Search templates, modifiers, and script constraints
When you construct a template for a structural search you are basically writing a script. To simplify your scripting process, IntelliJ IDEA offers you a list of predefined search templates that you can use as prototypes for your search template.

On how to access the list of the existing search and replace templates, see the structural search and replace section.
Each search or replace template consists of variables $variable_name$ to which you can add a condition (modifier) to narrow your search results. Modifiers depend on a variable in your search template.

Count modifier
The Count modifier specifies a number of occurrences.
For example, in the new java.lang.RuntimeException($x$) search template, for $x$ variable specify min and max numbers in the Count modifier field. To set the unlimited maximum count, provide an empty value in the modifier field.

IntelliJ IDEA adds [0,∞] to the variable and searches for the specified range of numbers.
Reference modifier
The Reference modifier lets you reference some other search template in the variable.
The reference will always contain the name of a preconfigured or saved template, and you can use auto-completion to fill out this field.
For example, for the $MethodCalls$ variable, type annotated methods in the Reference modifier field.

IntelliJ IDEA searches for method calls to methods with annotations.
Type modifier
The Type modifier adds a type of the value or expression that is expected for the specified variable.
For example, for the $expression$ variable, type int in the Type modifier field.
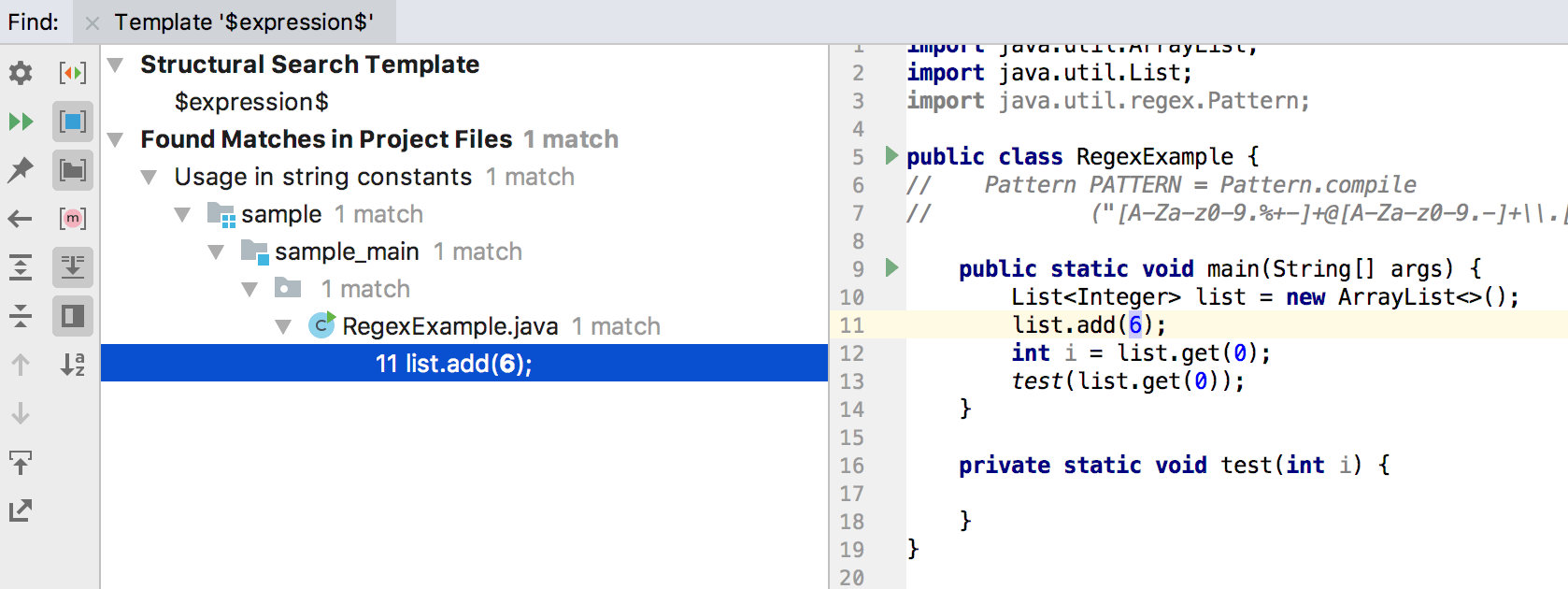
IntelliJ IDEA searches for places where boxing is performed for an integer.
Text filter
The Text modifier checks the variable against regular expressions or plain text.
For example, you can search for classes that implement a certain interface. In this case, add a fully qualified name of the interface in the Text modifier. Also, select the Within type hierarchy option, so the classes indirectly implementing Cloneable will also be included in the search. If this option is not selected, only the classes that directly implement Cloneable will be included.

Script constraints
The Script modifier adds Groovy script constraints to the search template. Script constraints are used when you search for certain language constructs.
For example, constructors with the specified number of parameters, or members with the specified visibility modifiers.
All variables used in a template can be accessed from script constraints. When you add a script constraint to your variable, IntelliJ IDEA matches it against the PSI tree, this variable is in fact a node in the PSI tree.
Let's say, you have a variable that matches a method, a toString() method. Then this variable is actually a PsiMethod node. Retrieving variable.parent will produce a PsiClass node, and so forth. variable.text then will give you the entire text of the method. If you just need the name of the method, you can use variable.name.
In another case the structural search and replace variable may match some expression, for example, a reference to a variable, a PsiReferenceExpression. An expression has no name of course, but retrieving the entire text of the expression, will give you the name of the variable to which it is referring.
You can check the syntax of script constraints that are used in the following existing templates:
sample method invocation with a constant parameter
classes
classes with parameterless constructors
static fields that are not final
interface that is not implemented or extended
fields/variables read
fields/variables with given name template updated
