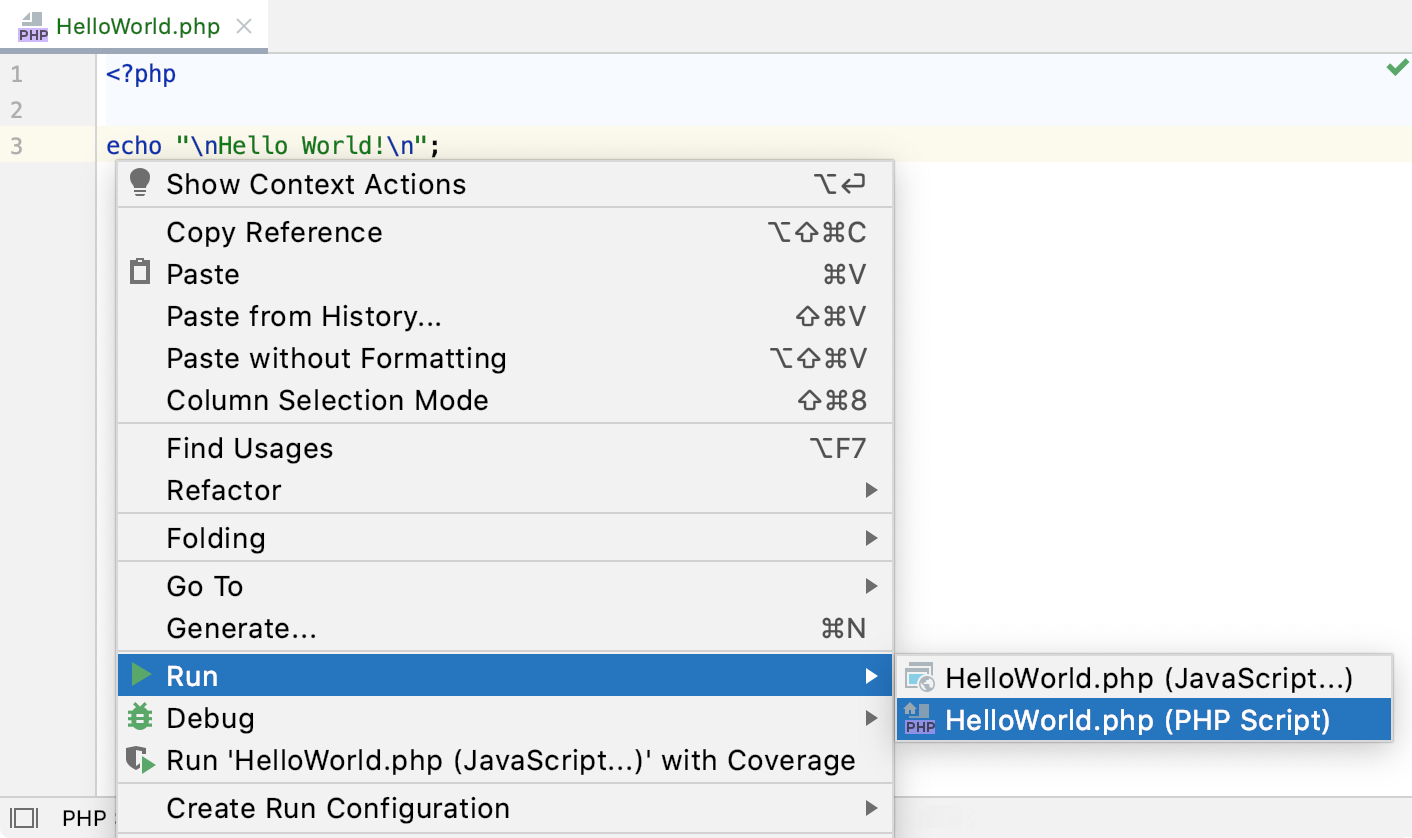
Similarly to NetBeans, you can also run it from the Project tool window by right-clicking a script and selecting Run from the context menu, and then select <script name> from the submenu.
Additionally, if you want to pass arguments or environment variables to your program or otherwise customize its startup, you can use run/debug configurations. A run/debug configuration is a named set of startup properties. You can run the same application with different configurations if you want to change its startup logic or output. When you run your application from the editor or from the Project tool window without selecting a configuration, PhpStorm creates a temporary configuration with default values. You can then edit and save it as a permanent configuration. 
With PhpStorm, you can also create run/debug configurations based on existing configuration templates, share your configurations with teammates via XML files, and much more. For more information about running applications and managing run/debug configurations, refer to Run applications.
Use Version Control
The most popular Version Control Systems including Git, Subversion, Mercurial, Perforce, and more are supported by PhpStorm. VCS integration for your project can be configured in on the Version Control page of the Settings /Preferences dialog. For details, refer to Version control.
Code editor
For an overview of the PhpStorm editor, refer to Editor basics.
Code completion
In PhpStorm, the list of code completion suggestions appears automatically after you type one or two characters. To narrow down this list, use:
Ctrl+Space. Reduces the list to keywords and the names of classes, methods, and fields available in the current context. Note that the list changes when you press Ctrl+Space for the second or third time.
Ctrl+Shift+Space. Shows only the types appropriate for the current context (smart type-matching code completion).
With PhpStorm, you can customize many of the code completion settings. For more information, refer to Code completion.
Code templates
In NetBeans, code templates are pieces of code associated with abbreviations. In PhpStorm they are known as live templates. Some templates are different; for example, private static final is abbreviated as psf in NetBeans while it is prsf in PhpStorm.
The list of available templates can be found in . There you can also add your own templates or modify any existing ones.
Code analysis
PhpStorm can analyze dependencies, data flows, and stack traces, find duplicates, and evaluate code quality. You can check available options in the menu.
Just like in NetBeans, you can use code inspections to detect anomalous code. In PhpStorm, inspections are highly customizable: you can disable them, suppress for the specific piece of code, change their severity levels, and create custom inspections. For more information, refer to Code inspections.
Similarly to hints in NetBeans, you can use intention actions and quick-fixes to quickly alter or correct your code.
Action Items
In NetBeans, the Action Items tab displays TODO comments, code problems, and compiler errors. In PhpStorm, you can get similar information using the following tool windows:
TODO: view TODO comments. For more information, refer to TODO tool window.
Problems: view errors and warnings found by PhpStorm inspections. For more information, refer to Code inspections.
Syntax highlighting
Just like in NetBeans, when you place the caret at a symbol, PhpStorm highlights all usages of this symbol in the current file. In PhpStorm, you can use the Highlight on Caret Movement option to enable and disable highlighting matched braces, current scope, and usages of element at caret. For more information, see Disable automatic highlighting of usages.
If you want to keep highlighting occurrences of a code element while moving the cursor away from it (Keep Marks option in NetBeans), in PhpStorm you can press Ctrl+Shift+F7.

Save changes
Unlike NetBeans where you have to manually save your changes, PhpStorm saves them automatically. Saving is triggered by various events, such as compiling, running, debugging, performing version control operations, closing a file or a project, or quitting the IDE. Additionally, you can configure PhpStorm to trigger auto-save when switching to another application or if the IDE is idle for a specified period.
Deploy on Save
In NetBeans, you can enable compilation and deployment on save. In separate settings, you can configure other on-save actions such as reformat code or remove unused imports. In PhpStorm, all these actions are available in .
For more information, refer to Trigger actions when saving changes.
Plugins
Although you cannot use NetBeans plugins in PhpStorm, a lot of functionality implemented in them plugins is available in PhpStorm out of the box. Besides, there are a lot of plugins for PhpStorm, so you can always find a plugin with functionality similar to that of your favorite NetBeans plugin. You can install plugins from the JetBrains Plugin Repository or from the disk.
Open plugin settings
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and select .
Use the Marketplace tab to browse and install plugins from the JetBrains Plugin Repository or from a custom plugin repository.
Use the Installed tab to browse bundled and installed plugins, enable, disable, update, or remove them. Disabling unnecessary plugins can increase performance.
For more information, see Plugins and Install plugins.
If you want to write a plugin for PhpStorm, have a look at:
Information for Plugin Developers on the PhpStorm Plugins page
Configure PHP development environment
A lot of PhpStorm features are available without any configuration right after you launch it. Still, to take full advantage of running, deploying, and debugging your PHP application, refer to the following sections: