Groovy
The Groovy plugin is bundled with IntelliJ IDEA and enabled by default.
IntelliJ IDEA supports the latest stable version of Groovy and Groovy 4 syntax.
User interface
The user interface for Groovy looks similar to a regular one. However, it includes the Groovy console that you can open from the main menu ().
The most interesting part of the user interface is the IntelliJ IDEA Editor since it lets you invoke almost any IDE feature without leaving it, which helps you organize a layout where you have more screen space because auxiliary controls like toolbars and windows are hidden.
Accessing a tool window via its shortcut moves the input focus to it, so you can use all keyboard commands in its context. When you need to go back to the editor, press Escape.
Below is a list of shortcuts that invoke the tool windows you will most often need:
Tool Window | Shortcut |
|---|---|
Project | Alt+1 |
Version Control | Alt+9 |
Run | Alt+4 |
Debug | Alt+5 |
Terminal | Alt+F12 |
Editor | Escape |
When you want to focus on the code, try the Distraction Free Mode. It removes all toolbars, tool windows, and editor tabs. To switch to this mode, on the main menu select View | Appearance | Enter Distraction Free Mode.
An alternative to Distraction Free Mode may be hiding all tool windows by pressing Control+Shift+F12. You can restore the layout to its default by pressing this shortcut once again.
The Navigation Bar is a compact alternative to the Project tool window. To access the Navigation Bar, press Alt+Home.
![]()
Most components in IntelliJ IDEA (both tool windows and popups) provide speed search. This feature allows you to filter a list, or navigate to a particular item by using a search query.
For more information, refer to User interface, Editor basics, and Tool windows.
Editor basics
A work in the editor is standard for Groovy as for any other languages with all the shortcuts offered by IntelliJ IDEA.
Check the following most useful editor shortcuts:
Action | Description |
|---|---|
Move the current line of code | Control+Shift+ArrowUp Control+Shift+ArrowDown |
Duplicate a line of code | Control+D |
Remove a line of code | Control+Y |
Comment or uncomment a line of code | Control+/ |
Comment a block of code | Control+Shift+/ |
Find in the currently opened file | Control+F |
Find and replace in the current file | Control+R |
Next occurrence | F3 |
Previous occurrence | Shift+F3 |
Navigate between opened tabs | Alt+ArrowRight Alt+ArrowLeft |
Navigate back/forward | Control+Alt+ArrowLeft Control+Alt+ArrowRight |
Expand or collapse a code block in the editor | Control+NumPad-+ Control+NumPad-- |
Generate | Alt+Insert |
Surround with | Control+Alt+T |
Highlight usages of a symbol | Control+F7 |
To expand a selection based on grammar, press Control+W. To shrink it, press Control+Shift+W.
IntelliJ IDEA can select more than one piece of code at a time. You can select next occurrence via Alt+J and deselect by pressing Alt+Shift+J. You can even select all occurrences at once, by pressing Control+Alt+Shift+J.
For more information, refer to Editor basics.
With IntelliJ IDEA you don't need to save code changes every time since you can undo refactorings and revert changes from Local History.
Groovy code style and formatting
IntelliJ IDEA automatically applies a code style you've configured in the Groovy code style settings as you edit. 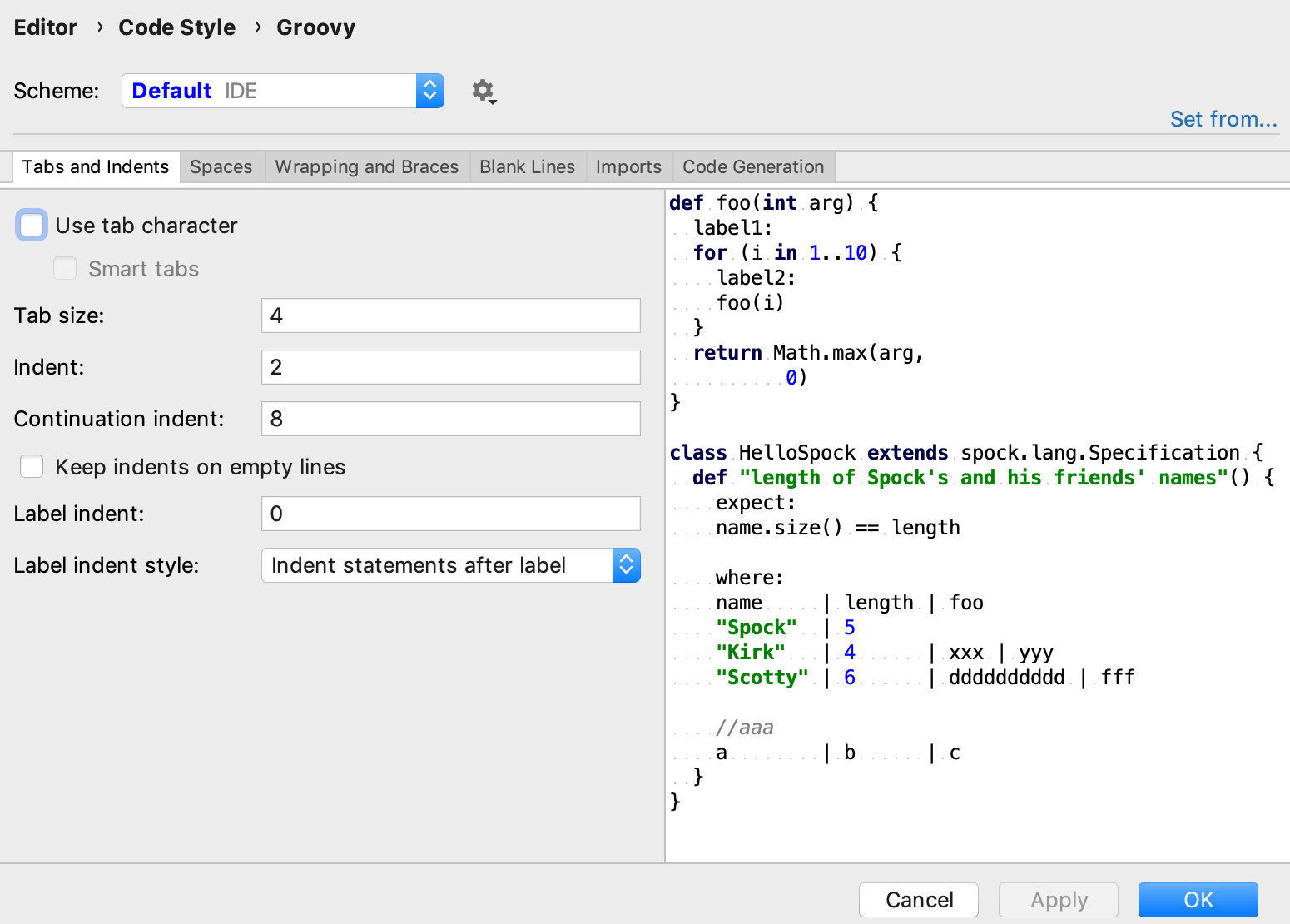
Check the following formatting shortcuts:
Action | Shortcut |
|---|---|
Reformat code | Control+Alt+L |
Auto-indent lines | Control+Alt+I |
Optimize imports | Control+Alt+O |
Note that by default, IntelliJ IDEA uses regular spaces for indents instead of tabs. If you have files with lots of indents, you may want to optimize their size by enabling the Use tab character option located in .
For more information, refer to Reformatting Source Code.