Data Sources and Drivers dialog
To access the Data Sources and Drivers dialog (Ctrl+Alt+Shift+S), perform one of the following actions:
In the Database Explorer ( ) , click the Data Source Properties button
.
In the Database Explorer ( ) , click the Add button
and navigate to .
Navigate to .
Overview
In the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, you can manage your data sources and database drivers.
Left pane controls
When you select an item from the list of data sources and drivers, settings of the item appear on the right side of the dialog.
Toolbar
Item | Shortcut | Description |
|---|---|---|
Alt+Insert | Create a data source or a driver. | |
Delete | Remove the selected item or items from the list. | |
Ctrl+D | Create a copy of the selected data source or driver. | |
Ctrl+B | Navigate to the driver settings that are associated with the selected data source. | |
| Move the selected data source to the global or project level. For more information about global and project levels, refer to Data sources. | |
| Switch between recently-used items. |
Context menu
Item | Shortcut | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Alt+Insert | Create a data source or a driver. |
| Delete | Remove the selected item or items from the list. |
| Ctrl+D | Create a copy of the selected data source or driver. |
| Ctrl+B | Navigate to the driver settings that are associated with the selected data source. |
| Move the selected data source to the global or project level. For more information about global and project levels, refer to | |
Change Driver | Associate a data source with a driver. | |
| Ctrl+Alt+Z | Revert changes for the selected item. |
Load Sources | Load source code of database objects for the selected category of schemas. | |
| Alt+F7 | Show data sources that use the selected driver. |
Data Sources
The Data Sources section includes settings of regular data sources and DDL data sources.
Regular
Settings pane of a regular data source includes the following tabs: General, Options, SSH/SSL, Schemas, Advanced.
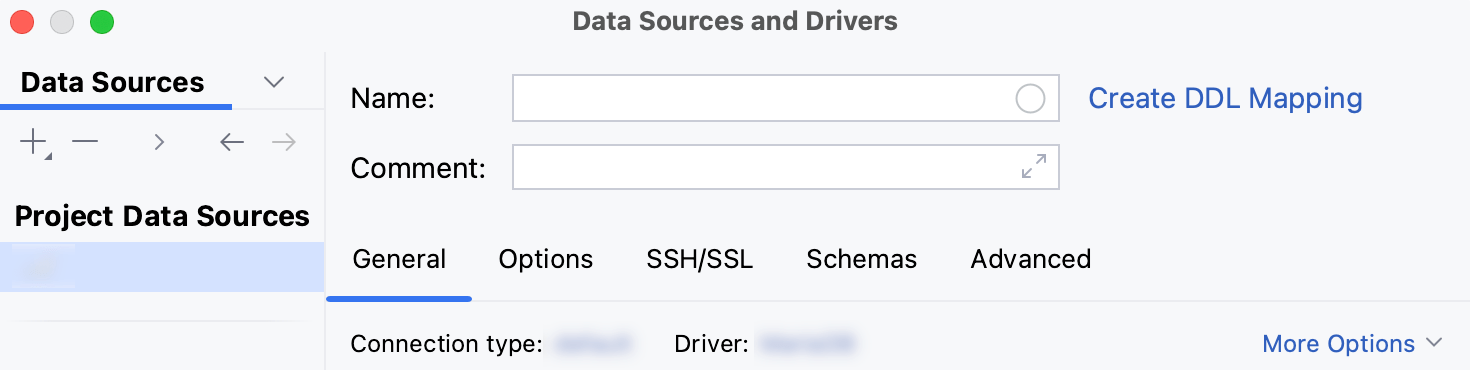
For more information about managing and creating regular data sources, refer to Data sources. To learn more about connection settings of a certain database, refer to the dedicated topic.
- Creating and configuring data sources of different databases
General
The General tab includes settings that you need to specify for a database connection.
The set of fields and controls on the tab depends on the option selected in the Connection type list.
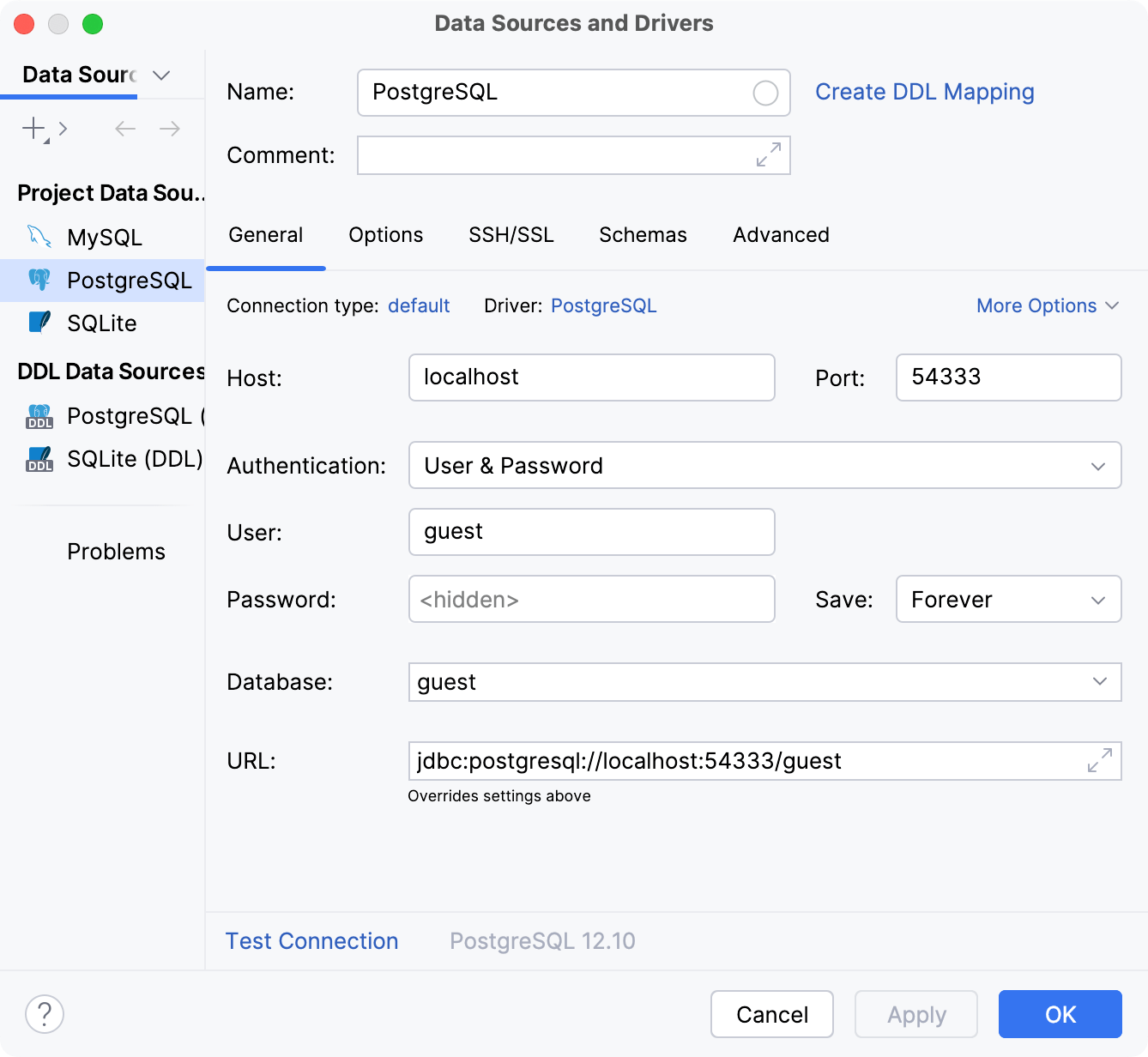
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Connection type | A connection type that you want to use for the database connection.
|
Driver | Specify the driver from the Drivers list that you want to use for the connection. |
File | The path to the database file. Use the Open icon ( The Save icon ( |
Path | The path to the database file or folder. Use the Open icon ( |
Host | The hostname (domain name) or the IP address (IPv4 or IPv6) of the computer where the database is located. If the database is on your local computer, specify localhost or 127.0.0.1. If you are using SSH, the database host must be accessible by the specified domain name or IP address from the computer on which the SSH proxy runs. See SSH/SSL tab. |
Port | The database port number. |
Database | The name of the target database or schema. |
User | The name of your database user account. |
Password | The password for the database user. |
Save | Save settings for the password field. You can select the following options for storing your password:
|
Create database | Adds an argument to the URL to create a database. This option is available only in some database management systems (for example, in the Apache Derby (Embedded)). |
URL | The URL that DataGrip will use to connect to the database. The user interface for specifying the URL is different depending on which option is selected in the Connection type list. |
Test Connection | Verifies that the database connection settings are correct and DataGrip can communicate with the database. To copy the communication information, click the Copy. |
Options
The Options tab includes settings of the database connection.
The set of fields and controls on the tab depends on the option selected in the Connection type list.
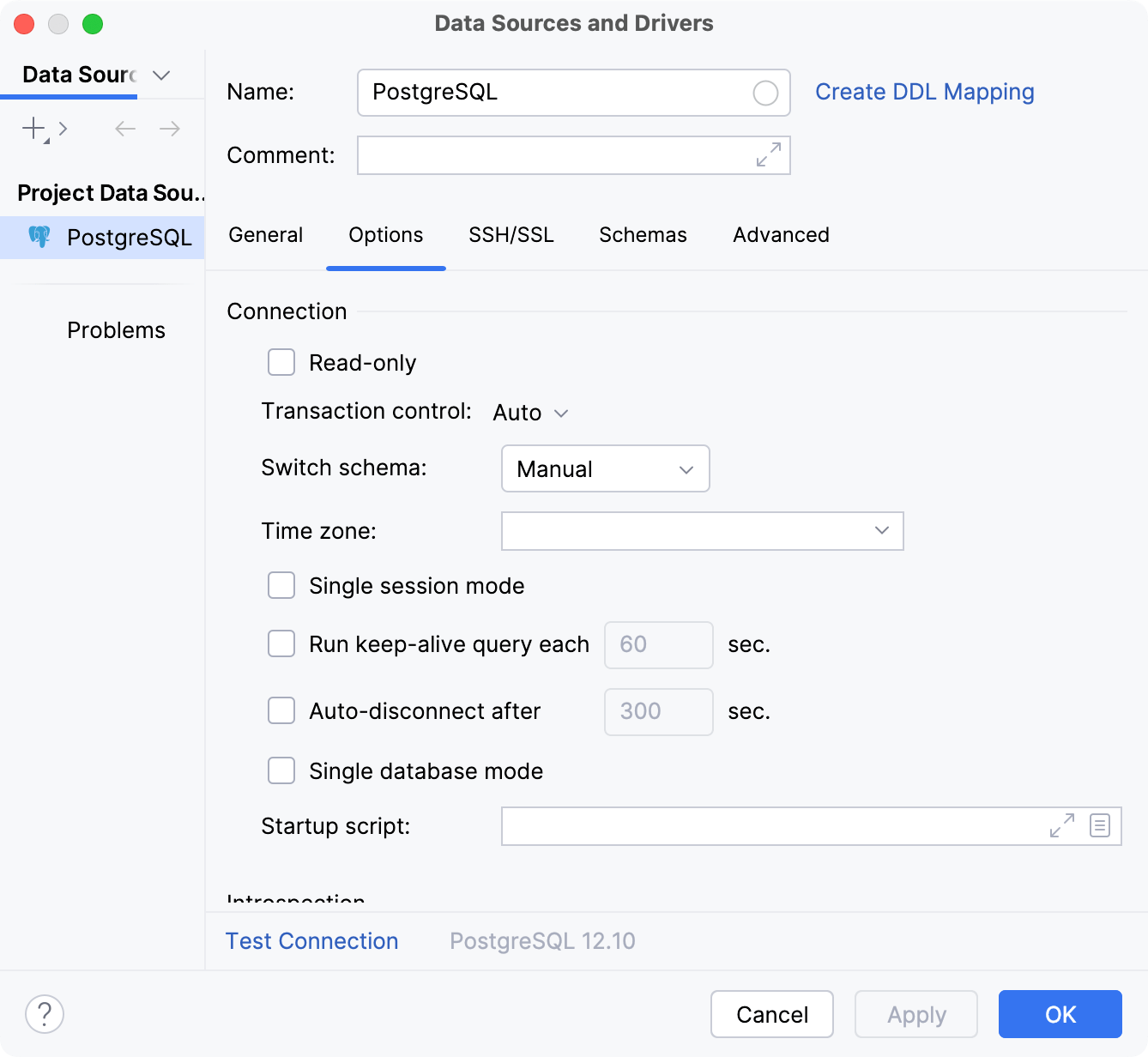
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Connection | |
Read-only | Set the read-only status. Select the checkbox to protect the data source from accidental data modifications. If the checkbox is selected, you cannot modify the data in the Data editor. Data modifications might be possible in the query console if the driver does not support the read-only status. |
Transaction control | Set the isolation level for database transactions and the mode of how the transactions are committed.
|
Switch schema | Define a mode that DataGrip uses to switch schemas.
|
Time zone | Select a time zone to use with the data source. For example, select the time zone of the host that your data source is connected to. |
Single session mode | Enable the single session mode. Single session mode means that the data source and all consoles use one and the same session. This mode allows you to see the temporary objects in the database tree, or use the same transaction in different consoles. For more information about consoles, refer to Query consoles. |
Run keep-alive query each | Run a keep-alive query to keep the connection alive. You can define the custom query in the driver settings for unsupported databases. |
Auto-disconnect after | Disconnect from the database after the specified number of seconds. |
Single database mode | In the database tree view, show and enable only the database that you specified in the connection settings. When you connect to a data source, DataGrip can retrieve and display you all the databases that the data source has. But in some cases (for example, with certain settings of PgBouncer), you can or are allowed to work only with a certain database. In the database tree view with the Single database mode enabled, you see only the database that you specified in the connection settings. Consider using this setting for PostgreSQL, Azure SQL Database, Greenplum, Amazon Redshift. |
Enable DBMSOUTPUT | (Oracle, IBM Db2 LUW) Enable DBMS_OUTPUT by default for new sessions. |
Startup script | Run an SQL query each time you establish a connection. To use built-in IDE macros in your startup script, click Insert Macros. Note: if the Single session mode checkbox is cleared, each new query console creates a new connection. |
Introspection | |
Auto sync | Synchronize the actual state of the database automatically. The state of the database means the database tree view that you see in the Database Explorer. If the Auto sync checkbox is selected, the view of the data source is automatically updated:
If the Auto sync checkbox is cleared, the view of the data source in the Database Explorer is synchronized with the actual state of the database only when you click the Refresh button |
Load sources for | Load source code of views, procedures, packages and other database objects for the selected category of schemas: all schemas (All schemas), all schemas excluding system schemas (All excl. system schemas), or disable the feature (None). To change this setting for several data sources simultaneously, select the corresponding data sources. Right-click the selection and navigate to Load Sources and select an option. |
Default level | (Oracle) Default introspection level for the database objects. For more information about introspection levels, refer to the Oracle introspection levels topic. |
Use session template | Select a template to be used for your sessions. |
Warn when editing outdated DDL | Display a notification if the cached DDL differs from the actual DDL in the database. Every time you open source code, DataGrip displays you a version loaded during the indexing process. But if someone changes the source code from another workstation, the indexed version becomes outdated. If your version is older than the one in the database, you see the following notification: |
Track databases/schemas creation and deletion | When you create, delete, or rename a schema, DataGrip updates the list of available schemas in the introspection scope window. To see the introspection scope, click the button near the data source name in the Database Explorer.  |
Use pre-introspected objects for system catalogs that are not introspected | Toggles the usage of pre-introspected objects for system catalogs. For more information about introspection and system catalogs, refer to Pre-introspected objects from system catalogs. |
Automatic introspection interval N minutes | Run introspection for the data source once in the specified number of minutes. |
Virtual objects and attributes | Defines a path to external-data.xml that stores relations of virtual foreign keys, expressions of virtual columns, and statements of virtual views. For more information about virtual database objects, refer to Virtual objects section topics. |
Other | |
Code style | Select a code style that you want to use for schemas. For more information about code style customization, refer to Code styles for SQL. |
Before connection | Select tasks that DataGrip will perform before the first connection (at the start of a process in which the JDBC driver works). Tasks are run sequentially. |
Session Templates | Create templates for your sessions. Template settings override general connection settings of a data source. In a template, you can set the following options: Authentication, Read-only, Startup script, Driver. |
SSH/SSL
The SSH/SSL tab includes settings for the SSH or SSL connection.
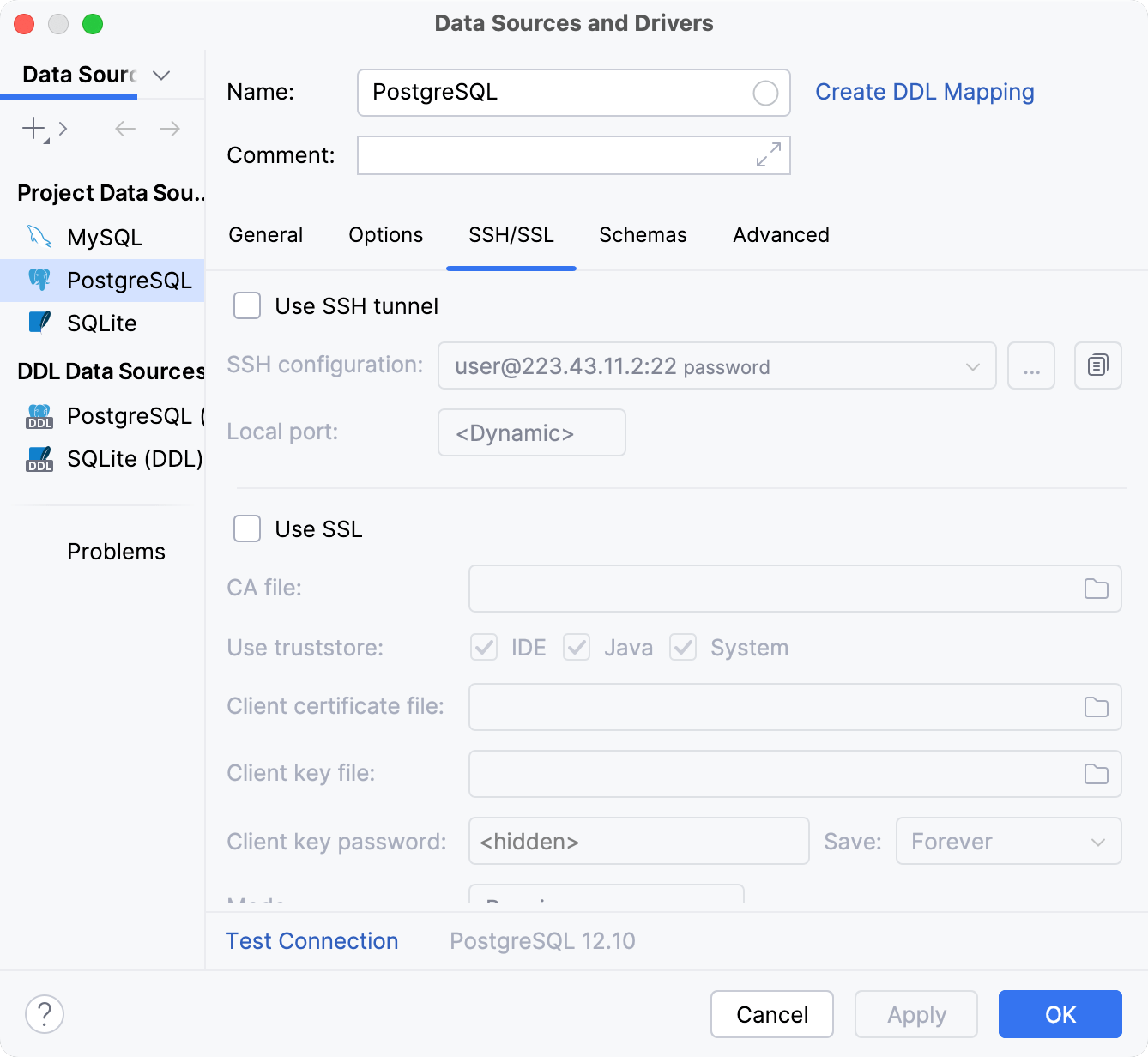
SSH
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Use SSH tunnel | Select this checkbox to enable connecting via SSH. Then choose one of the created SSH configurations from the list, or click |
SSH configuration | Select an SSH configuration to use for the connection. To create a new SSH configuration, click the Add SSH configuration button ( To copy the existing SSH configuration, click the Copy button ( |
Local port | Specify the local port number from which you want to forward the connection. There is no default value, which means DataGrip dynamically selects the port number. |
SSL
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Use SSL tunnel | Enable settings for configuring the SSL connection. |
Copy from | Copy SSH settings from the existing data source. Click the link and select the corresponding data source. |
CA file | Specify the path to the SSL Certificate Authority (CA) certificate file. The certificate file must be the same certificate as used by the server. |
Use truststore | Select the truststore to use the certificates that it contains.
JAVA and System certificates can require updates. |
Client certificate file | Specify the path to your (client) public key certificate file. |
Client key file | Specify the path to your (client) private key file. |
Schemas
Select the databases and schemas to be shown in the Database Explorer.
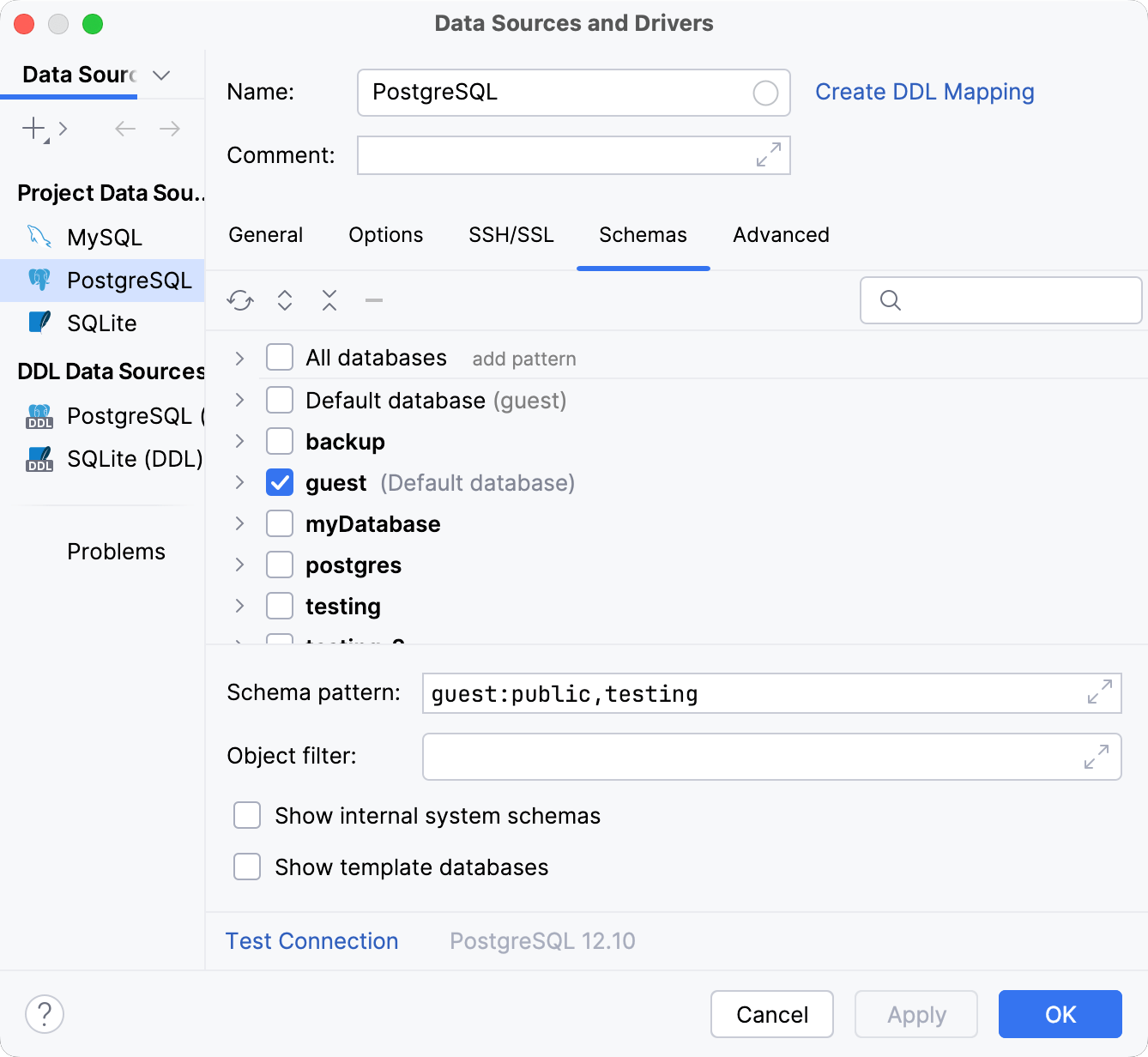
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Refresh the list of the databases and schemas. | |
Expand all nodes in all trees. | |
Collapse all nodes in all trees. | |
| Filter the contents in trees. Only the databases and schemas whose names contain the specified text are shown. |
Schema pattern | Define a pattern to select the necessary databases and schemas. To get the info about the syntax to be used, place the caret into the field and press Ctrl+Q.
Consider the following examples:
|
Object filter | Limit the set of tables and other database objects that are shown in the Database Explorer for each data source. For example, if you limit the resolve scope to All other tables will be out of the scope. DataGrip does not resolve objects that are not displayed in the Database Explorer.  Use the following pattern when you compose an expression for the Object filter field.
|
Show internal system schemas | Show or hide internal system schemas (for example, |
Show template databases | Show or hide template databases (for example, |
Advanced
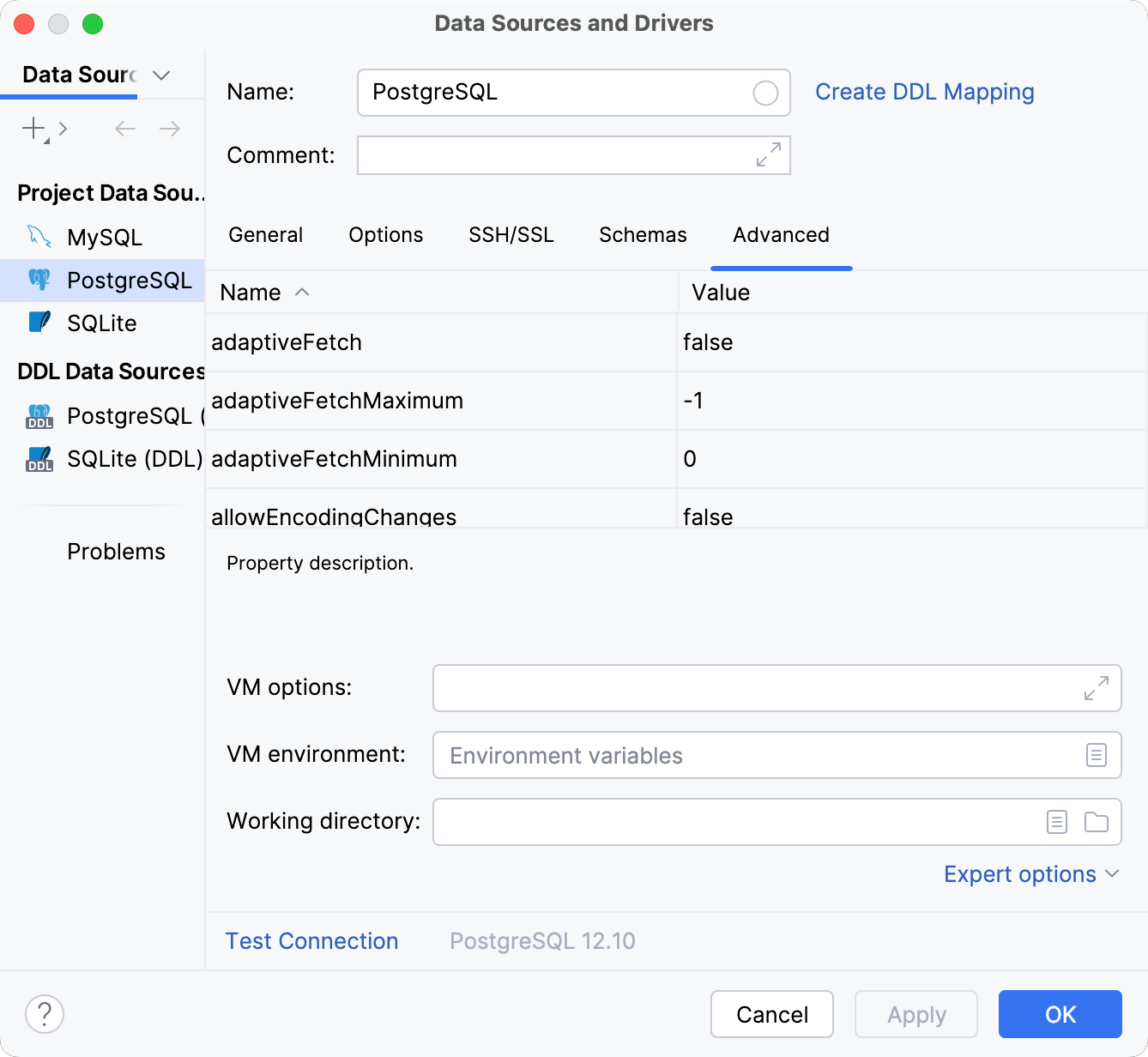
The Advanced tab includes the database connection properties, options and environment variables for the JVM database driver.
The table on the Advanced tab displays a set of connection options that are passed to the database driver as key and value pairs.
When you select a cell in the Name column, the description of the corresponding option is shown underneath the table.
To add a row, start editing the values in the last row, where <user defined> and <value> are shown. A new row is added to the table automatically.
Item | Description |
|---|---|
VM options | JVM options for the database driver. For certain Oracle Database versions (for example, Oracle version 9), there might be connection problems when you and your database server are in different time zones. You can specify the time offset for your timezone in the VM Option field (for example, |
VM environment | Environment variables for the database driver JVM. For example, encoding-related issues in an Oracle database can be solved by setting the |
Working directory | The working directory for the process that handles working with data sources. Also, all relative paths are resolved relatively to this directory (for example, paths in driver properties). For example, if you create a file-based database like SQLite and do not set the path for the SQLITE file, the file will be created in this working directory. |
For more information, refer to your DBMS documentation.
DDL Data Sources
A DDL data source is defined by its name and can reference one or more DDL files and another data source (a parent data source).
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Name | The data source name. |
Sources | List of files that contain the necessary DDL definitions.
|
Extend | Optionally, you can select another data source as a parent in the Extend list. As a result, the data source that you are editing inherits all DDL definitions from its parent. If you do not want to use the parent data source, select <none>. |
Drivers
Settings pane of a driver includes the following tabs: General, Options, Advanced.
General
The General tab includes settings for driver files, URL templates, and driver classes.
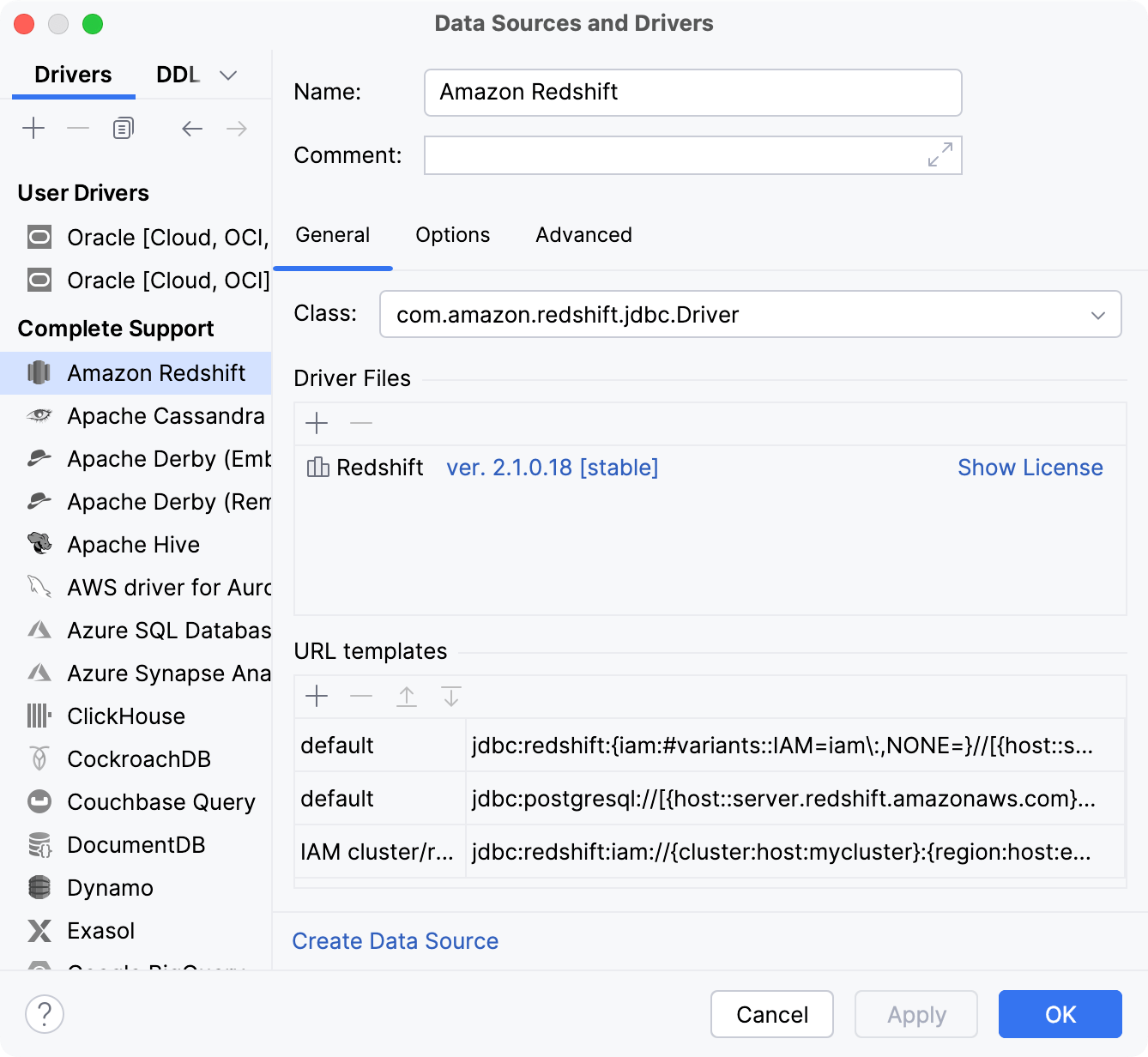
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Class | The fully qualified name of the driver class to be used. |
Driver Files | DataGrip uses JDBC drivers to interact with a database. You can download and use a driver from the DataGrip driver repository or specify the driver that you store on your computer. To download and use the latest driver version, click the Download ver. N link. You can also specify and use a driver with a particular version number. Click the ver. <version_number> link and select the driver version that you want to use. The selected version is downloaded and applied automatically. You can use the driver that is already available on your computer. In that case, click the Add button |
URL templates | The templates used to construct the database URL. The text in curly brackets represents variables. Consider the following examples:
Optional fragments are in square brackets, for example, Template names correspond to the names of the options in the URL option list. |
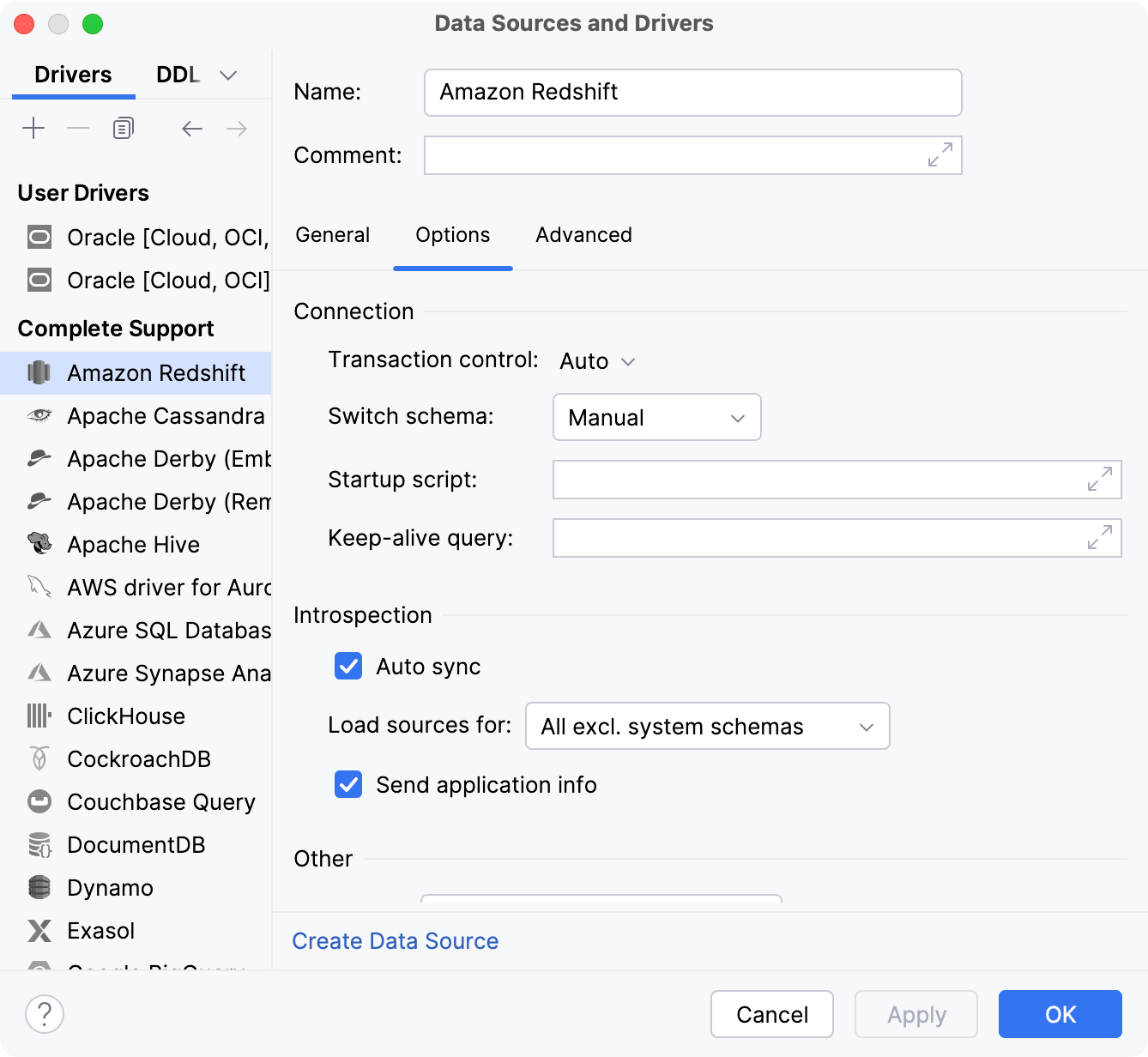
Options
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Connection | |
Transaction control | Set the isolation level for database transactions and the mode of how the transactions are committed.
|
Switch schema | Define a mode that DataGrip uses to switch schemas.
|
Startup script | An SQL query that will run each time you establish a connection. Note: if the Single session mode checkbox is cleared, each new query console creates a new connection. |
Keep-alive query | A keep-alive query that will run to keep the connection alive. |
Introspection | |
Auto sync | The default setting for the auto sync option. |
Load sources for | Load source code of database objects for the selected category of schemas. |
Send application info | When connecting to a database server, DataGrip sends the info about itself if this checkbox is selected. |
Connection | |
Dialect | The SQL dialect associated with the corresponding data sources. |
Code style | Selects a code style that you want to use for the data sources that use this driver. For more information about code style customization, refer to Code styles for SQL. |
Format synced sources | Apply the code style to source code of database objects after synchronization. |
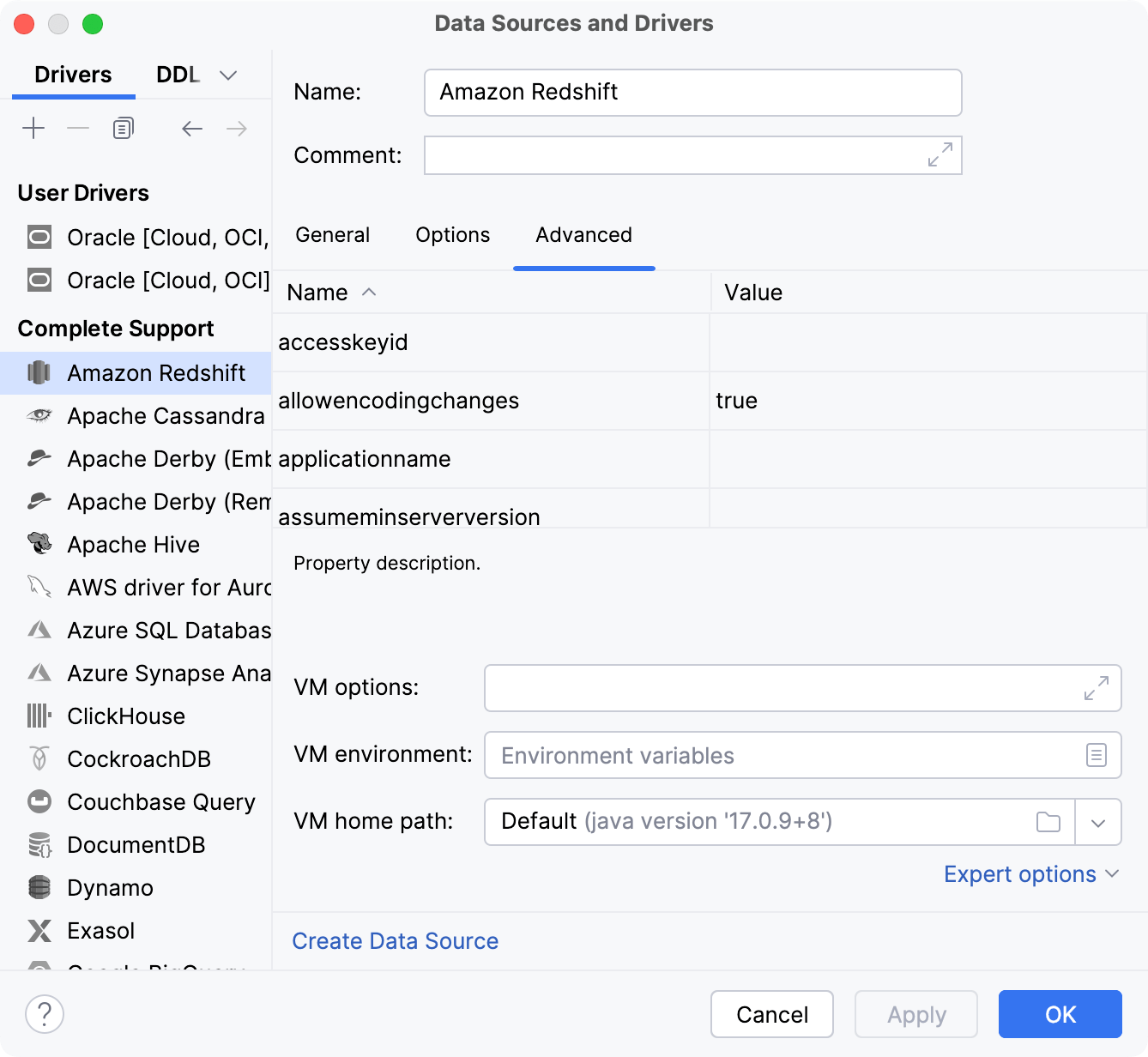
Advanced
The Advanced tab includes JVM options, environment variables, and options that can be passed to the database driver as key-value pairs.
To start editing a value in the table, double-click the corresponding Value field.
To add a row, start editing the values in the last row, where <user defined> and <value> are shown. A new row will be added to the table automatically.
Item | Description |
|---|---|
VM Options | The default options for the JVM in which the database driver runs. The driver is started as a separate process in the JVM. |
VM environment | Environment variables for the database driver JVM. For example, encoding-related issues in an Oracle database can be solved by setting the |
Expert options
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Disable incremental introspection | Do not perform the incremental introspection. The option is available for Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, PostgreSQL and similar databases, . With the incremental introspection, the introspector detects objects changed in the database after the previous introspection and loads only these objects. When you enable this option, the introspector always loads all objects. It might greatly increase the introspection time. |
Do not use xmin in queries to pgdatabase | Do not use the |
Introspect using JDBC metadata | Switch to the JDBC-based introspector. Available for all the databases. To retrieve information about database objects (DB metadata), DataGrip uses the following introspectors:
Consider using the JDBC-based introspector when the native introspector fails or is not available. The native introspector can fail when your database server version is older than the minimum version supported by DataGrip. You can try to switch to the JDBC-based introspector to fix problems with retrieving the database structure information from your database. For example, when the schemas that exist in your database or database objects below the schema level are not shown in the Database Explorer. |
Isolate class path | Isolate class path used by JDBC driver. |
Use IDE proxy settings | Passes IDE proxy settings to JDBC process. |
Kubernetes
With DataGrip, you can connect to a database running in a Kubernetes cluster.
The Kubernetes tab is not available for embedded databases (for example, SQLite, Apache Derby, or HSQLDB) that don't have dedicated ports.
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Use Kubernetes port forwarding | Enables port forwarding. |
Context | Select a Kubernetes context to use. |
Namespace | Select a namespace, which determines the available set of resources. |
Resource type | Select the type of resource. |
Resource | Select a resource to connect to. |
Host port | Enter a local port to forward data to and from. |
Container port | Enter a remote port of the cluster resource. |
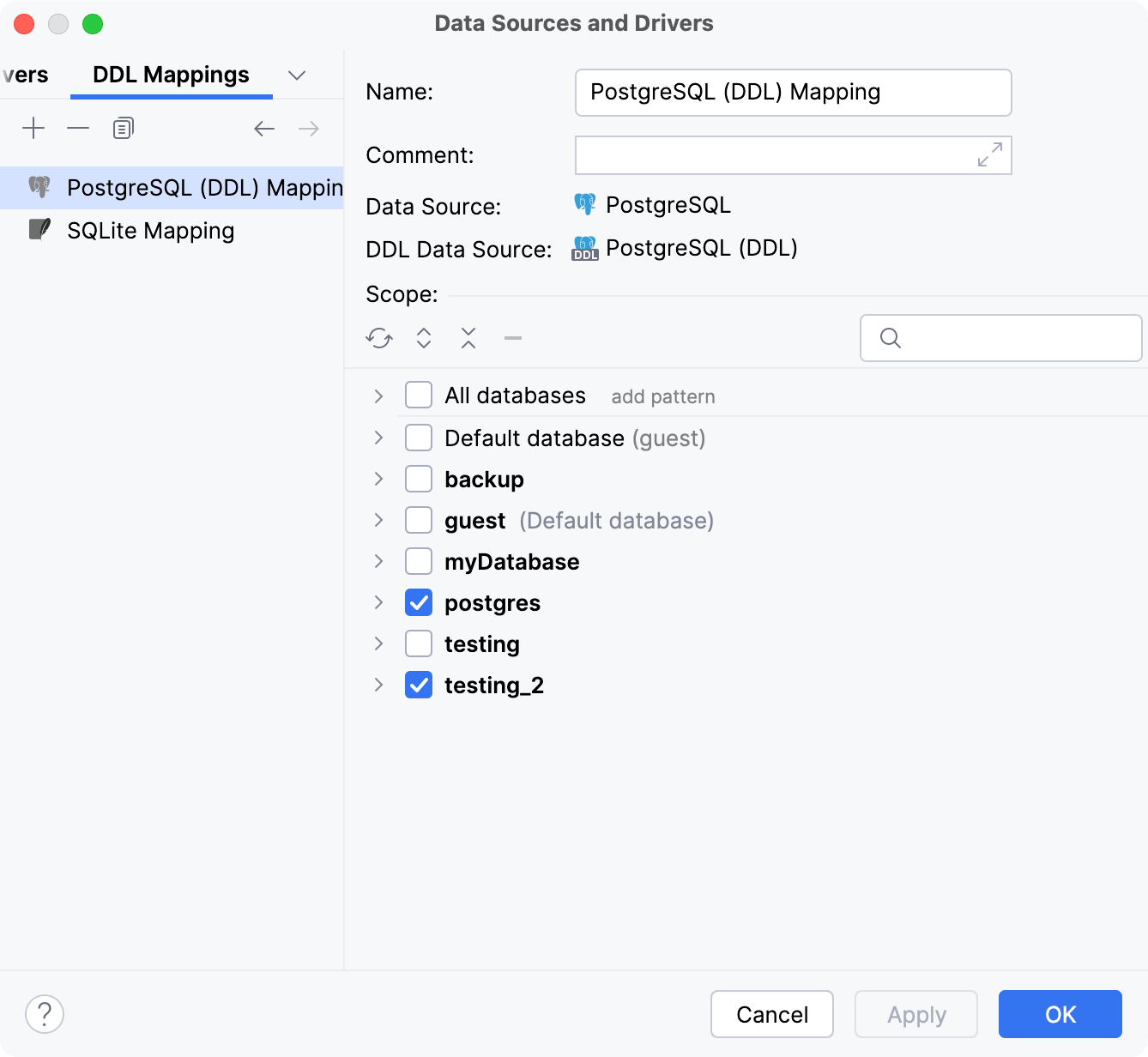
DDL Mappings
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Name | Name of the DDL mapping. |
Data Source | Sets the regular data source. |
DDL Data Source | Sets the DDL data source. |
Scope | Sets the scope of regular data source database objects that will be mapped to the DDL data source SQL files. |
Problems
If potential problems are detected, there is a number to the right of Problems. In that case, if you click Problems, you see the list of problems as well as controls for fixing them.