Debug JavaScript in Chrome
IntelliJ IDEA provides a built-in debugger for your client-side JavaScript code.
The instructions below walk you through the basic steps to get started with this debugger.
Before you start
Make sure the JavaScript and TypeScript and JavaScript Debugger required plugins are enabled on the Settings/Preferences | Plugins page, tab Installed, see Managing plugins for details.
Configure the built-in debugger as described in Configuring JavaScript debugger.
To have the changes you make to your HTML, CSS, or JavaScript code immediately shown in the browser without reloading the page, activate the Live Edit functionality. See Live Edit in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript for details.
Debug an application that is running on the built-in server
IntelliJ IDEA has a built-in web server that can be used to preview and debug your application. This server is always running and does not require any manual configuration. All the project files are served on the built-in server with the root URL http://localhost:<built-in server port>/<project root>, with respect to the project structure.
Start debugging
Set the breakpoints in the JavaScript code, as required.
Open the HTML file that references the JavaScript to debug or select the HTML file in the Project tool window.
From the context menu of the editor or the selection, choose Debug <HTML_file_name>. IntelliJ IDEA generates a debug configuration and starts a debugging session through it. The file opens in the browser, and the Debug tool window appears.
In the Debug tool window, proceed as usual: step through the program, stop and resume the program execution, examine it when suspended, view actual HTML DOM, run JavaScript code snippets in the Console, and so on. .
Example
Suppose you have a simple application that consists of an index.html file and an index.js file, where index.html references index.js. To start debugging this application using the built-in server, open index.html in the editor and choose from the context menu:
IntelliJ IDEA creates a run/debug configuration automatically, and a debugging session starts:
To restart the new run/debug configuration, click in the upper right-hand corner of the IntelliJ IDEA window or choose from the main menu:
Reload the current page in browser
Besides restarting your application by clicking in the Debug tool window, you can also click
to reload the page where you have currently navigated. This works the same way as the Reload Page functionality (Ctrl+R) in Chrome.
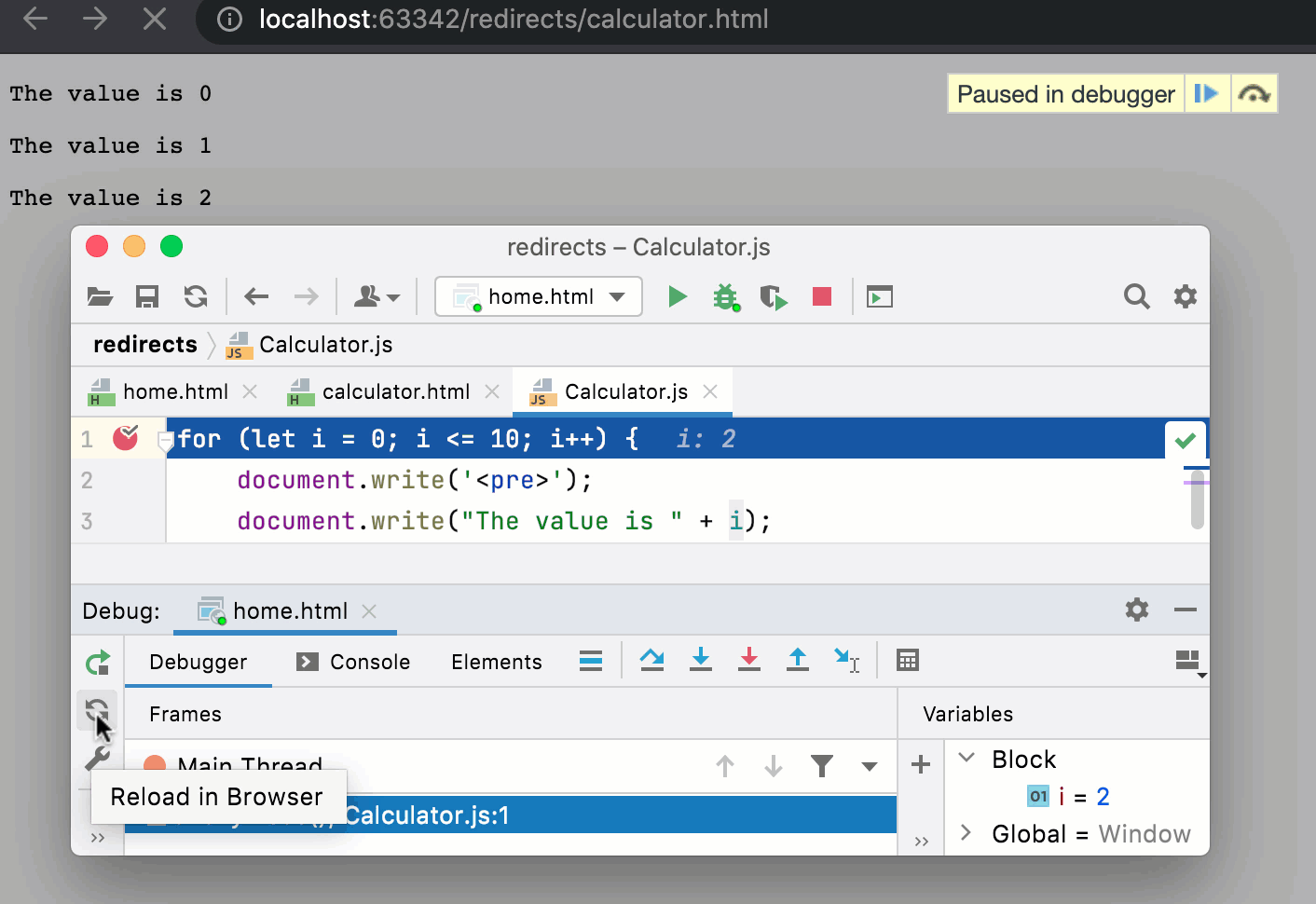
The example below shows a simple application that consists of two HTML pages and a JavaScript script. The starting home.html page has a Submit button on pressing which the calculator.html page opens with the results of the Calculator.js script execution.
During a debugging session, clicking would reload the home.html page with the Submit button. Clicking
reloads the calculator.html page so all the previous script output is cleared and the debugger returns to line 1 in Calculator.js.
Debug an application that is running on the localhost in the development mode
If your application is running in the development mode on localhost, you can start debugging it from the built-in Terminal (Alt+F12), from the Run tool window, or from the Debug tool window. Just hold Ctrl+Shift and click the URL at which the application is running.
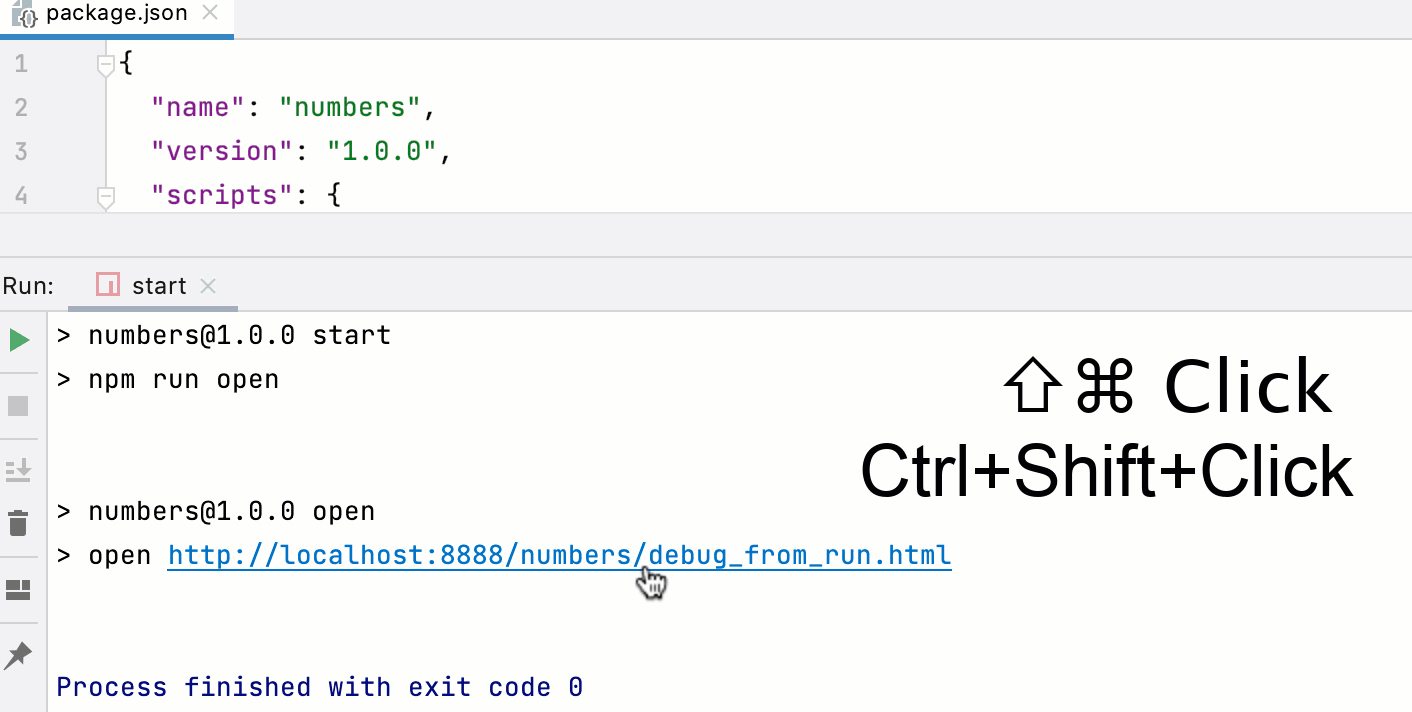
Set the breakpoints in your code.
Start the application in the development mode, for example, using an npm script.
The Run tool window or the Terminal shows the URL at which your application is running. Hold Ctrl+Shift and click this URL link. IntelliJ IDEA starts a debugging session with an automatically generated configuration of the type JavaScript Debug.
This also works for debugging Vue.js, Angular, React, and Node.js applications.
Debug an application that is running on an external web server
Often you may want to debug client-side JavaScript of an application that is running on an external development web server, for example powered by Node.js.
Set the breakpoints in the JavaScript code, as required.
Run the application in the development mode. Often you need to run
npm startfor that.When the development server is ready, copy the URL address at which the application is running in the browser - you will need to specify this URL address in the run/debug configuration.
Create a debug configuration of the type JavaScript Debug: from the main menu, select , click
on the toolbar and select JavaScript Debug from the list. In the Run/Debug Configuration: JavaScript Debug dialog that opens, specify the URL address at which the application is running. This URL can be copied from the address bar of your browser as described in Step 2 above. Click OK to save the configuration settings.
Select the newly created configuration from the Select run/debug configuration list on the toolbar and click
next to the list. The URL address specified in the run configuration opens in the browser and the Debug tool window appears.
In the Debug tool window, proceed as usual: step through the program, stop and resume the program execution, examine it when suspended, view actual HTML DOM, run JavaScript code snippets in the Console, and so on. .
See Debugging React Applications and Debugging Angular Applications for examples.
Debug asynchronous code
IntelliJ IDEA supports debugging asynchronous client-side JavaScript code. IntelliJ IDEA recognizes breakpoints inside asynchronous code, stops at them, and lets you step into such code. As soon as a breakpoint inside an asynchronous function is hit or you step into asynchronous code, a new element Async call from <caller> is added in the Frames pane of the Debugger tab. IntelliJ IDEA displays a full call stack, including the caller and the entire way to the beginning of the asynchronous actions.
The image below shows an example of a JavaScript debugging session.
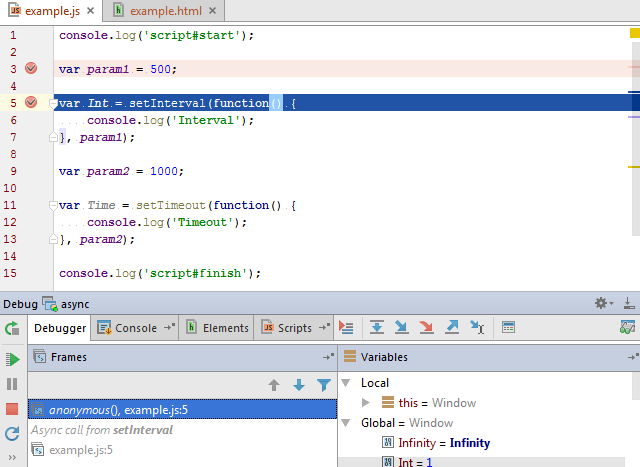
The debugger stops at line3(breakpoint), then at line5(breakpoint). On clicking Step into, the debugger will stop at line5 (on function), then will move to line6.
The asynchronous debugging mode is turned on by default. To disable asynchronous stack traces, set js.debugger.async.call.stack.depth in Registry to 0.
Debug workers
IntelliJ IDEA supports debugging Service Workers and Web Workers. IntelliJ IDEA recognizes breakpoints in each worker and shows the debug data for it as a separate thread in the Frames pane on the Debugger tab of the Debug tool window.
Note that IntelliJ IDEA can debug only dedicated workers, debugging for shared workers is currently not supported.
Set the breakpoints in the Workers to debug.
If you are using Service Workers, make sure the Allow unsigned requests checkbox is selected on the Debugger page (). Otherwise your service workers may be unavailable during a debug session.
Create a debug configuration of the type JavaScript Debug as described above in Debugging client-side JavaScript running on an external web server.
Select the newly created configuration from the Select run/debug configuration list on the toolbar and click
next to the list.
The HTML file specified in the run configuration opens in the browser and the Debug tool window opens with the Frames list showing all the Workers:

To examine the data (variables, watches, and so on) for a Worker, select its thread in the list and view its data in the Variables and Watches panes. When you select another Worker, the contents of the panes are updated accordingly.